Tshirt Manufacturers: How to Choose a China Clothing Manufacturer for Quality, Cost, and Speed
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 27th, 2025
17 minute read
Tshirt Manufacturers: How to Choose a China Clothing Manufacturer for Quality, Cost, and Speed
Tshirt manufacturers set the pace, price, and quality of your program—and the right China Clothing Manufacturer can make your first delivery smooth and repeatable. Brands in the US and EU want clarity on MOQs, fit and print quality, transparent costing, and proof of compliance. This article strips guesswork from supplier selection with an evidence-based playbook built on factory-floor experience in China and Bangladesh.
- Know when to use OEM vs ODM vs CMT for tees—what you own, what the factory owns, and how it changes speed and cost.
- Shortlist smarter with a vetting flow that weighs capability, compliance, and capacity—and then pressure-test with a sample trial.
- Budget confidently with a decomposed t-shirt cost model, realistic MOQs, and lead-time drivers you control.
- Ship with fewer surprises using a staged, QA-led timeline from tech pack to bulk, aligned to AQL checkpoints.
- Reduce regulatory risk with traceability documentation and certifications mapped to UFLPA (US) and CSDDD (EU).
[INTERNAL LINK: China clothing manufacturer guide → Pillar page idea] [MENTION: AAFA] [MENTION: Textile Exchange] [CITE: “US/EU brand expectations on due diligence and traceability, 2024–2025 industry report”]
The most reliable tshirt manufacturers combine OEM/ODM support, stable MOQs (300–1000 pcs/style/color), 60–90 day lead times after sample approval, and verifiable compliance. For US/EU buyers, prioritize transparent cost breakdowns, cotton origin traceability, and certifications (OEKO-TEX, WRAP, BSCI)—especially when partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer.
What Tshirt Manufacturers Do: OEM, ODM, and CMT Explained
Answer-first: OEM suits brands that need development support, ODM suits speed with pre-developed styles, and CMT suits teams that own patterns and materials. Align model choice with control, timeline, MOQ, and compliance responsibilities.
The engagement model you choose sets your workflow and risk. OEM adds design/development capacity, ODM accelerates launches using factory-owned blocks, and CMT puts trims, fabrics, and testing squarely on your team. For US/EU programs, clarity on ownership—patterns, IP, lab tests, and certifications—matters for both traceability and speed.
| Model | Ownership | Speed | MOQ | Cost | Risk | Use When |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Brand owns final design/IP; factory co-develops | Moderate; faster with clear tech packs | Mid-range; 300–1000 pcs/style/color | Mid; development fees may apply | Shared; QC/spec clarity needed | You want development support, print/fabric R&D, and scale |
| ODM | Factory owns base design; brand customizes | Fast; fewer rounds, established blocks | Lower mid; varies by factory limits | Lower; reduced development overhead | Lower technical risk; brand-level differentiation risk | You need speed/capsule drops with minor customization |
| CMT | Brand owns patterns/fabrics/trims/testing | Variable; can be fast if inputs are ready | Flexible; depends on brand material control | Lower CM rate; higher brand-side costs | Higher brand-side risk; logistics and testing on you | You have strong technical team and supply chain, need control |
OEM: When You Need Development Support
OEM unlocks fit development, print strike-offs, and fabric trials without building a full internal team. Expect proto → fit rounds → PP sample sequencing, with print and embellishment QA embedded: screen print opacity checks, DTG wash resistance, sublimation clarity, and embroidery thread weight balance. Tight tech pack collaboration—graded specs, stitch codes, shrinkage allowance, and color standards—cuts rounds and meeting minutes. Eton teams in China and Bangladesh typically align OEM tees to 60–90 day bulk lead times post PP approval when lab testing and strike-offs are approved on schedule. [MENTION: SGS] [CITE: “Turnaround norms for OEM apparel in East/South Asia, 2024”]
ODM: When Speed and Fewer Choices Are Acceptable
ODM leans on factory-owned bodies and fabric/construction presets. You get speed—single fit round, preset necklines, standard rib specs—plus known print bases. Trade-offs include smaller space for silhouette differentiation and shared blocks across customers. Align IP and branding via proprietary graphics, packaging, and color exclusives. ODM shines for capsule drops, seasonal merch, or events that demand fast calendar turns. For US/EU programs, document traceability and lab test history even for preset bodies; ODM does not remove compliance obligations. [MENTION: WRAP] [CITE: “Brand differentiation risks in ODM footwear/apparel, 2023 analysis”]
CMT: When You Control Materials and Patterns
CMT shifts materials, trims, and testing to the brand. If you own patterns and book greige or yarn-dyed cotton, the factory cuts/sews per your BOM. Speed depends on your readiness: graded patterns, fabric in-hand, finalized prints, and QA test plans. Budget for inbound freight and potential yield loss claims. CMT works for specialty fits or when you maintain fabric IP. Ensure robust defect classification (critical/major/minor), needle policy, and carton QC—your team sets the testing scope. [MENTION: Intertek] [CITE: “CMT model cost distribution and risk by buyer capability, 2024 industry brief”]
[INTERNAL LINK: OEM vs ODM explained → Cluster page idea] [INTERNAL LINK: Tech pack template for tees → Resource hub idea]
How to Choose Tshirt Manufacturers in China and Bangladesh
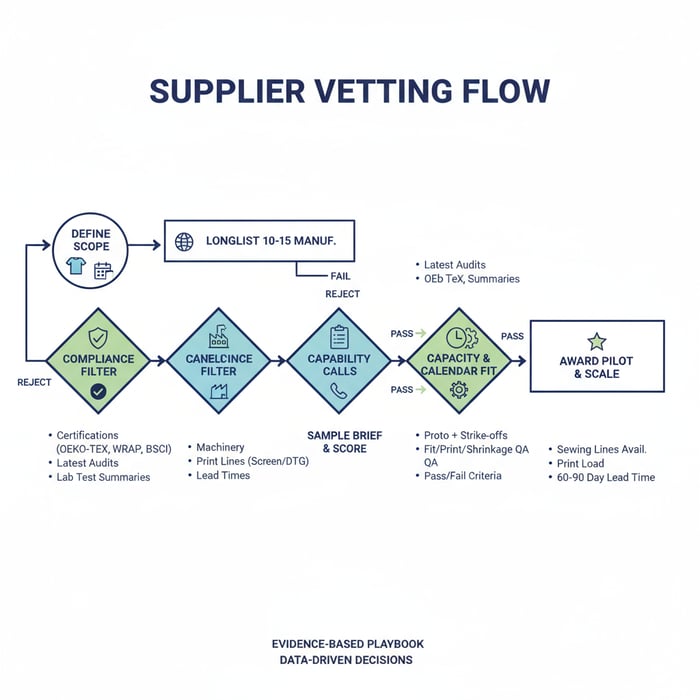
Answer-first: Shortlist 3–5 factories that match your MOQ, fabric/print capability, and certifications. Validate references and audit reports, then run a sample trial with pass/fail criteria before awarding bulk.
Start with clarity: desired GSM ranges, cotton type (carded vs combed; ringspun vs open-end), print methods, and delivery window. Use a structured workflow to filter marketplace lists into a defensible shortlist while capturing compliance and capacity signals tailored to US/EU expectations.
- Capability: Knit lines, auto cutters, screen/DTG/sublimation capacity; embroidery units; lab test history.
- Compliance: OEKO-TEX Standard 100, WRAP, BSCI/SEDEX, ISO 9001; Better Work participation where applicable.
- Capacity & Calendar Fit: Sewing lines available; printing bottlenecks; seasonal load; achievable 60–90 day lead time.
- Traceability: Cotton origin documentation (gin, mill, lot), transaction records, chain-of-custody assurance.
- References & Audits: Buyer references; latest third-party audits; corrective action plans.
- Finance & Terms: Payment terms; Incoterms (FOB/CIF/DDP); credit/trade insurance.
- Define scope: target GSM, cotton type, decorations, MOQ, delivery window.
- Longlist: identify 10–15 tshirt manufacturers in China/Bangladesh with matching capability.
- Compliance filter: request certifications, latest audits, and lab test summaries.
- Capability calls: verify machinery, print lines, and current load; record lead-time estimates.
- Sample brief: send tech pack; request proto + print strike-offs with pass/fail criteria.
- Score samples: fit, print adhesion, colorfastness, shrinkage, and measurement tolerance.
- Award pilot: select 1–2 factories for a controlled pilot before scaling.
Capability & Compliance Signals
Confirm core signals before sampling. Capability: circular knitting partners, cutting accuracy, sewing line balance for tees, and the exact print methods you need (plasticol screen, water-based, DTG, sublimation). Compliance: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 for harmful substances control, WRAP for social compliance, BSCI or SEDEX for audit rigor, ISO 9001 for process quality, and Better Work where present. Request lab test histories on colorfastness, pilling, shrinkage, and print adhesion. For US/EU programs, add fiber origin proof and chain-of-custody documentation to satisfy UFLPA/CSDDD expectations. [MENTION: OEKO-TEX Association] [MENTION: BSCI] [CITE: “Comparative reliability of apparel factory audits and certifications, 2024”]
Running a Low-Risk Sample Trial
Set hard criteria. Fit: approve graded specs and tolerances; measure at shoulder width, chest, body length, sleeve length, and hem. Print: check opacity, edge sharpness, wash resistance (home laundry cycles), and hand-feel. Fabric: verify GSM, shrinkage allowance, and dimensional stability after wash. QA: classify defects, hit AQL targets (commonly 2.5 for majors), and log corrective actions. Pass/fail in black and white cuts subjectivity and speeds a fair award. [MENTION: ASTM] [CITE: “Standard test methods for textiles applicable to retail apparel, 2023–2024 update”]
[INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability & compliance overview → Cluster page idea] [INTERNAL LINK: Our sampling SOP for tees → Eton knowledge hub]
Tshirt Manufacturing Costs, MOQs, and Lead Times in 2025
Answer-first: Expect MOQs of 300–1000 pcs per style/color. Lead time runs 60–90 days post-approval, with China stronger on agility and complex prints, and Bangladesh efficient at scale. Costs are driven by fabric GSM and cotton type, decoration method, labor, overhead, QA, and freight.
Use a decomposed cost view to avoid surprises and align Incoterms to your budget model. Lock decisions early—fabric type, print method, trim package, and test scope—then align approvals to calendar gates. This is how US/EU brands hold margin while maintaining compliance.
| Component | What Drives It | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric | GSM, cotton type (carded vs combed; ringspun vs open-end), yarn-dye vs piece-dye | Higher GSM and combed/ringspun raise cost and perceived quality |
| Trims | Labels, care tags, hangtags, polybags, cartons | Consolidate trims across styles to reduce unit cost |
| Print & Decoration | Screen setup count, ink type, DTG/sublimation runs, embroidery stitch count | Screen printing efficient at scale; DTG flexible at lower MOQs |
| CM (Cut & Make) | Labor rates, line efficiency, style complexity | Bangladesh wins at scale; China wins on agility |
| Overhead | Factory utilities, compliance admin, sampling | ODM reduces development overhead vs OEM |
| QA & Testing | Lab tests, AQL inspections, rework | Plan tests early; fewer repeats and delays |
| Freight | Incoterms (FOB/CIF/DDP), mode (sea/air), seasonality | Nearshoring and consolidation cut transit time and cost |
- Speed-to-market remains a top sourcing priority — 2024 (Source: [CITE: “McKinsey State of Fashion 2024”])
- China and Bangladesh lead knitwear exports (HS 61) — 2024 (Source: [CITE: “WTO World Trade Statistical Review 2024”])
- UFLPA requires verifiable cotton origin documentation — 2023 (Source: [CITE: “US CBP UFLPA Operational Guidance”])
MOQ Levers and Their Trade-offs
Consolidate colorways to reach fabric and print economies; reuse screens across graphics families; align rib/neckline specs to reduce changeovers; pre-book greige to lock fabric availability. Expect MOQ boundaries tied to print lines and fabric mills. Higher MOQ can lower unit cost while raising inventory risk; right-size programs to forecast and channel pace. [MENTION: Alibaba Academy] [CITE: “MOQ and cost elasticity in screen printing vs DTG, 2024”]
Lead-Time Drivers You Can Control
Approve fast and first-time-right: lock BOMs early, define lab tests at brief, and avoid mid-cycle design changes. Set strike-off approval windows; align PP sample dates to line booking; plan holiday calendars. Batch fit feedback, standardize tolerances, and use clear color standards to reduce rework. China’s agility favors complex prints; Bangladesh scales basics efficiently. [MENTION: McKinsey] [CITE: “Lead-time compression levers in apparel sourcing, 2024”]
[INTERNAL LINK: Freight & Incoterms basics → Cluster page idea] [INTERNAL LINK: Our cost breakdown method for tees → Eton blog]
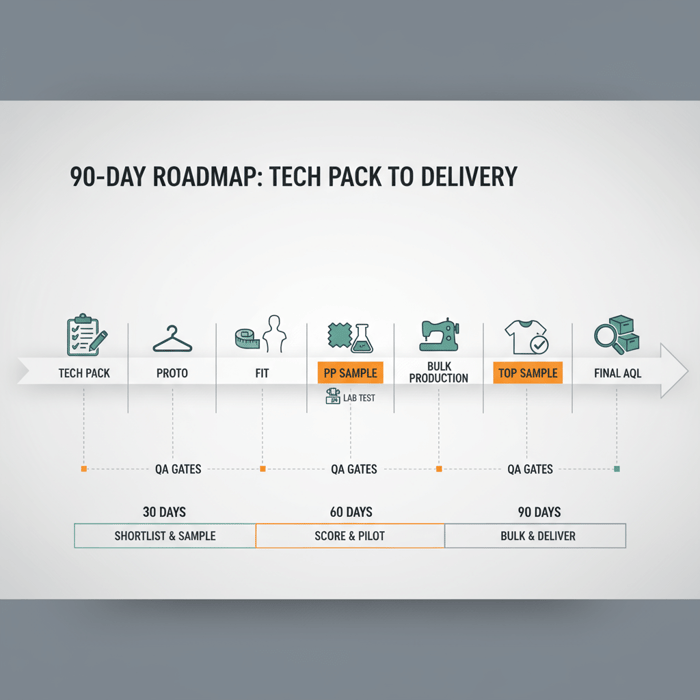
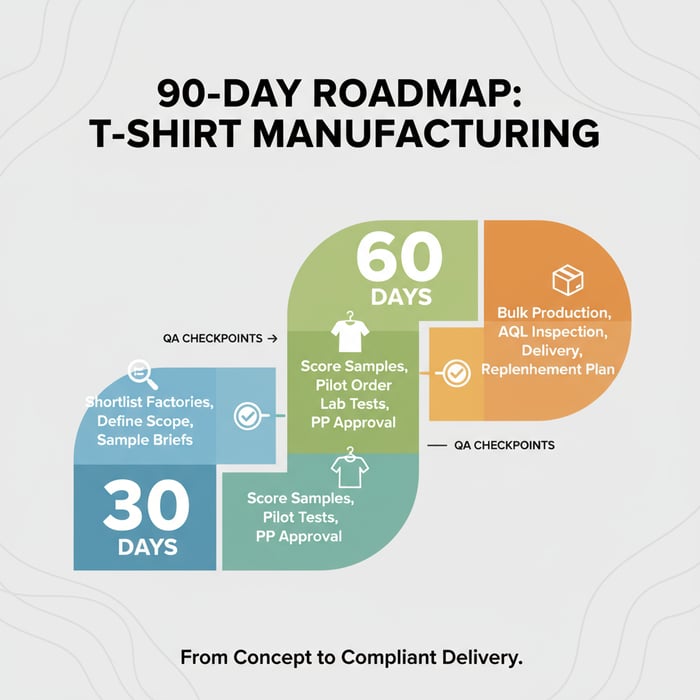
How-To: From Tech Pack to Production — A Step-by-Step Guide
Answer-first: Build a tight tech pack, approve proto and PP samples with pass/fail criteria, and align AQL inspections. Sequencing gates—tech pack → proto → fit → PP → bulk → TOP—prevent delays and lock quality.
- Tech Pack: graded specs, tolerances, stitch types, GSM, shrinkage allowance, print placements, color standards.
- Proto: silhouette validation; basic construction; initial print tests and strike-offs.
- Fit Round(s): measurement lock; wearer trials; tolerance alignment.
- Pre-Production (PP) Sample: materials and trims final; print methods finalized; lab tests triggered.
- Bulk Production: line setup; in-line QC; defect logging; corrective actions.
- TOP (Top of Production) Sample: bulk confirmation; packaging/carton checks.
- Final AQL Inspection: pass/fail scores; shipment release.
Building a Bulletproof Tech Pack
Detail what the factory needs to succeed: graded specs with tolerances, stitch codes, seam locations, GSM targets, shrinkage allowance, and print placements with dimensions. Add color standards (Pantone), print method notes (screen ink type, DTG pretreatment), and packaging requirements. Keep BOMs clean—unique codes for every trim—and specify lab tests at project start. This trims sampling rounds and gives your factory a fair shot at first-time-right execution. [MENTION: Pantone] [CITE: “Tech pack completeness and sampling cycle reductions, 2023 study”]
Sampling, Fit, and PP Approvals
Use standardized fit comments; avoid vague language and record measurable changes. Approve strike-offs for each ink and substrate combination; document wash outcomes and colorfastness. PP sample locks the bulk recipe—construction, print, trims, and packaging—so late changes should be rare and justified. Eton’s teams gate PP approvals with lab test triggers to prevent late surprises. [MENTION: ISO 105-C06] [CITE: “Colorfastness testing protocols for retail apparel, 2024 revision”]
QC & AQL Inspections
Define defects by class: critical (safety), major (function/appearance), minor (cosmetic). Align AQL levels (e.g., 2.5 majors, 4.0 minors) and schedule pre-final and final checks. Add carton QA—barcode, size ratio, and packaging integrity—so DCs accept cartons without rework. Record corrective actions and trace recurring issues to root cause (pattern, cutting, sewing, printing). [MENTION: ANSI/ASQ Z1.4] [CITE: “Effectiveness of AQL in apparel QA outcomes, 2024 assessment”]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our AQL toolkit for apparel → Resource hub] [INTERNAL LINK: Fit comment library for tees → Eton knowledge base]
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Answer-first: Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service blends China’s agility with Bangladesh’s scale. We support tech packs, sampling, compliant production, and QA gates for tees, outerwear, and technical apparel—aligned to US/EU expectations.
As an OEM partner, Eton runs dual-base planning: China for complex prints, fast capsules, and lower latency; Bangladesh for core programs and scale. Our approach is transparent: staged approvals, lab test pathways, and third-party inspection options. OEM workflows include sample calendars, capacity reservations, and communication cadence tailored to your calendar.
| Brand Need | OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Fast Capsule Drop | China-based sampling; screen vs DTG decision support; strike-off sprint | Proto-to-PP in weeks; lead-time compression with defined QA gates |
| Core Program Basics | Bangladesh line blocks; yarn-dye planning; scale print runs | Lower unit cost at higher MOQs; stable replenishment calendar |
| Compliance-First US/EU | Traceability document collection; certification stack; lab test workflows | UFLPA/CSDDD-ready files; reduced import risk |
Use Case 1: Fast Capsule Drop
Target mid-MOQs with China’s agile print capacity. Choose screen printing for bold, opaque graphics at scale; opt for DTG for multicolor art and small batches. Consolidate colorways, align rib specs, and pre-book strike-offs. Expect quicker PP approvals when graphics and tolerances are locked. Freight: DDP for speed or FOB with expedited sea/air splits for margin balance. [MENTION: DHL] [CITE: “Transit time and cost trade-offs for apparel capsules, 2024”]
Use Case 2: Core Program Basics
Place basics in Bangladesh to pull cost at higher MOQs. Plan yarn-dye vs piece-dye early; reuse screens across seasonal graphics; standardize trims. Incoterms: FOB to control freight or CIF with negotiated rates. Capacity: reserve lines for replenishment cadence; QA: embed in-line defect logging and carton checks. [MENTION: Maersk] [CITE: “Unit cost reduction through screen reuse and trim standardization, 2024 case review”]
See our Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service: Eton OEM for apparel. [INTERNAL LINK: OEM service overview — product page] [INTERNAL LINK: Contact Eton — conversion page idea]
Regional Comparison: China vs Bangladesh vs Turkey vs USA for T-shirt Production
Answer-first: China excels in agility and complex prints at mid-MOQs; Bangladesh wins on large-scale basics; Turkey offers EU nearshoring speed; USA handles small premium runs at higher cost. Pick by agility, scale, compliance infrastructure, and freight plan.
Region choice changes speed, unit cost, and risk. Compare strengths, ideal orders, and notes—then overlay Incoterms and transit plans to fit your calendar and margin goals.
| Region | Strengths | Ideal Orders | Risks/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Agility, complex prints, mid-MOQs, fast sampling | Capsules, graphic-heavy tees, mid-scale programs | Higher labor cost vs Bangladesh; strong compliance infrastructure |
| Bangladesh | Scale, lower unit cost, knitwear capacity | Core basics, large replenishment orders | Longer transit; plan traceability and social compliance rigor |
| Turkey | EU nearshoring speed; quality knit expertise | Mid-size runs; faster EU deliveries | Higher cost vs Asia; balance speed vs margin |
| USA | Small-run speed; premium quality control | Limited capsules, events, premium tees | Highest cost; capacity constraints for scale |
- China: Pro—agility and print capability. Con—unit cost higher than Bangladesh.
- Bangladesh: Pro—scale and cost. Con—longer lead/transit; plan compliance and audits.
- Turkey: Pro—nearshoring speed to EU. Con—cost premium vs Asia.
- USA: Pro—fast boutique runs. Con—highest unit cost; limited scale.
- Asian knitwear export leaders maintain share — 2024 (Source: [CITE: “WTO, 2024 — HS 61 exports”])
- Nearshoring gains attention for speed — 2024 (Source: [CITE: “McKinsey State of Fashion, 2024”])
Criteria Overview
Score regions against agility, scale, print complexity, compliance infrastructure, and transit reliability. Assign weights by program type—capsule vs core basics—and map Incoterms to freight cost and control. Keep calendar realities in view: holidays, peak seasons, and capacity reservations. [MENTION: WTO] [CITE: “Comparative regional performance in apparel sourcing, 2024 synthesis”]
Decision Framework
Use a two-pass score: 1) Technical fit (fabric, print, MOQ, lead time) and 2) Compliance/logistics (certifications, traceability, transit). If two regions tie, pick the one with stronger document readiness for UFLPA/CSDDD and better freight routing. The aim: speed and margin without regulatory surprises. [MENTION: OECD] [CITE: “Risk-based decision frameworks in textile sourcing, 2023 guidance”]
Risks, Compliance & Localization (US & EU)
Answer-first: Document fiber origin, map your supply chain, and align certifications to recognized bodies. US buyers should prepare UFLPA due diligence; EU buyers should plan for CSDDD. Build a traceability file and corrective action workflow.
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber origin documentation gaps | Medium–High (cotton) | High (import holds) | Collect gin/mill records; chain-of-custody; third-party traceability |
| Audit non-conformance | Medium | Medium–High | WRAP/BSCI audits; corrective action plans; follow-ups |
| QA failures (print/shrinkage) | Medium | Medium | Strike-offs; lab tests; AQL inspections; root-cause analysis |
| Transit delays | Medium | Medium–High | Buffer calendars; routing options; Incoterm alignment; 3PL support |
Risk Matrix
Prioritize fiber origin documentation—especially for cotton tees—and align lab testing, audits, and corrective action plans to your buyer SOP. Traceability files should include transaction records, bills of lading, mill/lot references, and supply chain maps with names and addresses. [MENTION: AAFA] [CITE: “Traceability frameworks and import risk reduction, 2023–2024 industry reports”]
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
US: UFLPA requires verifiable evidence of cotton origin and supply chain due diligence—prepare a document pack covering fiber source, chain-of-custody, and transaction proofs. EU: CSDDD mandates risk-based due diligence—align supplier codes of conduct to OECD guidance and deploy corrective action workflows. Add certification stack references (OEKO-TEX Standard 100, WRAP, BSCI) and lab test records to shipment files. [MENTION: US CBP] [MENTION: European Commission] [CITE: “Importer guidance for UFLPA compliance, 2023; EU CSDDD obligations, 2024”]
[INTERNAL LINK: Compliance & traceability checklist → Resource hub] [INTERNAL LINK: Supplier code of conduct aligned to OECD → Template page]
Conclusion & Next Steps
Answer-first: Shortlist with a compliance-first lens, test with samples and defined QA, then scale where the region fits your mix of cost and speed. Eton can turn your tech pack into a repeatable tee program across China and Bangladesh.
- 30 days: define scope, longlist, filter for capability/compliance; run sample briefs.
- 60 days: score samples, award pilot, align lab tests and PP approvals; confirm freight plan.
- 90 days: complete bulk, pass AQL, ship; build a replenishment calendar and traceability file.
Move from concept to delivery with Eton’s dual-base OEM support for tees, outerwear, and technical apparel. Contact us to map your next launch: Eton Garment Limited. [INTERNAL LINK: Contact Eton → Conversion page idea] [INTERNAL LINK: Tech pack template for t-shirts → Resource hub idea]
Author: Senior Apparel Sourcing Strategist, 12+ years in OEM/ODM knitwear and outerwear production.
Reviewer: Head of Quality, Eton Garment Limited.
Methodology: Synthesized factory-floor practices and recognized guidance (WTO, OECD, CBP, EU); calibrated for US/EU markets.
Limitations: Costs/lead times vary by season, fabric, and capacity; regulations evolve—confirm with legal/compliance teams.
Disclosure: Produced by Eton Garment Limited (OEM/ODM apparel manufacturer). Last Updated: 2025-10-27.
[INTERNAL LINK: {{author_name}} — {{author_title}} {{author_bio_url}}]
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024 (2024). https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights
- World Trade Organization — World Trade Statistical Review 2024 (2024). https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/statis_e/wts2024_e/wts2024_e.htm
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection — UFLPA Operational Guidance for Importers (2023). https://www.cbp.gov/trade/forced-labor/UFLPA
- European Union — Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (2024). https://commission.europa.eu
- OECD — Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains in the Garment and Footwear Sector (2023). https://mneguidelines.oecd.org
- Textile Exchange — Material Change Insights (2024). https://textileexchange.org
- Better Work (ILO/IFC) — Annual Report (2024). https://betterwork.org
- American Apparel & Footwear Association — Traceability & Sustainability Report (2023/2024). https://www.aafaglobal.org
- WRAP — WRAP Certification (Accessed 2025). https://wrapcompliance.org
- World Resources Institute — Apparel Sector Climate Insights (2023). https://www.wri.org
FAQs
Related Articles
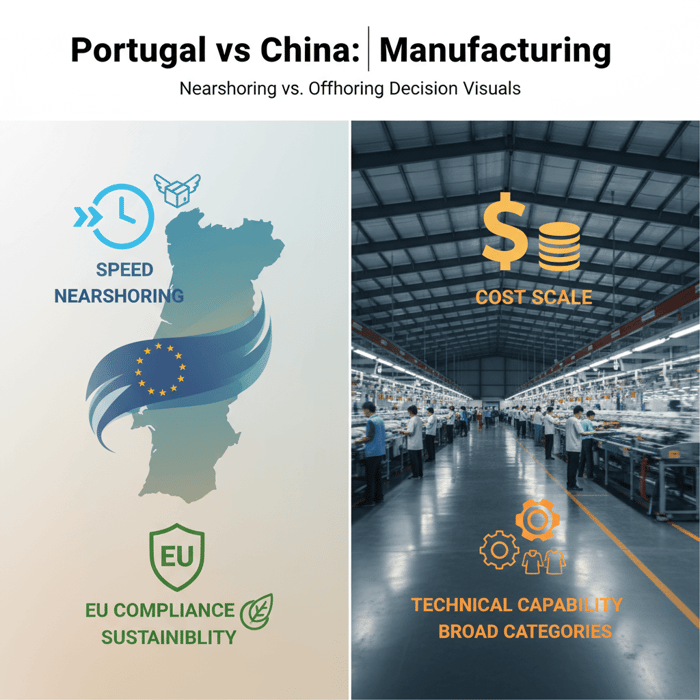
Portuguese Manufacturers vs China Clothing Manufacturer: A Buyer’s Guide for Fashion Brands
15 minute read
October 27th, 2025
Portuguese Manufacturers vs China Clothing Manufacturer: A Buyer’s Guide for Fashion Brands Portuguese... more »

Clothing Manufacturers for Startups from Development to Production: How to Choose the Right China Clothing Manufacturer
20 minute read
October 27th, 2025
Clothing Manufacturers for Startups from Development to Production: How to Choose the Right China Clothing... more »
Clothes with Pictures on Them: A Fashion Brand’s Manufacturing Guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 27th, 2025
Clothes with Pictures on Them: A Fashion Brand’s Manufacturing Guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »
american made workwear: Standards, Sourcing, and Global Alternatives with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 27th, 2025
american made workwear: Standards, Sourcing, and Global Alternatives with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

