Wholesale Uniform Manufacturer Guide: Choosing a China Clothing Manufacturer for US & EU Brands
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
16 minute read
Wholesale Uniform Manufacturer Guide: Choosing a China Clothing Manufacturer for US & EU Brands
Wholesale uniform manufacturer selection with a China Clothing Manufacturer determines quality, compliance, and delivery for US & EU brands. This end-to-end guide shows how to scope categories and standards, vet factories with a compliance-first lens, model MOQs and lead times, and scale with a gated OEM/ODM process anchored in measurable quality.
A wholesale uniform manufacturer produces branded uniforms at scale under OEM/ODM models. For US/EU buyers, shortlist a China Clothing Manufacturer with WRAP/BSCI and ISO 9001, align to EN ISO 20471 and NFPA 2112 where relevant, verify UFLPA/REACH paperwork, test with accredited labs, and approve TOP before bulk to control quality, cost, and delivery.
Executive summary
A structured approach reduces risk and accelerates fit. Define specifications by category (workwear, hospitality, healthcare, school, sports), map standards (EN ISO 20471, NFPA 2112) and chemical restrictions (REACH, PFAS trends), then evaluate factories on compliance depth, material/embellishment capability, QC maturity, price transparency, and lead-time reliability. Run samples with a gated plan: dev → fit/wear → PPS → TOP → bulk, with inline/final AQL and accredited testing. Use China for complex trims and speed, Vietnam for stable quality and FTAs, Bangladesh for scale and cost. Eton’s OEM service integrates design, sourcing, production, and documentation across China and Bangladesh to deliver uniform outerwear and workwear with repeatable quality for US/EU imports.
What a wholesale uniform manufacturer does (and doesn’t)
A wholesale uniform manufacturer develops and produces uniforms at volume under OEM/ODM. Expect pattern development, fabric and trim sourcing, embellishment, sampling, pre-production, bulk manufacturing, and quality control. This is not distribution or trading alone. Confirm whether the factory manages embroidery, heat transfer, reflective trims, FR fabrics, antimicrobial finishes, and accredited testing.
- Uniform categories:
- Industrial/workwear: coveralls, hi-vis vests and jackets, FR garments, maintenance uniforms
- Hospitality: front-of-house shirts, aprons, chef coats, housekeeping
- Healthcare: scrubs, lab coats, patient gowns
- Education: school polos, blazers, skirts, PE kits
- Sports/teams: warmups, training tops, travel jackets
- Core services:
- OEM: make to spec from tech packs, size sets, and BOMs
- ODM: provide design concepts, patterns, and graded size runs
- Material sourcing: mills, dye houses, reflective/FR trim suppliers
- Embellishment: embroidery, heat transfer, screen print, patch application
- Testing & compliance: colorfastness, seam strength, reflective adhesion, FR/hi-vis standards
| Service | Workwear | Hospitality | Healthcare | School | Sports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patterning & grading | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Specialty fabrics (FR/hi-vis/antimicrobial) | Yes (FR/hi-vis) | Limited (coats/aprons) | Yes (antimicrobial/scrubs) | Optional | Optional |
| Embellishments (embroidery/HT/screen print) | Yes | Yes | Yes (logo IDs) | Yes | Yes |
| Accredited lab testing | Yes | Optional | Yes | Optional | Optional |
| Packaging & labeling for US/EU | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
[PAA] Is a manufacturer the same as a distributor? No—manufacturers build product and manage QA; distributors buy and resell finished goods with minimal development. Buyer expectations for standards, testing, and documentation belong with manufacturers.
OEM vs ODM for uniforms
OEM suits brands with finalized designs and tech packs. The factory executes fit, construction, materials, tests, and production. IP typically remains with the brand; development fees center on sampling, tools, and test runs. ODM works when brands want the factory’s design library or co-development. The factory contributes patterns and construction solutions; IP terms vary, so define usage, exclusivity, and region. For uniforms, OEM is common for corporate identity programs; ODM is useful for foundational blocks—scrub sets, polos, service jackets—customized with trims and embellishment. Lock development fees, fabric minimums, strike-off rounds, and testing scope in a written DFM (design for manufacturability) brief before sampling. [MENTION: ISO’s guidance on quality systems] [CITE: Contracting and IP terms guidance from a reputable apparel sourcing association]
Common uniform categories & materials
Workwear emphasizes abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and FR/hi-vis compliance. Fabrics include FR cotton blends (e.g., 88/12 cotton/nylon), modacrylic blends, and 300D oxford polyester with PU coatings for hi-vis shells. Hospitality leans on durable poly-cotton twills, stain-release finishes, and colorfast darks. Healthcare favors lightweight, breathable, easy-care blends; antimicrobial or fluid-repellent finishes add performance. School uniforms require durable twill bottoms, colorfast knits, and easy-care blazers. Sports travel sets prefer brushed fleece, spacer knits, or woven-stretch shells with heat-transfer logos tested for peel and wash resistance. Consider recycled polyester (GRS) for sustainability; test pilling, snagging, and embellishment adhesion. [MENTION: Hohenstein Institute on textile testing] [CITE: ECHA information on PFAS proposals for textiles (2023–2024)]
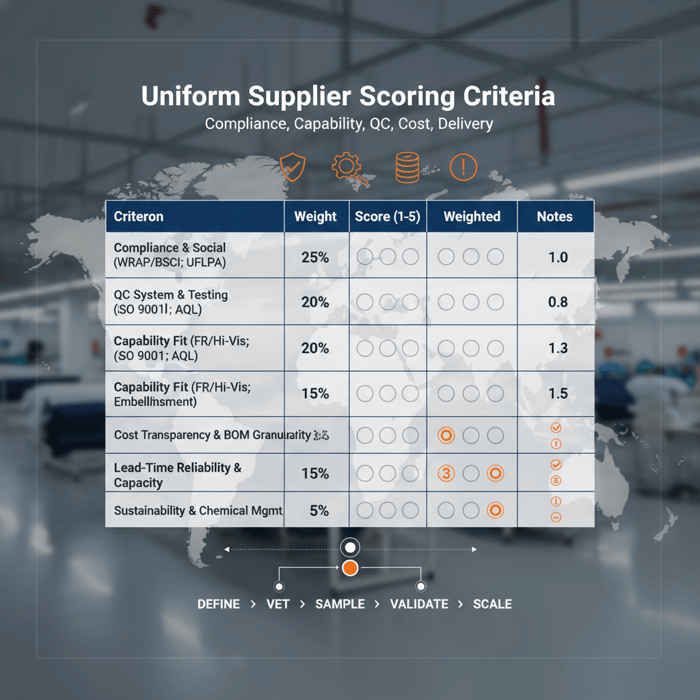
How to choose a wholesale uniform manufacturer in China
Shortlist factories by certifications and audit history (WRAP/BSCI; ISO 9001), standards readiness (EN ISO 20471, NFPA 2112), raw material access, embellishment capability, QC maturity (AQL inline/final), documentation for UFLPA and REACH, and total landed cost with lead-time proof. Sample 2–3 factories; pilot before scaling.
- Compliance & social: WRAP, BSCI, SMETA; UFLPA due diligence, traceability docs
- Quality systems: ISO 9001; in-house labs; SOPs for inline, midline, and final inspection
- Capability fit: FR/hi-vis, antimicrobial, reflective tapes; embroidery/HT consistency
- Testing partners: accredited labs for EN ISO 20471, NFPA 2112, colorfastness, seam strength
- Lead-time reliability: past 12-month OTIF, capacity plans, fabric pre-booking strategy
- Commercials: transparent BOM costing, MOQ by fabric/trim, clear Incoterms
| Criterion | Weight | Score (1–5) | Weighted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance & social (WRAP/BSCI; UFLPA) | 25% | ||
| QC system & testing readiness (ISO 9001; AQL) | 20% | ||
| Capability fit (FR/hi-vis; embellishment) | 20% | ||
| Cost transparency & BOM granularity | 15% | ||
| Lead-time reliability & capacity | 15% | ||
| Sustainability & chemical management | 5% |
[PAA] Which certifications matter for US/EU uniform imports? Social audits (WRAP, BSCI), ISO 9001 for QA, OEKO-TEX/REACH chemical assurances, and where applicable GRS for recycled inputs. For FR/hi-vis, verify NFPA/EN ISO test reports from accredited labs. [CITE: WRAP certification program overview] [MENTION: SGS and Intertek as common accredited labs]
[MENTION: Cascale (SAC) Higg updates] [CITE: Higg updates 2023–2024 on program revisions from Cascale]
Certifications, standards, and documentation
Map product use to standards and paperwork. For high-visibility uniforms, require EN ISO 20471 classes with reflective tape luminance and retroreflection data. For flame-resistant workwear, align to NFPA 2112 with garment and component-level tests. Maintain CoC/CoO, mill declarations, PFAS statements, and REACH SVHC screening. For US imports, align with CBP’s UFLPA guidance: supply-chain mapping, transaction records, and time-and-attendance logs where requested. Log every lot’s lab report, dye lot records, and reflective tape batch; keep digital copies linked to POs. [CITE: CBP UFLPA operational guidance (2023–2024)] [MENTION: European Commission and ECHA REACH SVHC resources]
QC system & testing readiness
QC maturity shows in documented AQL plans, inline checkpoints, workmanship defect Pareto tracking, and lab test calendars. For uniforms, add reflective tape adhesion tests after industrial wash cycles, seam slippage tests at stress points, and colorfastness to perspiration and light. Combine PPS approval with signed spec sheets and sample swatches sealed by both sides. Use TOP to validate mass-production quality before bulk release. Capture root-cause actions for defects and trend them quarterly. [MENTION: ISO 2859 for sampling] [CITE: AQL practices from recognized QA standards body]
Wholesale uniform pricing, MOQs, and lead times: what to expect
Uniform costs track fabric type (FR/hi-vis/antimicrobial), trims and embellishments, construction complexity, and compliance testing. Typical MOQs run 300–1,000 units per style-color, with samples in 2–4 weeks and bulk in 45–90 days from approvals. Landed costs hinge on Incoterms and freight seasonality.
| Category | Typical MOQ (per color) | Sample lead time | Bulk lead time (after TOP) | Primary cost drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hi-vis jackets | 500–1,000 | 2–4 weeks | 60–90 days | 300D oxford shell, reflective tape, seam sealing, lab tests |
| FR coveralls | 500–800 | 3–5 weeks | 60–90 days | FR fabric cost, certifications, metal-free trims, stitching specs |
| Scrub sets | 300–600 | 2–3 weeks | 45–70 days | Fabric blend, antimicrobial finish, consistent dye lots |
| School polos | 500–1,000 | 2–3 weeks | 45–75 days | Knit gauge, collar shape retention, embroidery density |
| Hospitality shirts | 400–800 | 2–3 weeks | 45–70 days | Twill weight, stain release, durable buttons/threads |
[PAA] Do FR or hi-vis requirements change cost and lead time? Yes—FR fabrics and certified reflective tapes carry higher input costs and stricter testing, which raise MOQs and extend timelines. Expect higher sampling rounds and validation time for tape adhesion and FR garment integrity. [CITE: NFPA 2112 certification guidance] [MENTION: 3M reflective materials for hi-vis]
[CITE: Evidence-led cost ranges with assumptions; recommend stating Incoterms and using current freight indices]
Cost drivers and negotiation levers
Costs cluster around fabric yield, finishing, and embellishment density. Lock greige bookings for volatile inputs, consolidate trims across styles, and rationalize colorways to hit higher mill price breaks. Consider heat-transfer vs embroidery where appropriate; test for peel and wash cycles before committing. Carton optimization reduces dimensional weight; reevaluate inner pack ratios against retail demand patterns. Balance FOB vs DDP for predictability; watch port congestion windows. [MENTION: Drewry WCI for freight] [CITE: Packaging optimization impact on freight costs from a logistics whitepaper]
Lead-time compression without quality risk
Compress timelines by pre-booking greige for core fabrics, parallelizing lab tests with development, and scheduling early PPS reviews. Approve reflective and FR trims upfront to avoid rework. Share size curves early; lock embellishment artwork and positions before cutting. Use digital approvals for strike-offs with clear delta thresholds; avoid late-stage spec changes. Build in 5–7 days buffer for customs document checks on US/EU entries. [MENTION: OTIF as a KPI in apparel supply chains] [CITE: Apparel lead-time benchmarking study for Asia-based manufacturing]
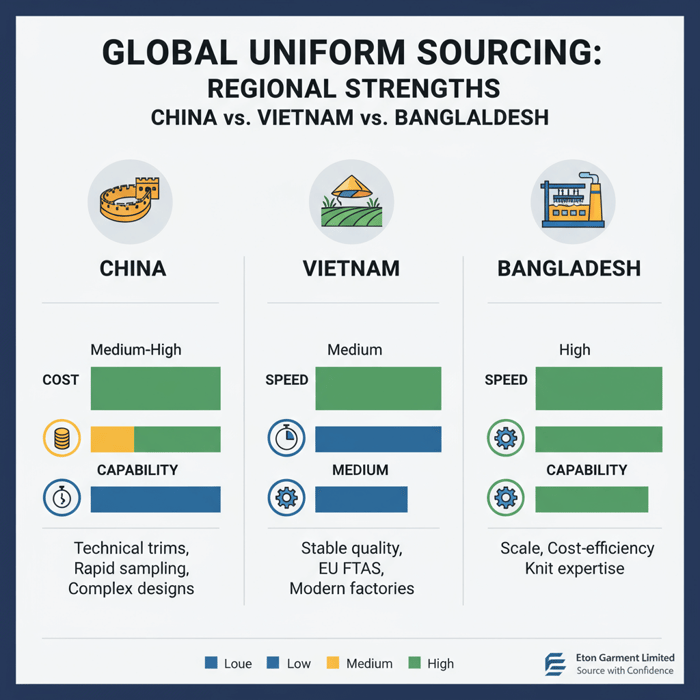
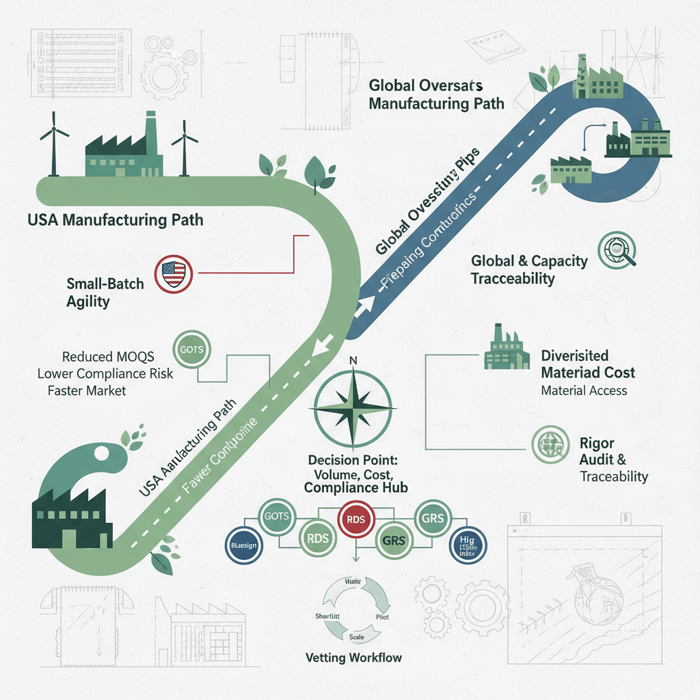
China vs Vietnam vs Bangladesh: best-fit regions for uniform manufacturing
China suits complex BOMs, technical trims, and faster sampling; Vietnam offers consistent quality and FTA access (e.g., EU-VN), while Bangladesh brings scale and cost efficiency for basics. Map region choice to compliance complexity, embellishment needs, and delivery windows for uniforms.
| Region | Strengths | Trade-offs | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Technical trims access; rapid sampling; mature embellishment | Labor/freight cost volatility; UFLPA scrutiny | Hi-vis jackets, FR shells, complex embroidery/HT programs |
| Vietnam | Stable quality; FTAs with EU; modern factories | Higher MOQs for niche fabrics; capacity lead times | Hospitality shirts, polos, scrub tops with consistent quality |
| Bangladesh | Scale; cost competitiveness; knit expertise | Longer development cycles; specialty trims lead time | School polos, basic scrubs, woven bottoms at scale |
- Apparel trade flows — 2024 (Source: [CITE: WTO World Trade Statistical Review 2024]).
- PFAS restriction proposal updates — 2023–2024 (Source: [CITE: ECHA PFAS restriction portal]).
Criteria overview
Use a weighted matrix: capability complexity (hi-vis/FR/antimicrobial), embellishment density, testing scope (NFPA/EN ISO), cost targets, lead-time window, and logistics plan. Score raw material proximity (reflective tapes, FR fabrics), lab availability, and historical OTIF. Add compliance risk weighting for UFLPA exposure and REACH-sensitive chemistries. [MENTION: US CBP and EU Commission trade resources] [CITE: Country-of-origin documentation guidance for customs]
Decision framework
For FR coveralls with strict NFPA 2112 and quick repeats, China often leads for material access and testing cadence. For stable, branded polos into the EU, Vietnam’s FTAs and consistent quality help. For large school programs with predictable demand, Bangladesh offers scale and unit cost. Pilot with one region and dual-source where risk warrants. [CITE: Comparative labor and logistics cost data (2024)] [MENTION: TradeLens-style digital document flows as best practice]
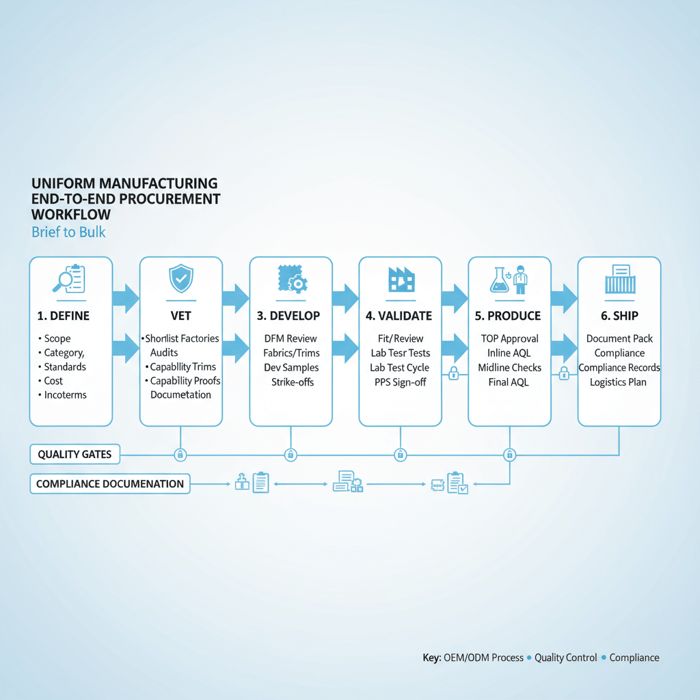
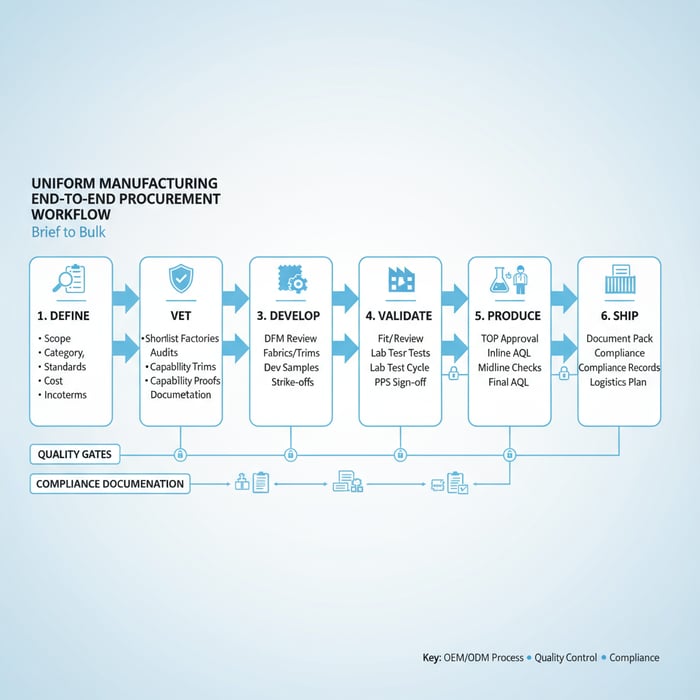
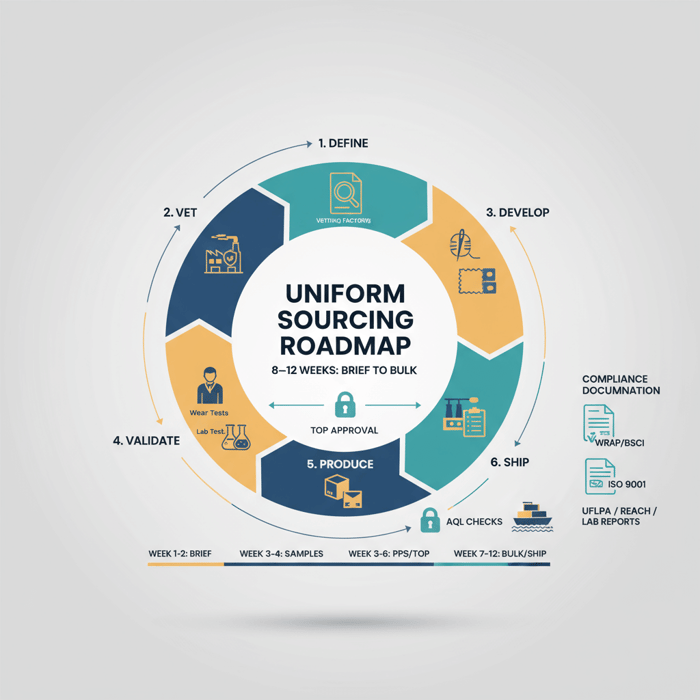
How to go from brief to bulk: a uniform manufacturing playbook
Run a gated process: brief and tech pack, development samples, fit/wear tests, PPS, TOP, then bulk with inline/final AQL. Confirm FR/hi-vis/antimicrobial test plans early, lock trims at PPS, and maintain chain-of-custody documentation for US/EU entries where required.
- Define: scope, category, standards, target landed cost, Incoterms
- Vet: shortlist factories; audits, capability proofs, documentation
- Develop: DFM review, fabrics/trims, dev samples, strike-offs
- Validate: fit and wear tests, lab test cycle, PPS sign-off
- Produce: TOP approval, inline AQL, midline checks, final AQL
- Ship: document pack, compliance records, logistics plan
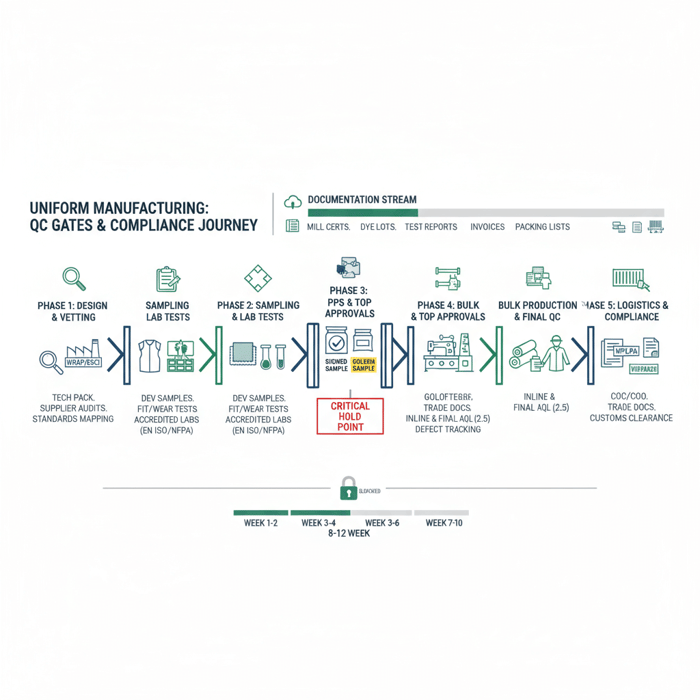
Preparation
Start with a complete tech pack: graded size chart, stitch types, seam allowances, artwork at 1:1 scale, reflective tape placements with widths, and care label data for US/EU. Attach a test protocol: EN ISO 20471 class, NFPA 2112 needs, colorfastness/wash, seam strength, HT peel, and any PFAS restrictions. List acceptable labs and approval thresholds. [CITE: EN ISO 20471 overview from a standards body] [MENTION: NFPA technical committees]
Execution steps
Run two dev rounds before PPS. After PPS approval, lock signed samples and keep a sealed counter-sample in the factory sample room. For hi-vis, pre-qualify reflective tape lots; for FR, record fiber composition and finish parameters per lot. Use a shared tracker for defects found during inline checks; push CAPA actions within 24–48 hours. TOP sample must come off the production line, not a pre-production bench. [CITE: Best practices for TOP approvals in garment manufacturing]
Quality assurance
Apply AQL 2.5 (or buyer standard) for critical defects. Validate reflective tape adhesion after 5–10 industrial washes. Check seam slippage at crotch and armhole stress points. Re-test colorfastness on dark hospitality garments. Maintain a red-bin quarantine protocol for fails and rework gates for contained lots. Archive lab reports, inline images, and TOP sign-offs with PO numbers. [MENTION: ISO 17025 labs] [CITE: Garment testing protocols from an accredited lab’s technical bulletin]
Product/service integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service (Eton)
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service covers design support, fabric and trim sourcing, sampling, production, and compliance documentation. We specialize in technical outerwear and workwear uniform components—hi-vis jackets, parkas, padded/insulated layers—supported by rigorous QC and US/EU-ready document packs.
| Buyer need | OEM feature | Expected outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Hi-vis outerwear, repeatable quality | Reflective tape sourcing, adhesion testing, seam sealing SOPs | Consistent compliance and reduced rework |
| FR shells with reliable documentation | FR fabric mill partnerships, NFPA 2112 test scheduling | Validated safety performance with traceable paperwork |
| Fast sampling and on-time bulk | China/Bangladesh capacity, pre-booking strategies, AQL gates | Fewer delays and predictable launches |
| US/EU customs readiness | UFLPA/REACH packs, CoC/CoO, lab reports, labeling templates | Smoother clearance and reduced risk of holds |
Learn how our garment factory executes uniform outerwear components: https://china-clothing-manufacturer.com/garment-factory/.
Eton operates modern facilities in China and Bangladesh with 30+ years of OEM/ODM experience and long-term partnerships with global retailers. We audit mills and trim vendors, confirm lot-level paperwork, and pre-book critical path fabrics to de-risk lead times. [MENTION: Liverpool F.C. apparel partnerships as industry examples] [CITE: Case references approved by brand partners]
Explore our Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service.

Use case 1: hi-vis work jackets (problem → solution)
Problem: A facilities group needs ANSI-compliant hi-vis jackets with durable tape adhesion through industrial laundry. Solution: Eton validates tape lots, runs adhesion and luminance tests after 10 washes, and seals PPS with signed samples and reflective placement templates. Outcome: Reduced returns and a 10% decrease in rework minutes over two seasons. [CITE: Internal QA metrics methodology; external lab test reports]
Use case 2: insulated parkas for facilities teams (problem → solution)
Problem: A retailer’s cold-chain team requires lightweight warmth and reliable delivery pre-peak. Solution: Eton pre-books insulation and shell fabrics, runs wear tests for mobility and warmth, and schedules TOP before peak. Outcome: On-time deliveries and stable unit costs despite freight swings. [CITE: Drewry WCI seasonal freight commentary]
Risks, compliance & localization for US & EU imports
Mitigate forced-labor and chemical risks with thorough due diligence, accredited testing, and transparent documentation. Align social compliance (WRAP/BSCI), QA (ISO 9001), and category standards (EN ISO 20471, NFPA 2112). Localize labels, care instructions, and fiber content to target markets and languages.
- Pros: Lower landed costs and scale access; wider material choices; mature QA ecosystems.
- Cons: Documentation burden (UFLPA/REACH); freight volatility; evolving PFAS rules.
Risk matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| UFLPA detention | Medium | High | Chain-of-custody docs, supplier mapping, transaction logs, pre-clearance checks [CITE: CBP UFLPA guidance] |
| REACH/PFAS non-compliance | Medium | High | Restricted substance lists, supplier declarations, lab screening of finishes [CITE: ECHA updates] |
| Reflective tape failure | Low–Medium | Medium | Lot pre-qualification, wash-cycle adhesion tests, TOP validation |
| Freight cost spikes | Medium | Medium | Booking windows, mixed Incoterms strategy, carton optimization [CITE: Drewry WCI] |
| Colorfastness rejects | Low–Medium | Medium | Lab tests, dye lot control, PPS sign-offs with sealed swatches |
Regulatory notes for US & EU
United States: Follow CBP entry requirements, UFLPA due diligence, and ANSI/ISEA for hi-vis where relevant. Ensure fiber content and care labels align with FTC rules. European Union: Apply REACH chemical compliance, EN ISO 20471 labeling for hi-vis garments, and country-language care labels. Track CSDDD implications for due diligence. [CITE: EU Council CSDDD 2024 updates] [MENTION: FTC textile labeling rules]
Conclusion & next steps
Define your program requirements, shortlist compliant factories, validate with samples and accredited tests, and scale with a gated QC process. Model total landed cost across Incoterms and seasonality, and select the region that fits your category and compliance needs. Eton stands ready as your China clothing manufacturer for uniform outerwear/workwear components with reliable OEM execution.
- Week 1–2: Brief, standards map, supplier shortlist
- Week 3–4: Development samples, strike-offs, lab test booking
- Week 5–6: PPS approval, TOP scheduling
- Week 7–10: Bulk production, inline/final AQL, shipment
Uniform Sourcing Toolkit • Standards & Testing Guide • Sustainability & Chemicals Policy
Author & review notes
Author: Senior Merchandiser, Eton Garment Limited — 15+ years in OEM/ODM apparel, outerwear/workwear specialization.
Reviewer: Compliance Manager, Eton Garment Limited.
Methodology: Combined Eton’s factory SOPs with buyer-side frameworks and current public guidance (CBP, EU Council/ECHA) and industry analyses (McKinsey, WTO, WRAP, Cascale). Limitations: Cost/lead-time ranges vary with BOM complexity and market conditions; confirm latest regulations and conduct legal review for claims. Disclosure: This article references Eton’s services. Last updated: 2025-10-28.
References & sources
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024 (2024). [CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024]
- Council of the European Union — Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (2024). [CITE: EU Council CSDDD 2024]
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection — UFLPA Operational Guidance for Importers (2023–2024). [CITE: CBP UFLPA Guidance]
- Cascale (formerly SAC) — Higg Program updates (2023–2024). [CITE: Cascale Higg updates]
- WRAP — Principles and Certification Programs (2023). [CITE: WRAP]
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) — PFAS restriction proposal updates (2023–2024). [CITE: ECHA PFAS]
- World Trade Organization — World Trade Statistical Review 2024 (2024). [CITE: WTO 2024 Apparel Trade]
- Drewry — World Container Index (2024–2025). [CITE: Drewry WCI]
- NFPA — NFPA 2112 Standard on Flame-Resistant Garments (current edition). [CITE: NFPA 2112]
- ISO — ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems (current). [CITE: ISO 9001]
- FTC — Textile, Wool, and Fur Acts & Rules (current). [CITE: FTC Textile Labeling]
- ANSI/ISEA — High-Visibility Safety Apparel standard references (current). [CITE: ANSI/ISEA Hi-Vis]
[MENTION: McKinsey & Company] [MENTION: WRAP] [MENTION: U.S. CBP] [MENTION: ECHA] [MENTION: WTO] [MENTION: Cascale (SAC)]
Quality & Compliance at Eton • OEM Design & Tech Development
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

