T Shirt Material Wholesale: A Fashion Brand’s Guide to Sourcing with a China Clothing Manufacturer

 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
17 minute read
T Shirt Material Wholesale: A Fashion Brand’s Guide to Sourcing with a China Clothing Manufacturer
T shirt material wholesale is the fastest route to locking fabric quality, price, and compliance before your tee program lands in stores. Partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer like Eton aligns fiber choices, GSM ranges, and finishes with US/EU retail goals while compressing testing and approvals. Textile From Day One.
“T shirt material wholesale” means bulk tee fabric buying from mills or via manufacturers with locked fiber, yarn, knit, GSM, finishes, compliance, MOQs, and lead times. Compare cotton, blends, and performance fabrics on printability, shrinkage, and colorfastness, then validate with lab tests before bulk.

What “t shirt material wholesale” means and the specs that matter
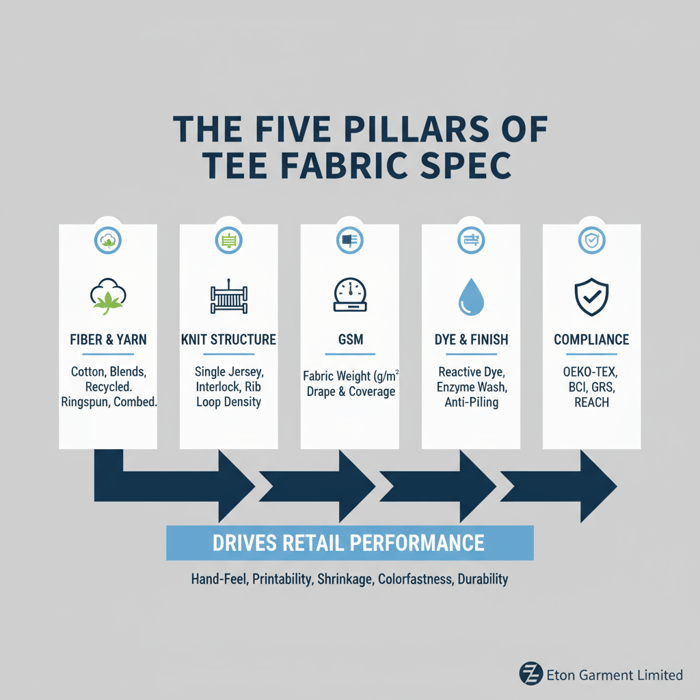
Wholesale tee fabric is bulk buying structured around fiber, yarn, knit, GSM, finishes, and compliance. Brands finalize specs with mills/manufacturers under MOQs and lead-time windows. A tight spec sheet anchors hand-feel, printability, shrinkage, and colorfastness thresholds so retail outcomes hold from launch through replenishment.
[CITE: “Wholesale fabric 101” style primer from a recognized apparel trade body]
[MENTION: Cotton Incorporated’s CottonWorks resources]
[MENTION: Fibre2Fashion technical overviews on knit structures]
[INTERNAL LINK: Fabric specification template — “Apparel Tech Packs & Spec Sheets” pillar page]
- Fiber blend: 100% cotton, poly-cotton, tri-blend, recycled polyester content.
- Yarn quality: ringspun vs open-end; combed vs carded; yarn count (Ne).
- Knit type: single jersey, interlock, rib; loop and stitch density.
- GSM: fabric weight aligned to drape, coverage, and durability targets.
- Dye/finish: reactive or disperse dye; enzyme, silicone, bio-polish, anti-pilling.
- Compliance: OEKO-TEX Standard 100, EU REACH, BCI, GRS chain-of-custody.
PAA: Is GSM alone enough to define tee quality? No. GSM sets weight, not yarn smoothness, stitch clarity, or dye/finish stability. Yarn grade and knit construction steer hand-feel, print surface, shrinkage, and pilling. Pair GSM with yarn/knit/finish to hit performance goals. [CITE: CottonWorks GSM vs performance explainer]
Fiber & Yarn Quality: ringspun vs open-end; combed vs carded
Ringspun cotton uses a continuous twisting process to produce smoother, stronger yarn with fewer protruding fibers. Open-end yarn relies on a rotor, creating a bulkier yarn with more irregularity. Combed cotton removes short fibers and impurities, giving a cleaner surface; carded cotton leaves more neps and lint. For premium basics, ringspun + combed yields a soft hand, clean print surface, and better pilling resistance. For promo tees, open-end + carded can hit lower price points with trade-offs in print clarity and hand-feel. Ringspun also supports tighter stitch definition at common tee yarn counts (e.g., Ne 20–30). [CITE: CottonWorks yarn formation overview]
[MENTION: ASTM textile terminology references]
[INTERNAL LINK: “Apparel Tech Packs & Spec Sheets” — yarn quality section]
Knit Structures: jersey, interlock, rib — use-cases and printability
Single jersey is the standard tee knit: light, breathable, with a face/back difference that delivers a familiar hand. Interlock is denser, more stable, with better opacity and smoother surfaces for fine print detail; it can feel heavier at similar GSM. Rib is stretchy and typically used for collars, cuffs, and trim; body panels in rib create a fitted silhouette with higher recovery but can distort prints. For core tees, single jersey in ringspun combed cotton balances drape and printability. For premium, interlock reduces grin-through and supports detailed graphics. Use rib strategically to preserve neck shape and comfort. [CITE: A textile engineering overview on knit stability and print behavior]
[MENTION: ISO/ASTM printability tests]
GSM & Finishes: enzyme, silicone, bio-polish
GSM sets perceived heft and drape. A 160–180 GSM single jersey suits mainstream retail basics; 180–200 GSM pushes premium weight and structure; 140–150 GSM fits promo and summer drops. Enzyme and bio-polish remove surface fuzz, improving softness and print clarity. Silicone softeners add slick hand; anti-pilling finishes boost durability for blends. Each finish carries a cost adder and potential shrinkage or shade impact, so lab tests and pilot runs are vital. Pair GSM with finish goals to avoid stiff hand or color shift post-wash. [CITE: Finish impact on hand-feel and pilling from an industry lab whitepaper]
[MENTION: OEKO-TEX finish chemical restrictions]
Best t shirt materials for wholesale: cotton, blends, and performance fabrics
Premium basics lean toward ringspun combed cotton for softness and print surface. Poly-cotton blends trade softness for lower cost and durability. Tri-blends add drape and a vintage hand. Performance knits with polyester/spandex support moisture management and stretch. Match material to print method, shrinkage target, and price architecture.
[CITE: Comparative study on cotton vs blends shrinkage and colorfastness]
[MENTION: Contrado print method compatibility notes]
[INTERNAL LINK: Printing compatibility guide — “Screen, DTG, Sublimation: Fabric Matching”]
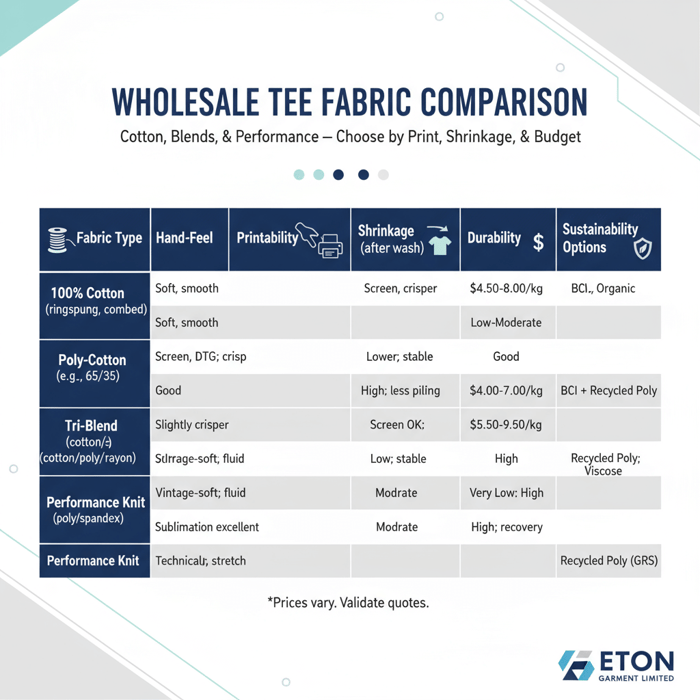
| Fabric Type | Hand-Feel | Printability | Shrinkage (after wash) | Durability | Indicative Price* | Sustainability Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% Cotton (ringspun, combed) | Soft, smooth surface | Screen, DTG friendly; crisp edges | Low–moderate with pre-shrink and set | Good with bio-polish, tighter knit | $3.50–$6.50/kg greige; $4.50–$8.00/kg finished [CITE: wholesale cotton benchmarks] | BCI, organic cotton |
| Poly-Cotton (e.g., 65/35) | Slightly crisper; less fuzz | Screen friendly; DTG requires pretreatment | Lower shrink; dimensional stability | High abrasion resistance; less pilling with finish | $3.00–$5.50/kg greige; $4.00–$7.00/kg finished [CITE: blend pricing ranges] | BCI cotton + recycled polyester (GRS) |
| Tri-Blend (cotton/poly/rayon) | Vintage-soft; fluid drape | Screen OK; DTG can be tricky; test | Low; rayon adds stability | Moderate; manage pilling with finish | $5.50–$9.50/kg finished [CITE: tri-blend wholesale ranges] | Recycled polyester; viscose/rayon sourcing check |
| Performance Knit (poly/spandex) | Technical; stretch; cool hand | Sublimation excellent; screen OK; DTG limited | Very low; high dimensional stability | High; abrasion and recovery strong | $6.00–$12.00/kg finished [CITE: performance knit ranges] | GRS recycled polyester; bluesign fabrics [MENTION: bluesign®] |
*Prices vary by fiber grade, yarn count, dye/finish, certifications, and order size. Validate current quotes with mills through your manufacturer partner. [CITE: recent commodity price indices]
Cotton (combed/ringspun) for premium basics
For premium basics, start with ringspun combed cotton in single jersey at 160–200 GSM. Ringspun delivers a clean print surface for fine screens and DTG; combed reduces neps that can cause ink skip. Use reactive dye for rich shade depth and colorfastness to wash/perspiration. Bio-polish improves pilling resistance. Run shrinkage tests at 40°C and 60°C, targeting dimensional change ≤4% after two washes. Lock a tighter stitch density to avoid grin-through under lighter colors. [CITE: ISO 105 colorfastness; ISO shrinkage test references]
[MENTION: CottonWorks knit construction design notes]
Poly-Cotton & Tri-Blends: durability, drape, cost
Poly-cotton blends balance cost and stability. A 65/35 blend reduces shrinkage and can improve abrasion resistance, serving promo tees and high-wash end uses. Tri-blends add rayon for drape and a soft, vintage hand with lower shrinkage, but can pill without proper finishing. Screen printing is reliable; DTG on blends requires pretreatment and careful ink profiles. For heathers, polyester content drives the visual texture; align print method with heather shade density. [CITE: DTG on blends testing note from a print lab]
[MENTION: Techpacker process guides on print testing]
Performance Knits (poly/spandex, moisture-wicking)
Performance tees favor polyester/spandex blends for quick-dry, stretch, and stable recovery. Use microfiber polyester for a cool hand and pair with moisture-wicking finishes. Sublimation yields vivid graphics; screen prints require lower temperatures and stretch additives. For US/EU programs, align recycled content to GRS and maintain chain-of-custody. Test colorfastness to perspiration and abrasion resistance (ASTM D4966). [CITE: Textile Exchange GRS standard page]
[MENTION: ASTM D4966 Martindale abrasion]
PAA: Are tri-blends suitable for DTG printing? Possible with pretreatment and adjusted ink limits, but results vary by rayon content and surface smoothness. Run DTG test prints and wash cycles before approval. [CITE: DTG process note from a recognized print technology source]
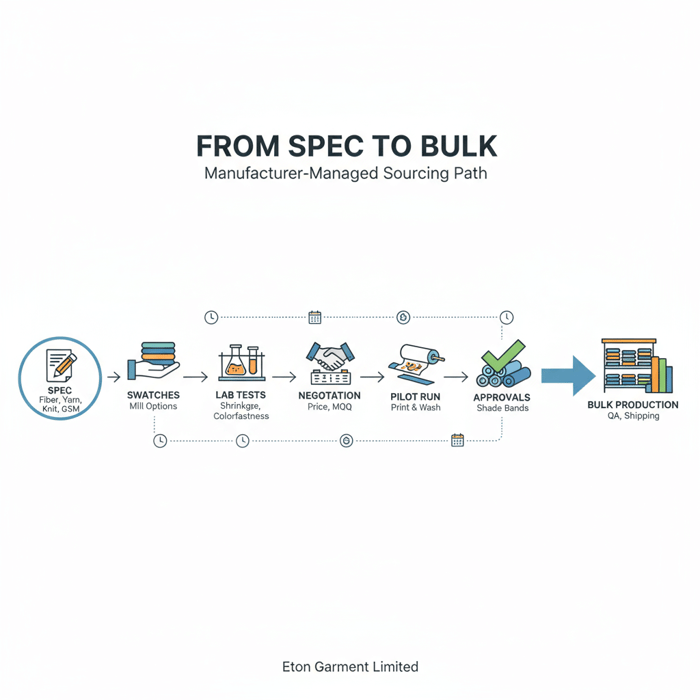
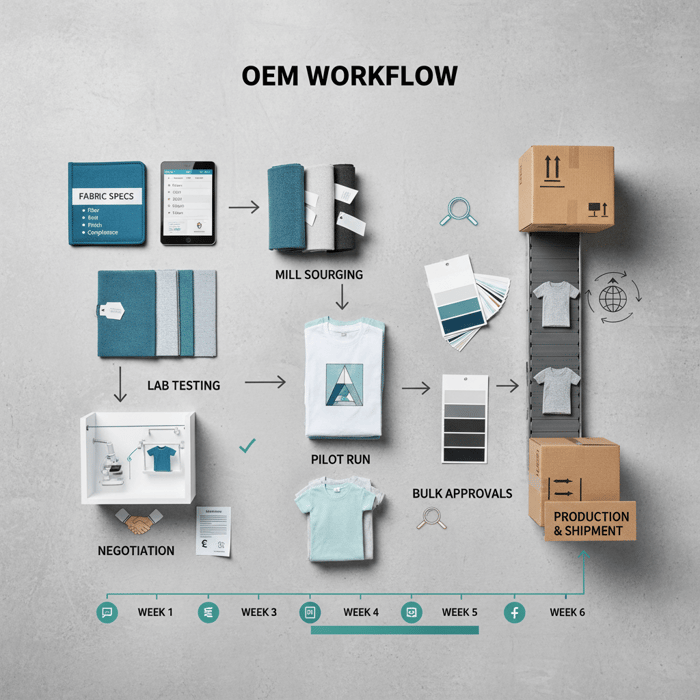
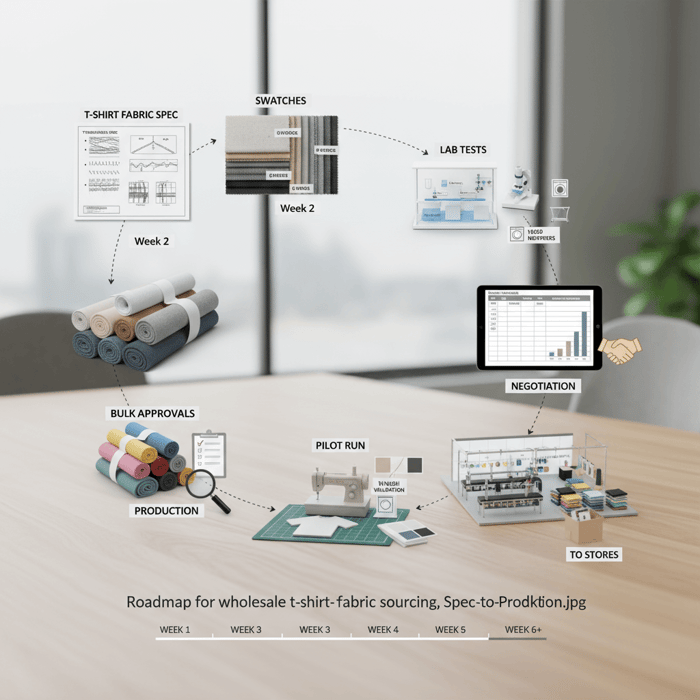
How to source t shirt material wholesale with a China Clothing Manufacturer
Define specs, request swatches, run lab tests, negotiate price/MOQ, lock dye/finish, approve shade bands, then launch via a manufacturer who aggregates mill capacity and manages QA and compliance end-to-end. This flow reduces risk and speeds tee program timelines.
[CITE: “Fabric sourcing workflow” best practices article]
[MENTION: Techpacker workflow templates]
[INTERNAL LINK: “Testing & Compliance” — lab and standards guide]
- Set the spec: fiber, yarn, knit, GSM, finish, compliance targets.
- Request mill swatches: at least three options per spec line.
- Run lab tests: shrinkage, colorfastness, pilling, dimensional stability, printability.
- Negotiate price/MOQ: leverage aggregated demand and shade band strategies.
- Pilot fabric: 100–300 meters for print/garment trials.
- Approve bulk shade bands: lock tolerances across dye lots.
- Production: maintain AQL roll sampling and rolling lab checks.
Preparation: spec, budget, compliance targets
Link fabric choices to price architecture and retail positioning. Pre-select certifications: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 for consumer safety, BCI for cotton sustainability, and GRS for recycled polyester claims. Define test thresholds in your tech pack and capture pass/fail criteria. Align calendar buffers to seasonality and target drop dates in US/EU markets. [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 criteria]
[MENTION: Better Cotton (BCI)]
[INTERNAL LINK: “Apparel Tech Packs & Spec Sheets” — compliance section]
Execution Steps: swatches, tests, negotiation
Request swatches in target GSMs and finishes; include alternate mill options to hedge capacity risk. Book lab tests for ISO 105 colorfastness to wash/perspiration and ISO/ASTM shrinkage/pilling. Run printability trials: screen, DTG, and sublimation where relevant. Negotiate price and MOQs based on yarn count, dye lot size, and finish complexity. Document shade approvals and tolerances (ΔE ranges), and capture finish recipes for traceability. [CITE: ISO 105; ASTM shrinkage references]
[MENTION: ECHA REACH guidance on restricted substances]
Quality Assurance & Bulk Control
Apply AQL sampling to fabric rolls; retain counter-swatches and master shade bands. Maintain rolling lab checks during bulk for shrinkage and colorfastness. Track deviations against spec and escalate corrective actions through the manufacturer’s QA team. Store lab data and chain-of-custody documents for compliance audits in US/EU markets. [CITE: AQL fabric inspection methodology]
[MENTION: US CBP import guidelines for apparel labeling]
Pricing, MOQs, and lead times for t shirt material wholesale
Price shifts with fiber grade, yarn process, GSM, dye/finish, and certifications. MOQs reflect dye-lot minimums and mill capacity. Lead times run yarn → knitting → dyeing → finishing. Manufacturer aggregation pools demand across mills to protect price and calendar reliability.
[CITE: Cotton price index; polyester feedstock trends]
[MENTION: Fibre2Fashion market analyses]
[INTERNAL LINK: “Fabric Sourcing 101” — cost drivers overview]
| Region | Typical MOQs | Lead Time (yarn→knit→dye→finish) | Price Drivers | Negotiation Levers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 500–1,500 meters per color [CITE: mill MOQ survey] | 18–30 days, off-peak; longer in peak seasons | Fiber grade, dye method, finish complexity, certifications | Shade band grouping, finish simplification, pooled demand |
| Bangladesh | 800–2,000 meters per color [CITE: regional mill benchmarks] | 20–35 days, with buffer for dye capacity | Yarn availability, dye-lot size, compliance documentation | Color consolidation, pre-book greige, certification bundling |
Price Drivers & Target Setting
Set targets by fiber (BCI vs organic premium), yarn (ringspun/combed costs), GSM, knit density, dye (reactive vs disperse), and finishes (enzyme, silicone, anti-pilling). Certifications add audit and documentation costs but reduce market risk in US/EU. Use multi-mill quotes to triangulate reality and capture seasonality signals. [CITE: BCI premium ranges; OEKO-TEX certification fee structures]
MOQs & Dye-Lot Strategies
Plan color orders that meet dye-lot minimums. Group close shades under approved shade bands to unlock lower MOQs. Align replenishment with greige pre-booking to cut future dye lead times. Record dye recipes and tolerances so mills can reproduce shades faithfully across reorders. [CITE: Dye-lot management practices from textile engineering sources]
Lead Times & Seasonality
Peak seasons stretch dye and finish windows. Build buffers around major retail drops in US/EU calendars. Pre-book greige and reserve lab capacity to avoid bottlenecks. Manufacturer-led scheduling helps shift orders between China and Bangladesh when one region tightens capacity. [CITE: Seasonal capacity trends report]
Data & Trends: Fabric market insights for US & EU brands
Cotton availability, recycled content claims, and lab capacity shape timelines. US/EU programs track certification demand and adjust calendars to lab throughput. Pricing moves with fiber indices and mill capacity. Keep compliance documentation current to avoid import delays.
[CITE: CottonWorks market updates]
[MENTION: Textile Exchange annual reports]
[INTERNAL LINK: “Testing & Compliance” — certifications guide]
- GRS claim verification demand rose in recent years (Source: Textile Exchange) [CITE: Textile Exchange annual report].
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100 adoption remains high across global mills (Year: recent) [CITE: OEKO-TEX updates].
- EU REACH updates tighten restricted substances lists (Year: recent) [CITE: ECHA REACH portal].
- US CBP labeling checks flagged documentation gaps in several audits (Year: recent) [CITE: CBP apparel import guide].
Certification Demand & Verification
US/EU programs lean on OEKO-TEX Standard 100 for consumer safety, BCI for cotton sourcing, and GRS for recycled polyester claims. Verification hinges on valid certificates, transaction certificates, and chain-of-custody. Maintain a documentation pack: cert copies, lab results, and supplier declarations for each fabric line. [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 criteria page]
[MENTION: Textile Exchange GRS and CCS documents]
Capacity & Calendar Planning
Capacity tightens in pre-holiday seasons and during regional closures. Use buffer rules (e.g., +20–30% time on dye/finish blocks), reserve lab slots early, and pre-book greige for rolling dye runs. Manufacturer coordination across China and Bangladesh supports flexible allocation when one region hits limits. [CITE: Industry capacity analyses]
How-To: Fabric testing and approvals for wholesale t shirt materials
Run shrinkage, colorfastness, pilling, dimensional stability, and printability tests at swatch and pilot stages. Define thresholds, document results, and proceed only when metrics hit spec. Re-test after any finish or dye change to protect print and shrinkage outcomes.
[CITE: ISO 105 colorfastness series]
[MENTION: ASTM D4966 abrasion resistance]
[INTERNAL LINK: “Testing & Compliance” — lab test matrix]
- Create the test matrix: align each spec item with a test method and threshold.
- Book the lab: reserve capacity early; share expected timelines.
- Test swatches: evaluate shrinkage, colorfastness, printability before pilot.
- Run pilot: 100–300 meters; validate stability and shade bands.
- Bulk validation: ongoing checks and retention samples for traceability.
Preparation: test matrix, thresholds, labs
Map tests to specs: ISO 105 colorfastness to wash/perspiration, dimensional stability after laundering, pilling resistance, and print adhesion or penetration based on method. Set pass/fail criteria with numeric thresholds and record data in your tech pack. Select independent labs and maintain reports for audit trails. [CITE: ISO method summaries]
[MENTION: Accredited lab directories]
Execution Steps: sampling to pilot
Swatch tests expose early failures in shrinkage or colorfastness. DTG trials confirm pretreatment and ink settings; screen tests set mesh and squeegee profiles; sublimation tests verify color depth at controlled heat/time. Pilot runs validate finishing recipes and shade bands across tension changes in knitting and dyeing. Retain control samples for each approval stage. [CITE: DTG print best practices from a print tech source]
[MENTION: ISO shade tolerance frameworks]
Quality Assurance: bulk verification & retention samples
Apply AQL to fabric rolls; run rolling lab checks for each dye lot. Keep retention samples for each lot tied to test reports and certificates. Track deviations, escalate with corrective action plans, and update specs or finishes if performance drifts. [CITE: AQL standards reference]
[MENTION: ECHA REACH updates influencing dye chemistries]
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service unifies spec creation, certified sourcing, lab testing, and production. One accountable partner aligns tee fabric decisions to price, quality, and compliance targets, then manages approvals and bulk timelines across China and Bangladesh.
[CITE: Case-based performance improvements; external validation welcome]
[MENTION: Liverpool F.C. and Forever 21 apparel programs as long-term partnerships]
[INTERNAL LINK: Eton’s OEM Services — leadership profile and QA methods]
| Brand Need | OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Spec clarity | Fiber/yarn/knit/GSM/finish definition | Consistent hand-feel and printability |
| Certified sourcing | OEKO-TEX/BCI/GRS mill selection | US/EU compliance-ready fabric |
| Quality assurance | ISO/ASTM test workflow | Shrinkage and colorfastness control |
| Calendar control | T&A management across China/Bangladesh | Faster approvals and reliable drops |
| Document readiness | Chain-of-custody and lab reports | Audit trail for US/EU import checks |
Explore Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service to move from swatch to store with fewer handoffs and clearer accountability.
Use Case 1: Premium Basics — Problem → Solution
Problem: a US retailer needed a premium tee with a smooth print surface, low shrinkage, and tight shade control for replenishment. Solution: ringspun combed cotton, 180 GSM single jersey, reactive dye, bio-polish finish, and a defined ΔE shade tolerance. The OEM workflow set test thresholds, ran pilot approvals, and locked finish recipes; bulk held shrinkage ≤3.5% after two washes. [CITE: Shrinkage and colorfastness lab reports; anonymized case]
Use Case 2: Promo & Athleisure — Problem → Solution
Problem: an EU brand needed two fabric paths: cost-effective promo tees and moisture-wicking athleisure tops. Solution: 65/35 poly-cotton at 160 GSM for promo with anti-pilling finish; polyester/spandex performance knit for athleisure with wicking finish and sublimation-ready surface. Negotiated MOQs via shade band grouping; managed calendar with pre-booked greige. [CITE: Performance knit test outcomes; anonymized case]
Risks, Compliance & Localization
Reduce risk with verified OEKO-TEX, BCI, and GRS certifications, mapped regulatory notes (EU REACH; US import rules), and a risk matrix covering quality, delivery, and documentation. Localize labels and testing to US/EU requirements; maintain chain-of-custody files for audit readiness.
[CITE: ECHA REACH restricted substances list]
[MENTION: US CBP apparel import guidance]
[INTERNAL LINK: “Testing & Compliance” — compliance map for US/EU]
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100: strong consumer safety screening; certification costs apply.
- BCI: improves cotton sourcing practices; premiums vary by region and season.
- GRS: validates recycled claims; requires strict chain-of-custody documentation.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrinkage drift after bulk | Medium | High | Pilot tests; rolling lab checks; finish recipe control |
| Shade variation across lots | Medium | Medium | ΔE shade bands; dye recipe documentation; lot approvals |
| Mill capacity bottlenecks | High in peak | High | Multi-mill sourcing; pre-book greige; buffers |
| Missing compliance docs | Low–Medium | High | Chain-of-custody file; certificate validation; audit kits |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
EU: REACH governs restricted substances; keep test reports aligned to the latest lists and retain supplier declarations. US: CBP sets labeling rules (fiber content, country of origin, care), and import documentation must match declared goods. Maintain lab reports and certificates to defend claims at audit. [CITE: ECHA REACH; CBP labeling and import guide]
Conclusion & Next Steps
Define tee fabric specs, validate materials with lab tests, and source at scale through a China Clothing Manufacturer. Eton’s OEM path aligns quality, compliance, and timelines so your tee program moves confidently from swatch to store.
- Week 1: finalize spec and compliance targets.
- Week 2: collect swatches and book lab slots.
- Week 3: run tests; select final fabric.
- Week 4: negotiate price/MOQ; lock shade bands.
- Week 5: pilot run; print and wash validations.
- Week 6: bulk approvals and production start.
[INTERNAL LINK: “Fabric Sourcing 101” — resource hub]
[INTERNAL LINK: “Testing & Compliance” — lab and standards]
[INTERNAL LINK: “OEM Services” — engagement overview]
Author: Senior Sourcing Manager, Eton Garment Limited — 12+ years fabric sourcing in China/Bangladesh; ISO/ASTM testing oversight.
Reviewer: Head of QA & Compliance, Eton Garment Limited — Oversees OEKO-TEX/REACH/BCI/GRS documentation and lab approvals.
Methodology: Manufacturer-backed workflows, lab protocols aligned to ISO/ASTM, and standards from CottonWorks, Textile Exchange, OEKO-TEX, ECHA, CBP.
Limitations: Market data varies by season and mill; pricing and MOQs are indicative; confirm current compliance and labeling rules.
Disclosure: Eton provides OEM services and may recommend partner mills; independent lab testing is encouraged.
Last Updated: October 2025
- CottonWorks (Cotton Incorporated) — Fabric fundamentals; knit types; finishing (2023–2025). https://www.cottonworks.com
- Textile Exchange Standards — GRS, CCS (2024–2025). https://textileexchange.org/standards/
- OEKO-TEX — Standard 100 criteria and updates (2024–2025). https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/our-standards/standard-100-by-oeko-tex
- ECHA — EU REACH guidance for textiles and restricted substances lists (2024–2025). https://echa.europa.eu/regulations/reach
- U.S. CBP — Importing Textiles and Apparel; labeling and classification (2024–2025). https://www.cbp.gov/trade/basic-import-export
- ISO 105 — Textiles — Tests for colour fastness (edition references). https://www.iso.org/standard/
- ASTM D4966 — Abrasion Resistance of Textile Fabrics (Martindale). https://www.astm.org
- Better Cotton (BCI) — Program and licensing information (2024–2025). https://bettercotton.org
- Fibre2Fashion — Technical articles on knit structures and market updates (2023–2025). https://www.fibre2fashion.com
- Techpacker — Fabric sourcing and process templates (2023–2025). https://www.techpacker.com
- Contrado — T-shirt materials and print guidance (recent). https://www.contrado.co.uk/blog/t-shirt-materials
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

