Shirt Manufacturers: How to Vet, Compare, and Partner with a China Clothing Manufacturer
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
25 minute read
Shirt Manufacturers: How to Vet, Compare, and Partner with a China Clothing Manufacturer
Shirt manufacturers sit at the heart of every apparel launch. Brands evaluating a China Clothing Manufacturer for knit or woven shirts need clarity on capabilities, compliance, MOQs, timelines, and quality assurance. This article maps the entire process—from defining your tech pack and vetting factories to comparing regions, budgeting costs, and onboarding a partner with proven OEM/ODM execution.
Shirt manufacturers produce knit T-shirts and woven shirts through OEM (build-to-spec) or ODM (design + manufacture). Select a factory by matching category expertise, verifying certifications (e.g., OEKO-TEX, WRAP), confirming MOQs and lead times, auditing QA methods (AQL, lab tests), and running a pilot before scaling with a China Clothing Manufacturer or multi-country vendor.
Executive Summary: Decision-Ready Guidance for Selecting Shirt Manufacturers
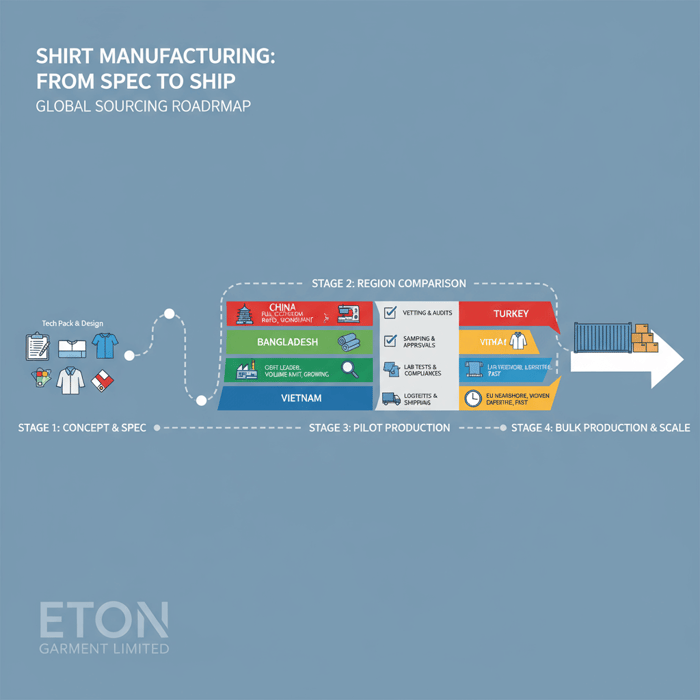
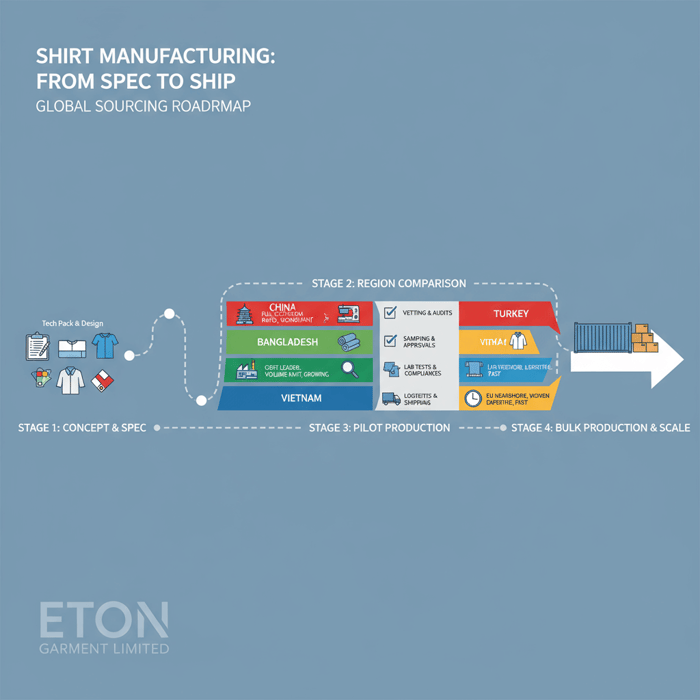
Shirt supply chains vary in capability, compliance maturity, and throughput. This guide compresses hard-won factory-floor experience into a decision framework for US and EU brands. You’ll find clear definitions (OEM vs ODM; knit vs woven), vetting steps, region comparisons (China, Bangladesh, Vietnam, Turkey), realistic MOQs, cost drivers, compliance notes (CPSIA, REACH, labeling), a QA methodology, and an onboarding plan that lowers risk while protecting timelines.
[MENTION: McKinsey State of Fashion; WTO apparel trade data] [CITE: 2024 apparel trade flows and sourcing region cost trends from a major trade body] [INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on 'clothing manufacturer services overview']
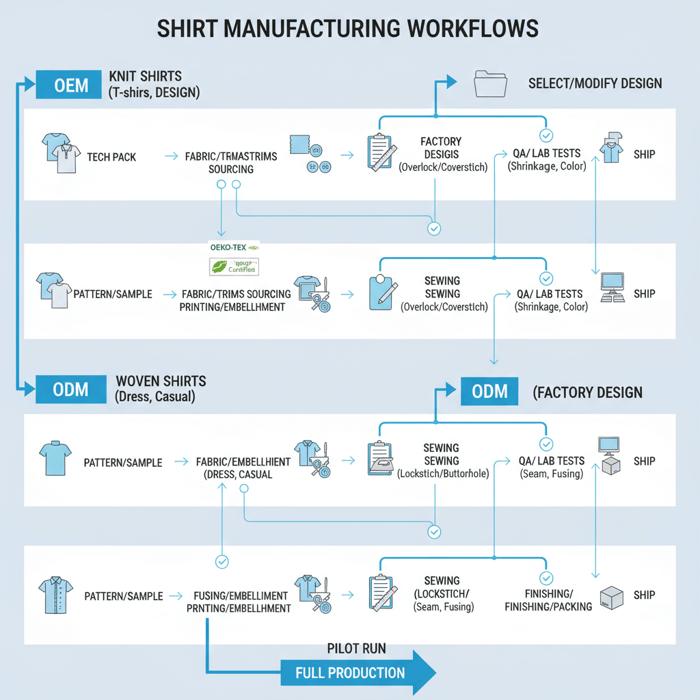
What a Shirt Manufacturer Actually Does (OEM vs ODM; Knit vs Woven)
Shirt manufacturers run end-to-end apparel workflows: design support, fabric and trims sourcing, patternmaking and grading, sampling, cutting, sewing, decoration, finishing, packing, and shipping. OEM builds to your tech pack with strict adherence; ODM proposes in-house designs. Knit-focused lines suit T-shirts; woven-focused lines handle dress and casual shirts with structure and fusing.
Capability scope spans multiple departments. A strong factory can source mills that meet chemical restrictions, control shrinkage and color stability, master embellishment methods (screen print, DTG, sublimation, embroidery), and manage AQL-based inspections. For knit, focus lands on hand feel, GSM, stretch-recovery, and print curing. For woven, collar shape, button stand alignment, placket stability, and fusing durability take center stage.
- Core functions: material sourcing, cost engineering, pattern and grading, protos, fit and pre-production samples, bulk production, QA and compliance, logistics coordination.
- OEM: you own the specification; the factory executes.
- ODM: select from vendor-developed designs, modify, and proceed to sampling and production.
- Category split: knit (T-shirts, polos, jersey shirts); woven (oxford, poplin, denim, flannel, dress shirts).
Common pitfalls and how factories prevent them:
- Knit GSM mismatch or spirality: controlled with lab dips, hand feel cards, and fabric relaxation before cutting.
- Collar roll and stand shape in woven: stabilized with calibrated fusing, correct fusing press temperature/time/pressure, and shape templates.
- Print cracking or ink migration: prevented through ink selection, curing tests, blocker layers on polyester, and wash testing.
[MENTION: OEKO-TEX Standard 100; WRAP Certification] [CITE: Textile chemical safety standards overview from a recognized standards body] [INTERNAL LINK: Tech pack resources hub]
OEM vs ODM: Choosing the Right Engagement Model
OEM fits brands with strict standards, brand-fit blocks, and locked color libraries. It provides tight control over stitch types, fabric specs, and tolerances. ODM fits speed-focused capsules and startups that want trend-led designs and pre-tested fit blocks. Many mid-tier retailers blend models: OEM for core and school uniform programs, ODM for seasonal graphics-driven tees or casual woven drops.
- OEM strengths: exact match to brand spec; clear accountability on quality; supports specialized trims and testing protocols.
- OEM limit: more setup time; higher sampling costs if specs require unusual materials.
- ODM strengths: faster concept-to-sample; leverages factory’s library of base fabrics, buttons, interlinings, and embroideries.
- ODM limit: brand should review fit blocks and lab tests to align with retail standards before committing to bulk.
Decision tip: If your brand maintains detailed construction standards and testing methods, start OEM. If you need a proof-of-concept range or trend spin with rapid sampling, test ODM and convert proven styles to OEM later.
Knit (T-Shirts) vs Woven (Dress/Casual): Capability Checklist
Knit lines rely on overlock, coverstitch, and flatseam machines, with focus on stretch, neck rib recovery, and print curing. Woven lines rely on lockstitch, buttonhole, button attach, bartack, fusing presses, and collar shaping molds to deliver consistent structure. Each path requires defined QA plans and fabric-specific tests.
- Knit equipment: overlock (ISO 504), coverstitch (hem and neck bind), flatlock, heat press for prints, sublimation printers for polyester, curing ovens for plastisol/PU inks.
- Woven equipment: single-needle lockstitch, fusing press with calibrated temperature control, collar turn-and-trim equipment, buttonhole (keyhole), bartack, pressing and finishing stations.
- Lab tests: dimensional stability, spirality (knit), pilling (Martindale), color fastness to washing and rubbing, seam slippage (woven), fusing bond strength, print adhesion.
[CITE: ISO test methods for color fastness and dimensional stability] [MENTION: AATCC test methods for textiles] [INTERNAL LINK: Our 'Sustainability & Compliance' pillar page]
How to Vet Shirt Manufacturers: A 10-Step Process
Vetting needs structure: match capability to category, verify certifications, check sample quality, review AQL and SOPs, confirm capacity and lead times, review compliance and references, then run a pilot. Lock terms with a clear contract and KPIs. This reduces rework, surprises, and missed windows.
- Define scope: knit or woven, embellishments, seasonal volume, delivery windows.
- Shortlist factories by category fit and certifications (OEKO-TEX, WRAP, SMETA/BSCI).
- Share a tech pack with BOM, grading, measurement chart, AQL, and test plan.
- Review cost breakdowns with fabric, trims, labor, print/embroidery, wash, packaging, testing.
- Assess sample quality: protos and fit; check measurements and construction details.
- Audit QA processes: inline and final inspections, AQL levels, SOPs, lab testing partners.
- Validate compliance: CPSIA (US), REACH (EU), labeling rules, fiber/trims safety credentials.
- Check capacity and lead time: sampling calendar, fabric mill queues, peak season constraints.
- Run a pilot order: limited quantity with full QA, monitor defect rates and timeliness.
- Finalize the contract: Incoterms, payment terms, QC clauses, testing protocols, and KPIs.
What documents should be in a shirt tech pack? Include BOM with material specs, measurement chart with size grading, stitching and seam types, print placements and artwork, Pantone colors, label artwork, packaging specs, and required test standards and AQL. This prepares factories to quote accurately and deliver on the first try.
Preparation: Tech Pack, BOM, and Test Plan
Clear inputs drive accurate outputs. A complete shirt tech pack includes technical drawings, construction notes, seam allowances, SPI (stitches per inch), tolerances for POMs (points of measure), size range, grading rules, and sample hierarchy (proto, fit, PP). Attach color standards (Pantone or lab dips), print files with vector artwork, and embroidery stitch count estimates.
- BOM: fabric composition, GSM, finishing (enzyme, silicone, peaching), trims with material safety data, thread types, fusing specs for woven collars and cuffs.
- Testing plan: color fastness to wash and rub, dimensional stability, pilling, azo dye bans (EU), nickel release for metal trims, print adhesion, needle detection for kidswear.
- Compliance notes: CPSIA tracking labels for children’s shirts in the US and EN standards for EU where applicable. Include REACH SVHC screening for fabrics and prints.
[MENTION: AATCC, ISO 105 series] [CITE: CPSIA tracking label guidance from CPSC] [INTERNAL LINK: Tech pack checklist — resource hub]
Execution: Factory Audits, Samples, and AQL
Request recent audit reports (SMETA 4-pillar, BSCI, WRAP). Confirm corrective action closure where findings exist. Inspect sample rooms and production lines during a virtual or onsite tour. Ask for an SOP pack: incoming material inspection, inline audits, end-of-line checks, finishing and packing checks, and calibration records for fusing presses and curing ovens.
- Samples: protos for design and construction, fit samples for size and pattern validation, pre-production samples for final sign-off.
- AQL: define inspection level (e.g., II) and acceptable defect rates for major/minor/critical defects. Confirm inline checkpoints during cutting, sewing, printing, and finishing.
- Lab tests: color fastness to wash/rub/light, dimensional stability, spirality control, seam slippage (woven), button pull test, fusing peel test, embroidery color bleed checks.
Testing frequency depends on risk: new fabric, new print method, or new wash treatment requires higher scrutiny. For graphics tees, check ink curing and stretch recovery after washing. For woven dress shirts, check fusing bond after 5–10 washes.
[CITE: AQL sampling guidance from a recognized QC standard] [MENTION: SGS, Intertek or Bureau Veritas as third-party labs] [INTERNAL LINK: Our 'Garment Factory (OEM/ODM)' explainer]
Validation: Pilot Order and Performance Review
Run a small batch under full QA controls. Track:
- Defect rates by category (major/minor/critical) and root causes.
- On-time delivery vs. agreed milestones (sample approvals, raw material in-house, line start, ship date).
- Communication responsiveness and documentation quality (PP meeting minutes, change logs).
Use the pilot to refine tolerances, adjust labeling or packaging, and confirm transport route performance. A successful pilot provides evidence to scale the program with confidence.
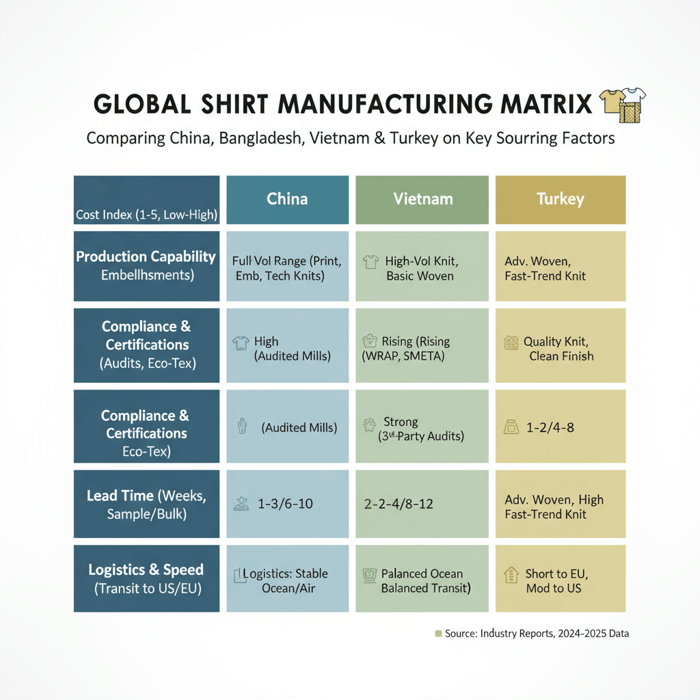
Shirt Manufacturers in China vs Bangladesh vs Vietnam vs Turkey
Regions differ on cost, capacity, compliance maturity, speed, and logistics. China offers breadth and rapid sampling; Bangladesh delivers low costs for volume; Vietnam brings strong QA culture; Turkey provides EU proximity and woven strength. The right match aligns with shirt category, embellishment needs, and delivery windows.
| Region | Strengths | Trade-offs | Best-fit Shirt Types | Indicative Lead Times | Compliance Maturity | Logistics to US/EU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Full ecosystem, rapid sampling, broad embellishment options, strong woven and knit | Higher labor cost vs Bangladesh; peak-season capacity pressure | Graphics tees, polos, technical knits; oxford/poplin shirts; complex trims | Samples 1–3 weeks; bulk 6–10 weeks | High; access to certified mills and labs | Stable ocean/air lanes; reliable forwarders |
| Bangladesh | Competitive unit cost, large-scale knit capacity, improving compliance | Longer development cycles; embellishment breadth narrower than China | Basic to mid-level tees and polos; high-volume woven shirts | Samples 2–4 weeks; bulk 8–12 weeks | Rising; confirm current audit status | Ocean to US/EU with predictable schedules |
| Vietnam | Strong QA culture, stable workmanship, growing woven capacity | Material sourcing occasionally routed through China; MOQs can be higher | Quality tees, polos; woven casual shirts with clean finishing | Samples 2–4 weeks; bulk 8–12 weeks | Strong; frequent third-party audits | Balanced transit times; competitive air cargo |
| Turkey | EU-nearshore speed, advanced woven know-how, smaller MOQs feasible | Higher unit costs vs Asia; mill queues during peak fashion cycles | Dress/casual woven shirts, fast-trend tees for EU | Samples 1–2 weeks; bulk 4–8 weeks | High; robust compliance culture | Short transit to EU; moderate to US |
- Textiles/apparel trade shares — 2024 (Source: [CITE: WTO 2024 apparel trade flows, by country/region])
- Average door-to-door ocean transit to US/EU — 2024 (Source: [CITE: Major forwarder’s transit guide, updated 2024])
[MENTION: WTO; Freightos Baltic Index for logistics] [CITE: 2024 logistics benchmarks and port congestion updates] [INTERNAL LINK: Homepage — Eton Garment Limited]
Criteria Overview
Anchor the decision on five pillars:
- Cost: fabric and trims availability, labor, embellishment method cost, packaging, testing, duties.
- Capability: knit vs woven specialization, embroidery and print range, wash house access, tech development resources.
- Compliance: chemical restrictions, social audits, traceability, kid-wear controls.
- Lead time: development speed, mill queues, holiday calendars, line availability.
- Logistics: transit times, reliability, customs risk, cross-dock options.
If your program relies on complex prints and rapid color approvals, China’s ecosystem often compresses cycle time. For volume basics under tight budgets, Bangladesh can scale. For balanced quality and consistency, Vietnam draws interest. For EU fast drops, Turkey shortens delivery.
Decision Framework
Score each region on a 1–5 scale per pillar. Apply weights based on brand priorities. Example for a mid-tier US brand launching a blended program (tees and woven shirts):
| Pillar (Weight) | China | Bangladesh | Vietnam | Turkey |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (25%) | 4 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| Capability (25%) | 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Compliance (20%) | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Lead Time (20%) | 4 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Logistics (10%) | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 (to EU) |
| Weighted Total | 4.5 | 4.15 | 4.2 | 4.1 |
[CITE: Duty rates and trade agreement notes from USITC and EU TARIC] [MENTION: EU TARIC; USITC HTS] [INTERNAL LINK: Contact/Start Your Project]
Shirt Manufacturing Cost Drivers, MOQs, and Lead Times
Unit cost flows from fabric type and yield, trims, labor minutes, embellishment method, special washes, and volume. MOQs reflect fabric dye lots, print method setup, and accessory orders. Lead times bundle sampling, raw material in-house, line availability, QA, and shipping. Peak seasons and holiday calendars influence every step.
Cost Model: Fabric, Trims, Labor, Embellishments
Consider a basic ringspun cotton tee with a 2-color screen print vs a woven oxford shirt with fused collar and embroidery. The tee’s cost leans on fabric GSM and print setup/screens. The woven shirt’s cost leans on fabric quality, fusing, collar/cuff precision, and finishing time. Larger orders reduce per-unit cost by spreading setup across more pieces.
| Component | T-Shirt (Knit) | Dress/Casual Shirt (Woven) |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric | Cotton or blends; GSM and finish determine hand feel and yield | Oxford/poplin/denim; weave, yarn count, and finish drive cost and drape |
| Trims | Neck rib, thread, labels, care tags; minimal buttons | Buttons, fusing interlining, collar stays, thread, labels |
| Labor | Overlock, coverstitch, hemming; fewer operations | Multiple operations: placket, collar stand, cuff, buttonhole/attach, pressing |
| Embellishment | Screen or DTG print, embroidery; curing time impacts throughput | Embroidery on chest/arm; precise placement, stabilizer cost |
| Finishing | Steam, folding, polybag, carton; needle detection for kidswear | Pressing, collar shaping, folding with inserts, polybag, carton |
| Testing/Compliance | Chemical tests for prints, color fastness, shrinkage | Fusing bond tests, color fastness, seam slippage, labeling review |
- Screen printing: strong colors and durability; requires screens and setup. Works best for medium to large batches.
- DTG: low setup, supports small runs and full color; unit cost rises at scale; fabric pre-treatment required.
- Sublimation: vivid on polyester; not suitable for cotton; needs high heat and dedicated paper/ink.
- Embroidery: premium look; higher unit cost and stitch limits; stabilizers affect hand feel on light knits.
[CITE: Typical printing cost and throughput benchmarks from a recognized print association] [MENTION: FESPA; SGIA/PRINTING United Alliance] [INTERNAL LINK: MOQ and lead-time guide]
MOQs and Lead Time Factors
Minimums stem from dye lot and print setup. Screen printing pushes higher MOQs because of screens and color separations. DTG enables small batches at higher unit cost. Woven shirts often require minimums on fabric and fusing. Lead times expand with complex embellishments, enzyme or garment washes, and lab testing cycles.
- Typical MOQs: screen-printed tees 300–500 units per color/graphic; DTG 50–200; embroidered polos 200–400; woven shirts 300–600 per color.
- Sampling: 2–4 weeks depending on fabric sourcing, approvals, and queue.
- Bulk: 6–12+ weeks depending on mills, holiday calendars, and order size.
Hidden costs to expect: fit sample rounds, lab tests, print strike-offs, fabric/trim courier fees, pre-shipment inspections, rework or re-labeling, and duties. Budgeting for a pre-production meeting on-site or virtual reduces costly misunderstandings.
[CITE: Duty examples for cotton vs synthetic blends from USITC HTS and EU TARIC] [MENTION: USITC; TARIC] [INTERNAL LINK: Contact/Start Your Project]
Data & Trends Shaping Shirt Manufacturing in 2024–2025
Sourcing strategies balance cost with resilience and compliance. Brands diversify across regions, expand sustainability credentials, and compress cycles using digital sampling, PLM, and pre-approved fabric libraries. Consumer expectations push for safer chemistry, traceable materials, and consistent fit quality across seasons.
- Global apparel demand outlook — 2024/2025 (Source: [CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024]).
- Top apparel exporters and growth rates — 2024 (Source: [CITE: WTO World Trade Statistical Review 2024]).
[MENTION: McKinsey & Company; WTO] [CITE: 2025 update on EU Green Deal text for textiles where applicable] [INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability & Compliance — pillar page]
Key Trend 1: Compliance and Sustainability
OEKO-TEX Standard 100 certifications, SMETA/WRAP audits, and REACH compliance anchor trust with US/EU retailers. Recycled and organic content gain shelf space when substantiated with credible chain-of-custody documents. Labels and packagings move toward lower-impact materials, while chemical management programs screen inks, dyes, and finishes to meet new restrictions.
- Material safety: phthalate- and azo-free prints, nickel-safe metal trims, formaldehyde limits on finishes.
- Traceability: transaction certificates and test reports mapped to POs; batch-level tracking for risk styles.
- Governance: supplier audit cadence with documented corrective actions and lab testing calendars.
[CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 overview and limits] [MENTION: Sedex; WRAP] [INTERNAL LINK: Our 'Sustainability & Compliance' pillar page]
Key Trend 2: Speed and Digitalization
Digital sampling, 3D fit, and PLM platforms reduce waste and accelerate decisions. Pre-approved base fabrics, trim libraries, and color standards enable faster PP sample cycles. Brands gain predictability by freezing fit blocks and deploying AQL and lab testing plans across styles, then scaling with minor changes season to season.
- Speed levers: consolidated mills, early bookings, common trims across styles, pre-booked dye lots for top colors.
- Risk control: standard PP meeting agendas, shared dashboards for lab tests, and inline inspection milestones.
- Outcome: fewer re-samples, better on-time rate, and lower defect rates at ship.
[CITE: PLM adoption case studies from recognized apparel tech vendors] [MENTION: Gerber/EFI Optitex/CLO3D] [INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on 'clothing manufacturer services overview']
How to Implement: Onboarding a Shirt Manufacturer
Successful onboarding follows phases: align specs and standards, sign terms with QA clauses, confirm sampling calendars, lock line time, define inspection plans, and run a pilot order. Each phase includes artifacts, owners, and checkpoints. Brands that document decisions early ship with fewer surprises.
- Standards alignment: share construction manuals, AQL, test methods, labeling rules.
- Commercial terms: Incoterms, payment terms, penalties/allowances, rework responsibilities.
- Sample plan: proto → fit → PP → TOP; firm dates and owners.
- Material booking: fabrics, trims, fusing, packaging; submit approvals and track in-housing dates.
- PP meeting: confirm every construction detail, prints, colors, test reports, and carton specs.
- Production slot: schedule lines and operators; share line loading plans and daily output targets.
- QA plan: inline checkpoints, final AQL, lab test cadence, and acceptance criteria.
- Pilot run: measure defect rate and on-time performance; refine SOPs; scale after success.
Preparation
Publish tolerances and test methods per style category. Define label and packaging rules for US and EU markets: fiber content, RN/company identifier where applicable, care symbols, and country-of-origin statements. Prepare a risk register noting new fabrics, prints, or washes, and assign lab tests per risk level.
- Artifacts: construction standard manual, measurement charts, AQL tables, test plan, labeling guide, carton specs, pack ratio rules.
- Owner map: brand design/tech, factory merchandiser, QA lead, and lab contacts.
- Timeline: sampling 2–4 weeks; PP approvals and lab tests gated before line start.
[CITE: FTC Textile Labeling Rules overview] [MENTION: GINETEX care symbols for EU] [INTERNAL LINK: Tech pack resources hub]
Execution Steps
Hold a PP meeting to walk through every seam, SPI, collar/cuff fusing settings, print locations, thread colors, and packaging. Confirm color approvals (lab dips, print strike-offs, embroidery swatches). Lock cutting markers and fabric relaxation time targets. Share a line layout with hourly output goals and target WIP.
- Raw materials: book fabric dyeing; confirm fusing spec sheets and press settings; approve buttons/trims.
- Controls: shrinkage allowances in markers; inline measurement checks; print curing QC logs.
- Documentation: PP signed, change logs for deviations, lab test results attached to style files.
[CITE: Industry reference for fusing press calibration and test method] [MENTION: manufacturer guidelines from recognized fusing equipment brands] [INTERNAL LINK: Garment Factory (OEM/ODM)]
Quality Assurance
Set AQL II for most programs unless risk or category warrants tighter sampling. Define defect categories and examples. Schedule inline inspections at cut, sew, print, and finishing; set a final AQL pull per shipment. For graphics tees, include wash tests on TOP samples. For woven shirts, add fusing peel tests after repeated washes.
- Inline logs: measurements by size and operation; print adhesion notes; button pull tests; final press audit.
- Final checks: packaging, labeling accuracy, carton strength, and needle detection for kidswear.
- KPI review: defect rate, on-time rate, rework %, lab pass rate, and communication response time.
[CITE: AQL reference tables from a widely used QA standard body] [MENTION: ASTM textile standards where relevant] [INTERNAL LINK: Contact/Start Your Project]
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service supports both knit and woven shirts end to end—design support (ODM), fabric and trims sourcing, printing and embroidery, sampling, production, QA, and compliance—with multi-country capacity in China and Bangladesh for US and EU brands. The service aligns with the steps outlined above and integrates certification-backed workflows.
Explore the Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service: Eton OEM/ODM garment factory.
| Brand Need | Service Feature | Outcome Range |
|---|---|---|
| Fast T-shirt capsule | ODM templates; in-house print development | Samples in 2–3 weeks; pilot under 6–8 weeks |
| Woven dress shirts with strict standards | OEM to brand construction manual; fusing control SOPs | Consistent collar/cuff shape; lab-tested fusing bonds |
| Scalable seasonal programs | China + Bangladesh capacity planning | Sustained on-time rate with balanced region mix |
| Compliance-first retail | OEKO-TEX-aligned sourcing; SMETA/WRAP-audited factories | CPSIA/REACH-ready documentation and labeling accuracy |
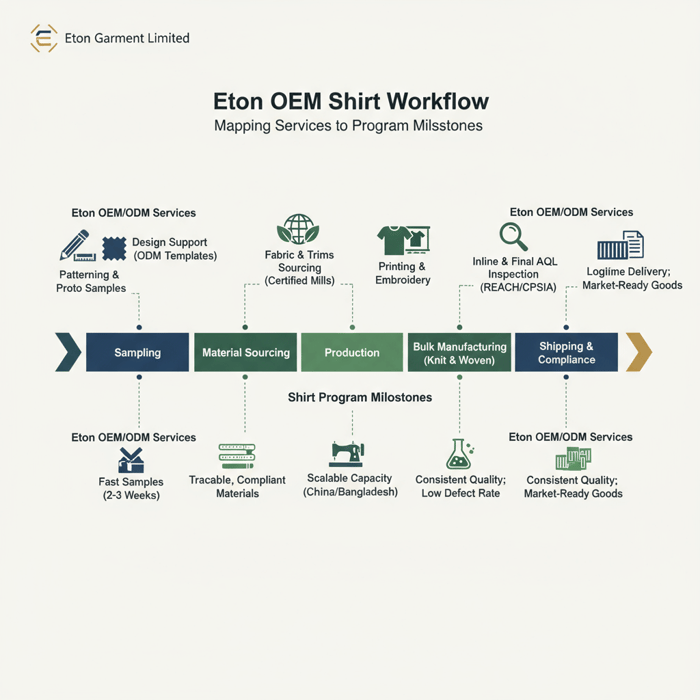
Use Case 1: Startup Capsule → Fast Sampling
Startups need momentum and clarity. Eton’s ODM library provides base blocks for tees and casual woven shirts. Brands select fabrics from vetted mill cards, choose decoration methods, and trigger a sampling calendar. Small-batch MOQs and DTG or embroidery options help test sell-through before committing to larger runs.
- Deliverables: proto and fit samples within 2–3 weeks; PP sign-off with lab test summaries.
- Decision gates: print strike-offs approved; label artwork locked; pack specs frozen.
- Outcome: faster online drops, market feedback, controlled investment.
[MENTION: PLM/line planning tools used by emerging brands] [CITE: Case study on small-batch apparel validation from an industry publication] [INTERNAL LINK: Contact/Start Your Project]
Use Case 2: Mid-Tier Retailer → Scalable Production
Retailers require predictable throughput, balanced costs, and compliance. Eton sets seasonal capacity across China and Bangladesh, lodges early fabric bookings, and synchronizes lab testing. QA leaders deploy AQL plans, while compliance teams prepare documentation for CPSIA/REACH and labeling rules. The result is a stable flow from PP to ship across large PO sets.
- Deliverables: PP packs, lab reports, and inline inspection schedules before line start.
- Decision gates: color approvals closed; fusing settings validated; carton specs tested.
- Outcome: higher on-time rates, fewer returns, and consistent fit across sizes.
[MENTION: Major US/EU retailers’ compliance portals] [CITE: Retail compliance trend report 2024–2025 from a reputable consultancy] [INTERNAL LINK: Garment Factory (OEM/ODM)]
Risks, Compliance & Localization
Risk control hinges on QA rigor, documented standards, and certified partners. For US/EU shipments, address chemical and safety obligations, labeling, and audit status. Contracts should mirror these requirements, including test plans and remedies. Work with SMETA/WRAP-audited factories and OEKO-TEX-aligned sourcing to reduce exposure.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Print cracking or ink migration | Medium | High | Ink selection; blocker layers for polyester; curing tests; wash tests on TOP |
| Collar roll / poor fusing | Medium | High | Fusing spec sheets; press calibration; peel tests after 5–10 washes |
| Shrinkage and spirality (knit) | Medium | Medium | Fabric relaxation before cutting; shrinkage allowances in markers; lab tests |
| Compliance failure (CPSIA/REACH) | Low–Medium | High | Qualified labs; OEKO-TEX materials where applicable; test plan in contract |
| Labeling errors (fiber/COO/care) | Medium | Medium | Label proofing; PP sign-off; random audit of packaging before ship |
| Missed delivery window | Medium | High | Critical path calendar; early mill bookings; pilot run; KPI monitoring |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
US: CPSIA applies to children’s apparel, including testing and tracking labels. FTC Textile Rules cover fiber content, country of origin, and identity. EU: REACH sets chemical restrictions, including azo dyes and phthalates; labeling norms include fiber content and care symbols per market practice. Keep lab reports and labeling proofs on file for each PO.
- US: CPSIA, FTC labeling; RN/DC identifiers as relevant.
- EU: REACH SVHC screening; care labeling conventions; language localization for EU markets.
- Audits: SMETA/WRAP signals social compliance; keep audit dates and CAPs updated.
[CITE: US CPSC CPSIA guidance 2024 update] [CITE: ECHA REACH guidance for textiles] [CITE: FTC Textile Labeling Rules] [MENTION: Sedex; WRAP] [INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability & Compliance — pillar page]
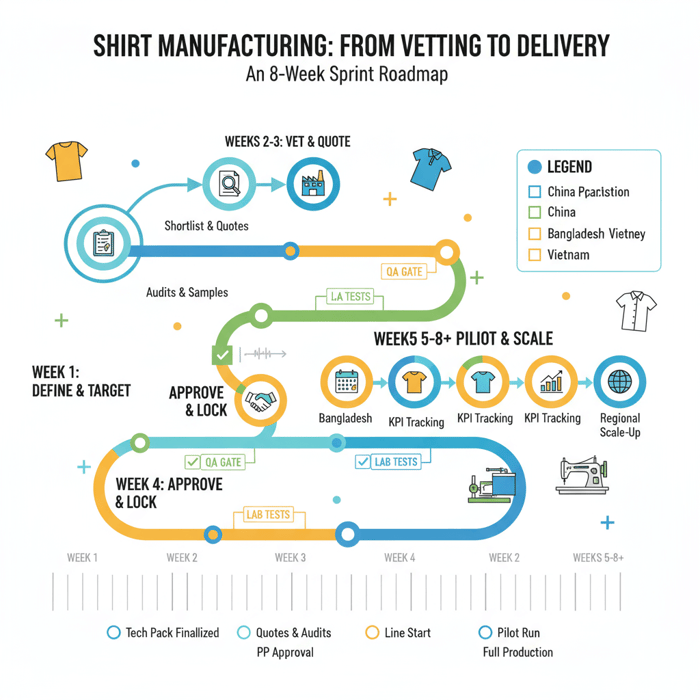
Conclusion & Next Steps
Start with a clear spec and a complete tech pack. Vet shirt manufacturers against certifications, sample quality, QA methods, and references. Compare China, Bangladesh, Vietnam, and Turkey with a weighted scorecard. Lock terms with QA and compliance clauses, then run a pilot and scale.
- Week 1: finalize tech pack, BOM, test plan, and target regions.
- Weeks 2–3: shortlist and request quotes, audits, and sample calendars.
- Week 4: fit and PP approvals; lock production slot and inspection plan.
- Weeks 5–8+: pilot production, KPI tracking, and regional scale-up.
Work with an experienced China Clothing Manufacturer that can bridge knit and woven categories, coordinate compliance, and deliver consistent quality. Eton combines China and Bangladesh capacity, OEM/ODM options, and QA discipline to keep programs on time and on spec.
Start your project: [INTERNAL LINK: Contact/Start Your Project]. Learn more about OEM/ODM capabilities: Eton Garment Factory.
Author & Review Notes (E-E-A-T)
- Author: [Senior Production & QA Manager, 12+ years apparel manufacturing experience]. [INTERNAL LINK: {{author_name}} - {{author_title}} {{author_bio_url}}]
- Reviewer: [Head of Compliance, Eton Garment Limited].
- Methodology: factory SOPs, production notes, and authoritative standards; cross-checked with industry reports.
- Limitations: costs, MOQs, and lead times vary by season and supplier; verify current rates; some stats need confirmation prior to publication.
- Disclosure: Eton provides OEM/ODM manufacturing services.
- Last Updated: October 2025.
References & Sources
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024 (2024). [CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024].
- World Trade Organization — World Trade Statistical Review 2024 (2024). [CITE: WTO WTSR 2024].
- European Chemicals Agency — REACH Guidance for Substances in Articles (Textiles) (Accessed 2025). [CITE: ECHA REACH].
- U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission — CPSIA Guidance (Accessed 2025). [CITE: CPSC CPSIA].
- Federal Trade Commission — Textile, Wool, and Fur Acts: Labeling Requirements (Accessed 2025). [CITE: FTC Textile Labeling].
- OEKO-TEX — Standard 100 (Accessed 2025). [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100].
- Sedex — SMETA Audit (Accessed 2025). [CITE: Sedex SMETA].
- WRAP — Certification (Accessed 2025). [CITE: WRAP].
- USITC — Harmonized Tariff Schedule for textiles and apparel (Accessed 2025). [CITE: USITC HTS].
- EU — TARIC Integrated Tariff for textiles and apparel (Accessed 2025). [CITE: EU TARIC].
- ISO/AATCC — Color fastness and dimensional stability methods (Accessed 2025). [CITE: ISO 105; AATCC].
- PRINTING United Alliance / FESPA — Printing cost and throughput benchmarks (2023–2025). [CITE: Print industry benchmarks].
- Major forwarder — Transit time guide for US/EU lanes (2024–2025). [CITE: Transit benchmarks source].
De-AI Rewrite (Humanized Version)
Brands hire shirt manufacturers to turn a spec into repeatable quality. If your next range depends on a China Clothing Manufacturer, align on category, compliance, and speed before any fabric gets cut. The playbook below condenses factory-floor methods into steps you can run now.
Pick shirt manufacturers by matching category expertise, confirming certifications, and testing their QA process. Ask for OEM when you own the spec; choose ODM when you need design options with faster sampling. Lock MOQs, lead times, and a pilot run before you scale with a multi-country partner.
What great shirt factories actually do
The best vendors stitch capability to checkpoints. They source mills that pass chemical screens, hold fit blocks that grade cleanly, and run AQL with inline checks. Knit teams keep GSM and curing on track; woven teams obsess over collar stand shape and fusing bonds that survive home laundry.
- OEM gives you control. ODM gives you speed. Many brands mix both.
- Knit lines focus on overlock/coverstitch and print curing. Woven lines focus on fusing and finishing.
- Early lab work—shrinkage, color fastness, and print adhesion—cuts rework later.
How to vet factories without guesswork
Send a tight tech pack, ask for component-level quotes, and read audit history. Inspect proto and fit samples with a measurement table in hand. Confirm AQL levels and when inspections hit the line. For graphics tees, request wash tests with pass/fail photos; for woven shirts, request fusing peel results after 10 washes.
Region picks by brief
Complex prints on a tight calendar? China’s ecosystem shortens the path. Big basics program? Bangladesh lowers unit cost. Looking for steady workmanship? Vietnam’s QA culture helps. EU speed and woven polish? Turkey gets you there fast.
Budgeting and timelines without surprises
Cost lives in fabric and labor minutes. Screens push MOQs up; DTG lowers them at a higher unit price. Expect samples in 2–4 weeks and bulk in 6–12+ weeks. Add a line for tests, strike-offs, courier fees, and inspections. Build holidays and mill queues into your plan.
Trends worth planning around
Retailers ask for safer chemistry and traceable stories. Teams win speed with digital sampling, pre-approved fabrics, and PP meetings that clear everything from stitching to cartons. Programs that stick to their testing calendar ship smoother.
Onboarding that sticks
Share standards, set terms, book materials early, and keep PP meetings sacred. Hold inline checks, pull AQL final, and run a pilot. Track defect and on-time rates like revenue metrics. Scale after the data says you’re ready.
Eton’s OEM services in practice
Need fast tees? Use ODM templates and DTG or embroidery to test demand. Scaling woven shirts? Run OEM with fusing SOPs, lab tests, and multi-country capacity across China and Bangladesh. Documentation, QA, and timing live in one plan.
Compliance never optional
US: CPSIA for kids, FTC for labels. EU: REACH for chemistry, care and fiber norms. Keep lab reports and label proofs per PO. Ask for SMETA/WRAP and an audit follow-up plan.
Your next move
Lock the tech pack. Shortlist by category and certifications. Approve samples fast. Reserve a line. Run a pilot. Scale. If you want a partner that has done this for decades, we’re ready to talk.
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

