Plus Size Clothing Distributors: How to Source Inclusively with a China Clothing Manufacturer
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
13 minute read
Plus Size Clothing Distributors: How to Source Inclusively with a China Clothing Manufacturer
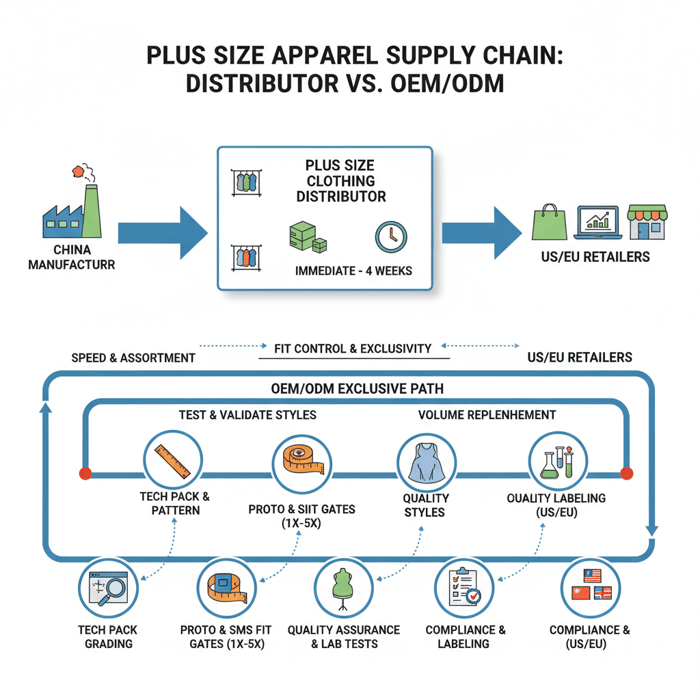
Plus size clothing distributors give brands fast access to ready-to-buy inclusive ranges, while a China Clothing Manufacturer offers OEM/ODM fit control and exclusivity. Brands in the US and EU that blend both paths secure speed, consistent grading from 1X–5X, and reliable replenishment for outerwear, athleisure, and core apparel.
Plus size clothing distributors supply bulk-ready inclusive apparel and are ideal for rapid range tests. Use distributors for speed and assortment, and move proven styles to OEM/ODM with a China Clothing Manufacturer for stable grading, fit control, compliance, and exclusivity.
What Plus Size Clothing Distributors Do—and When to Use Them
Distributors provide ready-to-buy plus-size assortments with short lead times and simple terms. Use distributors to test demand, learn size curves, and validate subcategories; shift to OEM/ODM for stable measurement blocks, exclusive design, and lower long-term returns.
Distributors sit between manufacturers and retailers. They buy stock from factories or importers, hold inventory, and sell cartons or ratio packs to boutiques and e-commerce teams. Speed is the draw—typical timelines range from immediate shipment to 2–4 weeks for replenishment. Control is lower—grading and fit belong to the upstream supplier, not your brand, which can raise return rates when curves drift.
- Capabilities: broad assortment, low MOQs, prepacked ratio curves, seasonal drops.
- Lead times: immediate shipment for in-stock; 2–6 weeks for replenishment.
- MOQs: often 12–60 units per style/color; ratio packs common.
- Replenishment: depends on upstream supply and import cadence.
- Returns: limited allowances; check terms for defects vs fit issues.
[MENTION: Global retail buying practices from BoF] [MENTION: Wholesale distributor models at BrandsGateway] [CITE: “Distributor vs wholesaler definitions” from a recognized apparel trade association] [INTERNAL LINK: Foundational guide on OEM vs ODM definitions]
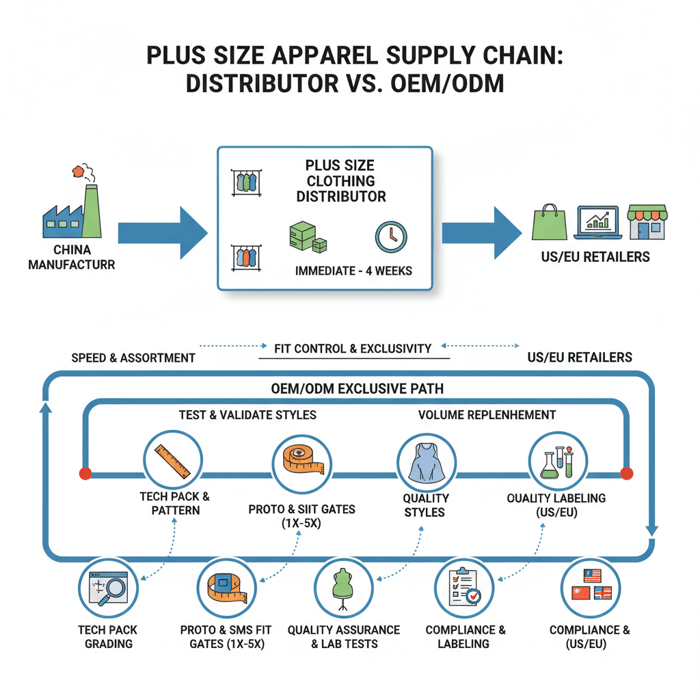
Distributor vs Wholesaler vs Manufacturer
Distributor: Holds inventory from multiple sources, sells bulk to retailers under their own catalog. Wholesaler: Resells bulk goods, often with less assortment curation and limited replenishment visibility. Manufacturer: Produces goods; with OEM/ODM, they develop patterns, grade sizes, and deliver client-specified fits and materials.
Example: A US boutique needs 1X–3X jersey dresses next week—distributor or wholesaler fits that need. A UK retailer wants exclusive 1X–5X outerwear with precise measurement tolerances—manufacturer via OEM/ODM is the path.
[CITE: “Definitions in supply chain management” from a university press] [MENTION: National Retail Federation] [INTERNAL LINK: Our sourcing glossary for apparel teams]
Size Curves & Ratio Packs
Ratio packs help retailers buy in a curve that matches demand. For plus-size apparel, US and EU curves often favor mid sizes (2X–3X) but vary by category and brand positioning. Align curves to past sell-through and planned replenishment windows to cut stock-outs.
| Region | Curve | Pack Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| US | 1X–3X heavy | 1X:2, 2X:4, 3X:4 | Core knits and denim often anchor mid sizes |
| US | 1X–5X balanced | 1X:2, 2X:3, 3X:3, 4X:2, 5X:2 | Outerwear and occasionwear require breadth |
| EU | EU 46–56 heavy | 46:2, 48:4, 50:4, 52:3, 54:2, 56:1 | Adjust for country-level demand and return data |
| EU | Athleisure curve | 46:1, 48:3, 50:4, 52:3, 54:2 | Stretch fabrics shift sales toward mid-upper sizes |
[CITE: “Size curve strategies in apparel” from a retail analytics firm] [MENTION: Edited (retail data platform)] [INTERNAL LINK: Article on ratio packs and inventory health]
How to Vet Plus Size Clothing Distributors for US/EU Retail
Focus vetting on grading accuracy, measurement variance, fit-model process, QC sampling, certifications, replenishment history, and US/EU compliance. Lock these in writing before first orders to reduce fit-related returns.
- Request measurement charts for each size with tolerances and grading rules.
- Check fit approval gates: proto try-on notes, fit-model profiles, pass/fail criteria.
- Audit QC sampling: incoming inspection, AQL targets, defect taxonomy.
- Review replenishment records: average lead time, fill rate, stockout history.
- Validate certifications: OEKO-TEX, social compliance audits, lab test protocols.
- Confirm US/EU labeling and fiber composition documents.
- Agree MOQs, ratio packs, and returns terms for fit vs defect cases.
- Run a small pre-buy with try-ons across 1X–5X and record variance.
[MENTION: OEKO-TEX Standard 100] [MENTION: SGS and Intertek for lab testing] [CITE: “AQL standards for textile QC” from a testing authority] [INTERNAL LINK: Quality control checklist for apparel buyers]
Fit & Grading Verification
Ask for grading rules and tolerances by measurement point (POM). For plus sizes, chest, waist, hip, across shoulder, sleeve, rise, and thigh are critical. Set variance targets and hold distributors to on-size and off-size checks through sampling.
| POM | 1X | 2X | 3X | 4X | 5X | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest (cm) | 122 | 130 | 138 | 146 | 154 | ±1.0–1.5 cm |
| Hip (cm) | 128 | 136 | 144 | 152 | 160 | ±1.0–1.5 cm |
| Across Shoulder (cm) | 47 | 49 | 51 | 53 | 55 | ±0.8–1.2 cm |
| Sleeve Length (cm) | 65 | 65.5 | 66 | 66.5 | 67 | ±0.8–1.2 cm |
| Back Length (cm) | 80 | 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | ±1.0–1.5 cm |
Fit process: use diverse plus-size fit models (body shape, height, posture), run three rounds (proto, SMS, PP), and document pass/fail with photos and comments. Stabilize fabrics (prewash or steam) before measuring to remove shrink/stretch bias.
[CITE: “Fit-model diversity and return rates” from a retail study] [MENTION: ASTM sizing standards] [INTERNAL LINK: Fit testing protocol with sample forms]
QA Sampling & Replenishment Proof
Request QC sampling plans and replenishment performance. Ask for shipment defect rates by style and a breakdown of corrective actions. For replenishment, gather proof: average days to ship, fill rates, and evidence of upstream capacity.
- AQL example: 2.5 for major defects, 4.0 for minor; 80-piece sample per lot.
- Defects taxonomy: measurement out-of-tolerance, seam strength fails, fabric pilling, zipper failures.
- Replenishment targets: 14–21 days for in-region stock; 30–45 days if import needed.
[CITE: “AQL reference table” from a testing body] [MENTION: Bureau Veritas] [INTERNAL LINK: Replenishment playbook for buyers]
Compliance Pack for US/EU
US: FTC Care Labeling Rule (16 CFR Part 423) governs care instructions; maintain fiber content and RN records. EU: Regulation 1007/2011 sets textile fiber naming and labeling rules. Hazardous substance testing with OEKO-TEX Standard 100 is common for retailer acceptance.
- US labeling: care, fiber content, manufacturer/importer identity, country of origin.
- EU labeling: correct fiber names, durable labels, language per market where required.
- Testing: colorfastness, pH, formaldehyde, azo dyes; mechanical strength for outerwear.
[CITE: FTC Care Labeling Rule (16 CFR Part 423)] [CITE: EU Regulation No 1007/2011] [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 summary and scope] [INTERNAL LINK: Labeling templates for US/EU markets]
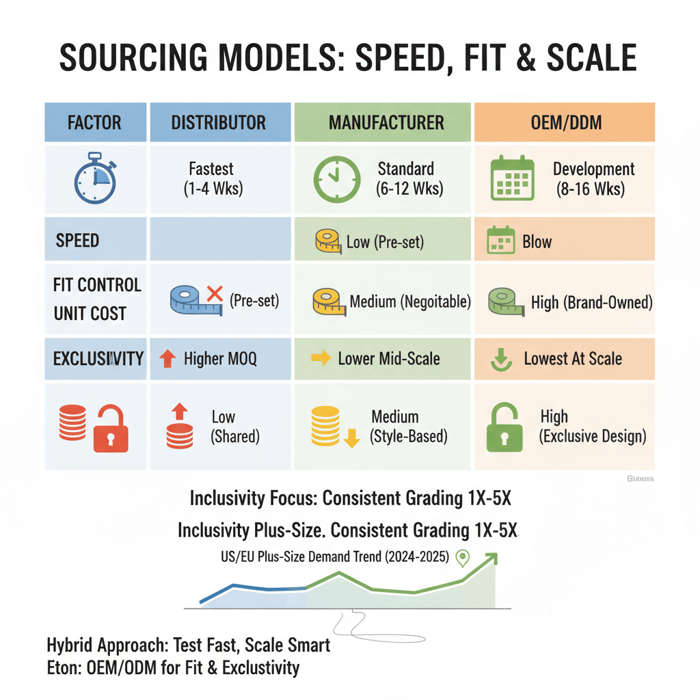
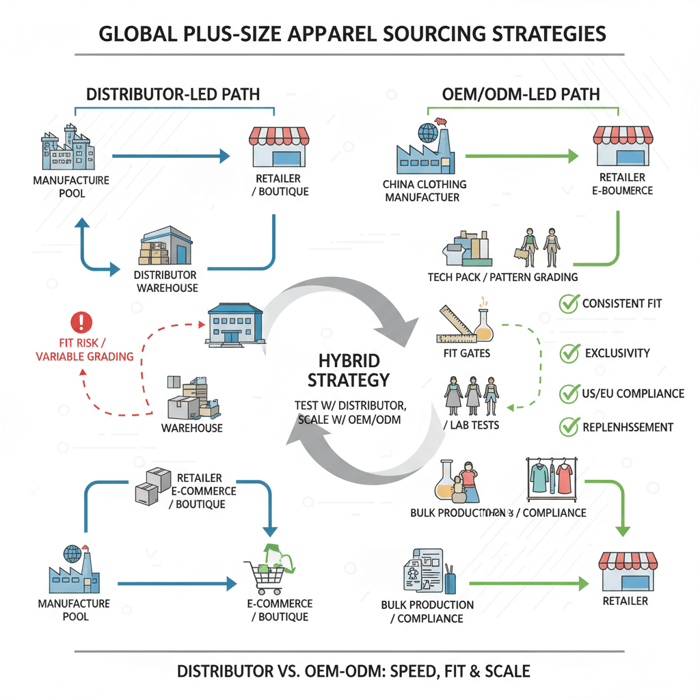
Distributor vs Manufacturer vs OEM/ODM for Plus-Size Apparel
Distributors offer speed and breadth; manufacturers with OEM/ODM win on fit control, exclusivity, and margin over time. Many brands test with distributors and scale hero styles with OEM/ODM to lock grading and reduce returns.
| Factor | Distributor | Manufacturer | OEM/ODM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Immediate to 2–6 weeks | 6–12 weeks | 8–16 weeks (dev + bulk) |
| Fit Control | Low | Medium | High (brand-owned blocks) |
| Exclusivity | Low | Medium | High |
| MOQ | 12–60 units/style | 300–800 units/style | 400–1,200 units/style |
| Unit Cost | Higher | Lower | Lowest at scale |
| Compliance Control | Indirect | Direct | Direct + documented |
| Replenishment Predictability | Variable | Stable | Stable + planned |
- Distributor pros: fast, assortment depth, low MOQs; cons: fit drift, limited exclusivity.
- Manufacturer pros: lower unit cost, direct QC; cons: longer lead, higher MOQs.
- OEM/ODM pros: precise fit, exclusive design, predictable scale; cons: setup time, development cost.
- Inclusive sizing priority remains high — 2024 (Source: [CITE: McKinsey & BoF State of Fashion 2024])
- US/UK search interest rising for plus-size suppliers — 2024–2025 (Source: [CITE: Google Trends data view])
Criteria Overview
Score options on fit control, exclusivity, landed cost, lead time, replenishment predictability, and compliance documentation. Weight factors by business phase—test phase may weight speed; growth phase may weight fit and margin.
- Fit control: weight 25%
- Exclusivity: weight 15%
- Landed cost: weight 20%
- Lead time: weight 15%
- Replenishment: weight 15%
- Compliance docs: weight 10%
[CITE: “Sourcing decision frameworks” from a supply chain journal] [MENTION: Gartner apparel sourcing research] [INTERNAL LINK: Sourcing scorecard template]
Decision Framework
Example scores (0–10 scale): Distributor: Fit 4, Exclusivity 3, Cost 5, Lead 9, Replenishment 6, Compliance 4. Manufacturer: Fit 6, Exclusivity 5, Cost 7, Lead 6, Replenishment 7, Compliance 7. OEM/ODM: Fit 9, Exclusivity 9, Cost 8, Lead 5, Replenishment 8, Compliance 8. Apply weights and select the highest weighted score.
Hybrid approach: test 3–5 styles via distributors; migrate winners to OEM/ODM with locked grading and material specs to stabilize returns and margins.
[CITE: “Hybrid sourcing case studies” from a retail operations report] [MENTION: BoF/McKinsey collaboration] [INTERNAL LINK: Case study on hybrid sourcing in plus-size outerwear]
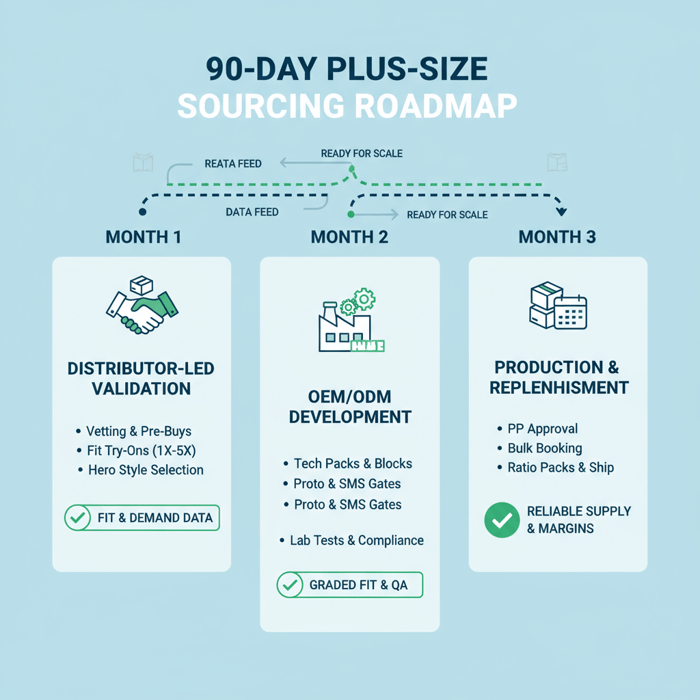
How to Build a Plus-Size Range with the Right Partners
Start with distributor-led validation, then lock hero styles with OEM/ODM. Use checkpoints for grading, fit, QA, and labeling to align US/EU requirements.
- Define subcategory focus: outerwear, athleisure, dresses.
- Set target curves: 1X–3X heavy or 1X–5X balanced.
- Create measurement blocks and tolerance tables.
- Run distributor pre-buys with fit try-ons.
- Select styles for OEM/ODM transfer; build tech packs.
- Execute proto, SMS, PP with fit gates and lab tests.
- Finalize compliance pack; plan bulk and replenishment.
Preparation
Build personas and demand profiles by market. For US boutiques, mid-size curves often sell fastest in knits; for EU outerwear, broader curves protect sell-through. Draft measurement blocks per category and fiber stretch. Record historical returns by POM to guide tolerance tightening.
[CITE: “Returns analysis by apparel POM” from an analytics provider] [MENTION: Edited] [INTERNAL LINK: Measurement block templates for plus-size]
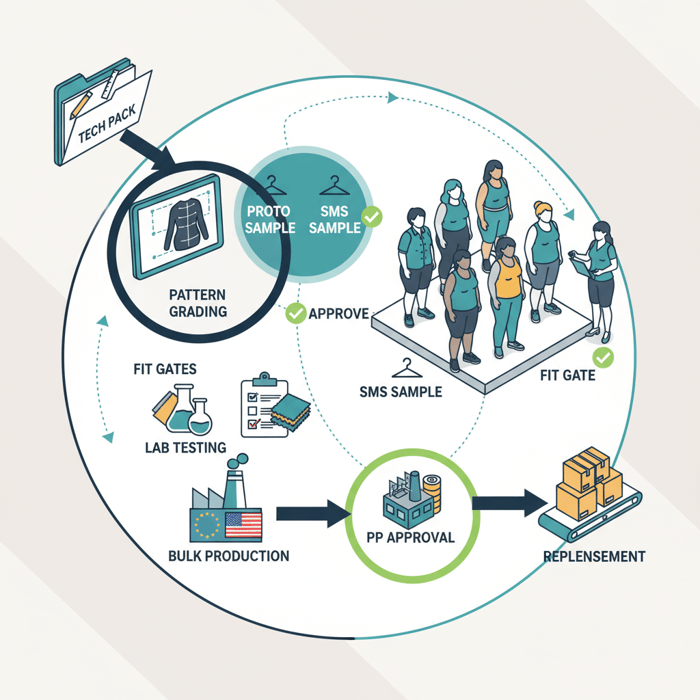
Execution Steps
OEM/ODM cadence: proto (2–3 weeks), SMS (2–4 weeks), PP (1–2 weeks) after fabric booking. Fit gates at each stage with measurement reports and annotated photos. Labeling setup: US care labels and RN identity; EU fiber naming per 1007/2011, language localization per market.
- Proto: prove silhouette, fabric behavior, initial grading.
- SMS: confirm sales samples for buyers; lock most POM tolerances.
- PP: final measurements; approve trims, branding, care labels.
[CITE: “Proto–PP apparel timelines” from a manufacturing source] [MENTION: OEKO-TEX laboratories] [INTERNAL LINK: Labeling checklist and RN registry guidance]
Quality Assurance
Set AQL: 2.5 major, 4.0 minor; include on-size and off-size checks. Run fabric tests: colorfastness, pilling, seam slippage for outerwear; stretch recovery for athleisure. Use third-party inspection reports and retain PP samples as golden size references.
[CITE: “Seam slippage and fabric performance” from a textile engineering journal] [MENTION: Intertek] [INTERNAL LINK: AQL guide with sampling tables]
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton’s OEM service customizes plus-size patterns, locks grading fidelity, and scales production across China and Bangladesh with audited facilities. Brands reduce fit-related returns and secure exclusive designs for US/EU retail.
| Your Need | OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Consistent 1X–5X fit | Pattern blocks + graded rules | Lower fit variance and returns |
| Exclusive outerwear | ODM design + fabric sourcing | Protected assortment and margin |
| US/EU compliance | Labeling pack + lab testing | Retail acceptance with fewer delays |
| Scale-up certainty | China/Bangladesh capacity | Stable replenishment timing |
Eton teams coordinate pattern grading, fit testing, and technical fabrics for plus-size outerwear. Thermal performance, seam integrity, and hardware durability get special attention in upper sizes to protect comfort and longevity. Start an OEM project through Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service.
Use Case 1: Fit Consistency for Core Outerwear
A US retailer migrates a 2X–4X parka from distributor stock to OEM. Eton locks grading rules, tightens tolerances on chest and hip, and validates fabric drape for mobility. Result: lower variance, fewer returns, and improved sell-through on mid-upper sizes.
[CITE: “Outerwear fit retention studies” from a textile performance source] [MENTION: Gore-Tex licensing programs] [INTERNAL LINK: Outerwear grading guide]
Use Case 2: Exclusive Drops with Technical Fabrics
A UK brand builds a plus-size softshell capsule. Eton sources OEKO-TEX compliant fabrics and sets stretch recovery targets. ODM designs lock seam placements and pocket ergonomics. Launch lands with clean fit notes and buyer confidence.
[CITE: “Stretch recovery metrics” from a fabric testing lab] [MENTION: OEKO-TEX Standard 100] [INTERNAL LINK: Technical fabric playbook]
2024–2025 Data & Trends for Plus-Size Apparel
Inclusive sizing remains a consumer priority, and US/UK search interest for supplier terms continues to rise. Brands are pairing distributor speed with OEM/ODM fit control to stabilize returns and margin.
- Inclusive sizing priority — 2024 (Source: [CITE: McKinsey & BoF State of Fashion 2024])
- US/UK search trend up for supplier queries — 2024–2025 (Source: [CITE: Google Trends view])
Key Trend 1: Inclusive Sizing Priority
Consumers expect inclusive ranges across categories. Return rates tie closely to fit accuracy and grading transparency. Brands that document fit processes and use diverse fit models during development see fewer size-related complaints.
[CITE: “Consumer expectations on sizing” from a retail survey] [MENTION: National Retail Federation] [INTERNAL LINK: Fit documentation toolkit]
Key Trend 2: Distributor + OEM Hybrid Sourcing
Hybrid models let teams learn quickly and scale with confidence. Fast buy-ins from distributors feed demand data; OEM/ODM locks patterns and fabrics for reliable repeats. The model reduces volatility in returns and improves replenishment planning.
[CITE: “Hybrid sourcing outcomes” from an apparel operations report] [MENTION: BoF] [INTERNAL LINK: Hybrid sourcing roadmap]
Risks, Compliance & Localization for US/EU
Document measurements, labeling, and substance testing to cut risk. Map regulatory steps to US/EU rules and use local language labeling where applicable.
- Pros: lower return rates, faster retail acceptance, predictable replenishment.
- Cons: upfront setup time, development cost, added documentation work.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fit variance | Medium | High | Lock grading; tighten tolerances; fit gates |
| Labeling noncompliance | Low–Medium | High | US FTC care labels; EU 1007/2011 fiber naming; local language |
| Fabric performance issues | Medium | Medium–High | Lab tests: colorfastness, pilling, stretch recovery |
| Replenishment delays | Medium | Medium | Capacity plans; dual-site production; buffer stocks |
| Social compliance gaps | Low–Medium | High | Audits; corrective actions; transparent reporting |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
US: Follow FTC Care Labeling Rule for care instructions, fiber content, and identity details; country-of-origin marking applies. EU: Apply Regulation 1007/2011 for fiber names and labeling durability; local language needs can vary. Test for harmful substances per retailer requirements; OEKO-TEX Standard 100 is widely accepted.
[CITE: FTC Care Labeling Rule] [CITE: EU Regulation No 1007/2011] [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100] [INTERNAL LINK: Compliance pack checklist]
Conclusion & Next Steps
Blend distributor speed with OEM/ODM control to secure fit, compliance, and exclusivity for plus-size apparel in the US and EU. Use the checklist and decision framework to act, and set a 90-day roadmap from discovery to PP approval.
- Week 1–2: Distributor vetting; small pre-buys with try-ons.
- Week 3–4: Select hero styles; draft measurement blocks and tech packs.
- Week 5–8: OEM proto and SMS with fit gates; start compliance pack.
- Week 9–12: PP approval; bulk booking; replenishment plan and ratio packs.
Ready to lock plus-size grading and exclusivity? Start your OEM project with Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service.
[INTERNAL LINK: Plus-size sourcing checklist] [INTERNAL LINK: OEM consultation booking] [INTERNAL LINK: Author bio and credentials]
- McKinsey & BoF — The State of Fashion 2024 (2024). [CITE: McKinsey & BoF report]
- Google — Google Trends: plus-size supplier searches (2024–2025). [CITE: Google Trends view]
- EU — Regulation No 1007/2011 on textile fibre names and labeling (2011). [CITE: EUR-Lex]
- FTC — Care Labeling Rule (16 CFR Part 423) (Current). [CITE: FTC guidance page]
- OEKO-TEX — Standard 100 (Current). [CITE: OEKO-TEX official site]
- SGS/Intertek/Bureau Veritas — AQL and fabric testing references (Current). [CITE: Testing body pages]
- NRF/Edited — Retail data references for sizing and sell-through (2023–2025). [CITE: Industry data pages]
- University Press — Supply chain definition references (Current). [CITE: Academic source]
- Textile Engineering Journal — Seam slippage and performance testing (Recent). [CITE: Journal article]
- Gartner/Operations Reports — Sourcing frameworks and hybrid case studies (Recent). [CITE: Research pages]
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

