OEM Clothing: How to Work with a China Clothing Manufacturer in 2025
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
21 minute read
OEM Clothing: How to Work with a China Clothing Manufacturer in 2025
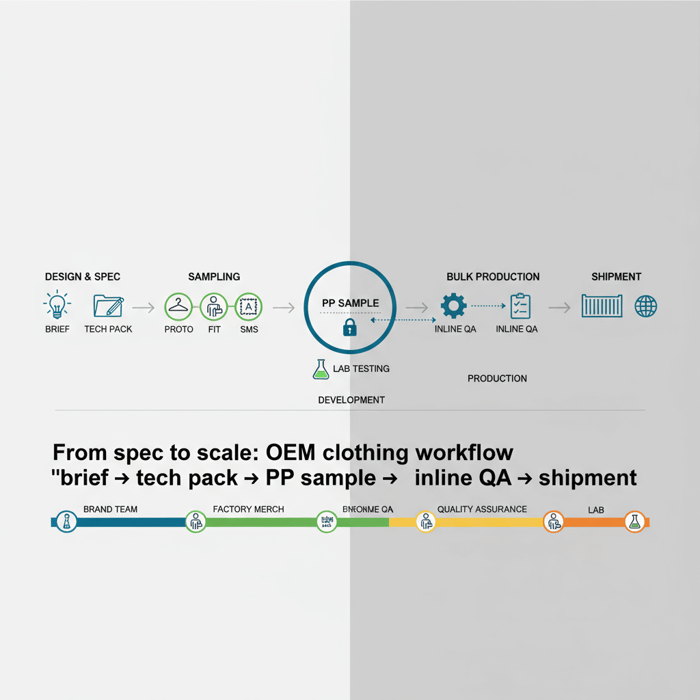
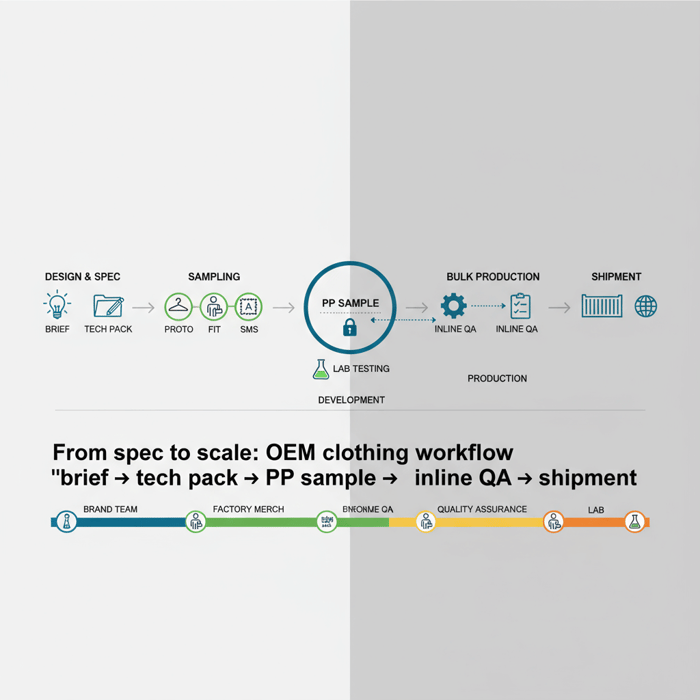
OEM clothing with a proven China Clothing Manufacturer turns your specs into production with speed, control, and compliance for US/EU markets. This end-to-end guide maps OEM vs ODM, tech pack essentials, costs/MOQs/lead times, QC gates, and risk mitigation—then shows how Eton routes outerwear and technical apparel between China and Bangladesh to hit margin and timing targets.
OEM clothing means a brand provides specifications and a factory manufactures to those specs at scale. For US/EU fashion brands, align a complete tech pack, vet a China Clothing Manufacturer for REACH/CPSIA compliance, set clear MOQs/lead times, and run a gated QA plan from fit through PP sample with inline AQL audits.
OEM Clothing Explained for Fashion Brands
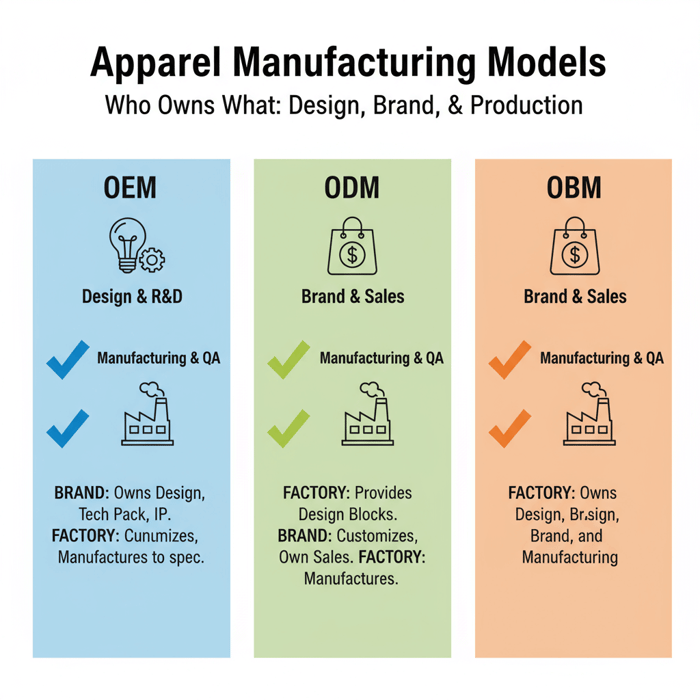
OEM clothing is manufacturing to brand-owned specifications. Choose it when the design and technical standards must remain under brand control while leveraging factory scale, precision, and repeatability. ODM adds the factory’s design library; OBM means the factory sells under its own brand.
[CITE: Concise definitions from an authoritative overview of OEM/ODM/OBM]
[MENTION: Techpacker’s OEM vs ODM overview], [MENTION: Investopedia definition of OEM]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on Tech Packs — how to build them for outerwear]
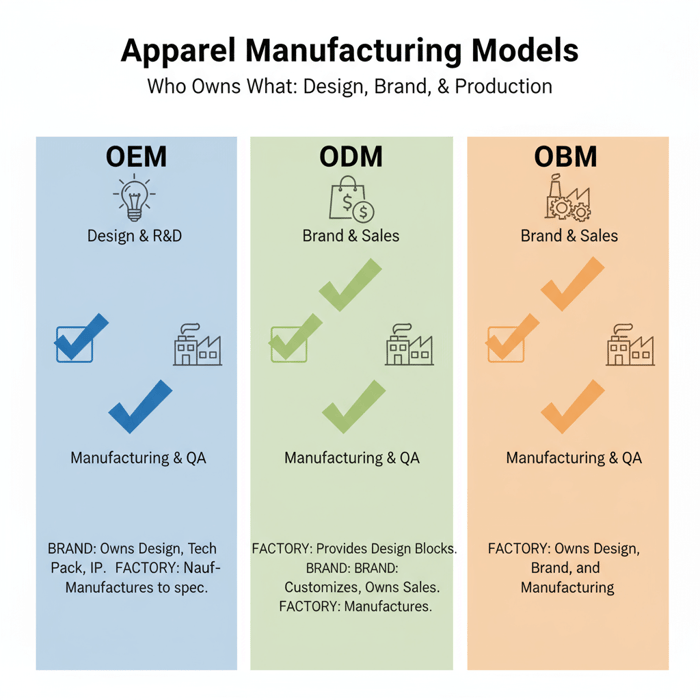
OEM vs ODM vs OBM — Definitions and Use Cases
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): The brand owns design, tech pack, and quality standards; the factory manufactures to spec. Use when differentiation, IP control, and consistent fit are critical. [CITE: Canonical OEM definition]
- ODM (Original Design Manufacturer): The factory provides designs or blocks; the brand customizes and buys under its label. Use for speed-to-market and lower development overhead.
- OBM (Original Brand Manufacturer): The factory sells its own brand. Use when a factory’s market-facing product aligns with your retail strategy or for co-brand capsules.
Model fit examples:
- OEM: A US premium outerwear brand specifies a seam-sealed 20k/20k shell with 700-fill power down and strict tolerance control.
- ODM: A growth apparel brand picks a proven puffer block, changes fabric/trim palette, and targets a 90-day launch.
- OBM: A retailer tests a factory’s branded rain jacket line in select stores for regional demand validation.
When OEM Is the Right Choice for US/EU Brands
OEM suits brands that need tight control of materials, fit, and finishing, and that own design IP. Margin planning benefits when yield, consumption, and QC are predictable across repeats. Legal and regulatory demands (REACH, CPSIA, labeling) are easier to manage when specifications and test methods are brand-led.
- Control: You specify BOM, stitch class, seam allowances, and test protocols; the factory executes.
- Scaling: Once PP is locked, repeat orders stay consistent with minimal rework.
- Compliance: REACH SVHC checks, AAFA RSL alignment, and CPSIA test plans follow your standards and traceability path. [CITE: ECHA REACH Candidate List (2024)]
ODM is pragmatic for commodity styles or where speed trumps differentiation. OBM is rare for brand-centric programs but can work in collaborations or private label expansions.
Outerwear Specifics: Why OEM Excels
Outerwear programs carry complexity—insulation standards, seam sealing, taped constructions, waterproof zippers, and lab testing for water column, breathability, colorfastness, and care performance. OEM’s spec-driven model fits the required precision across fabric approvals, PP measurements, and inline AQL audits.
- Insulation integrity: Down fill-power verification and polyfill loft retention require methodical test plans. [CITE: Industry testing lab protocol overview]
- Seam sealing: Tape width, adhesion, and wash durability need controlled materials and consistent application.
- Hardware and trims: Coil vs molded zippers, storm flaps, snaps, and toggles add failure vectors without disciplined vetting.
Answering “Is OEM better than ODM for outerwear and technical apparel?”—for performance jackets, OEM delivers tighter failure prevention at mass through spec ownership and factory execution rigor.
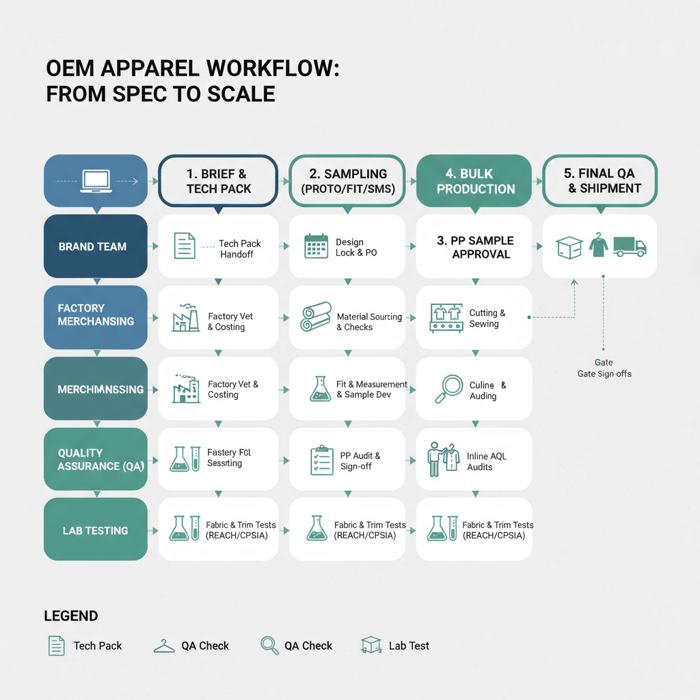
How to Work with a China Clothing Manufacturer for OEM
Success with a China OEM partner rests on a complete tech pack, a vetted garment factory, and gated reviews from prototype to PP. Align AQL levels, materials approvals, PP standards, and Incoterms early. Lock compliance proofs before POs to avoid costly late-stage pivots.
[MENTION: AAFA RSL], [MENTION: ISO 9001 for quality systems]
[INTERNAL LINK: Capability checklist for outerwear factories — what to verify before sampling]
- Define brief: Merch intent, margin targets, markets (US/EU), and delivery windows.
- Build a complete tech pack: Measurements, graded size chart, tolerances, stitch/seam specs, BOM with trims, packaging, and test methods.
- Vet factories: Certifications, capacity, compliance, lab partners, and needle detection capability.
- Sample gates: Proto → Fit → SMS → PP, with pass/fail criteria and documented measurement reports.
- Compliance locks: REACH/CPSIA test plans, labeling proofs, and traceability documentation.
- Production control: Inline and final AQL audits, fabric/trim lot tracking, and defect root-cause logs.
- Logistics and terms: Incoterms, carton specs, palletization, routing, and port calendars.
Build a Complete Tech Pack (BOM, Measurements, Tolerances, Stitching)
A complete tech pack reduces ambiguity and rework. Include front/back views, construction details, seam types, stitch classes, BOM with material specs and finishes, graded size chart, tolerances, measurement points, packaging, labels, care instructions, and test methods (colorfastness, wash, tensile, water column, breathability).
- Graded size chart with tolerances: Define +/- per POM to control fit drift.
- Seam and needle spec: Document seam class (e.g., SS, LS), stitch density, and needle size to prevent seam failure.
- BOM completeness: Fabrics, insulation, linings, tapes, zippers, snaps, cord locks, labels, hangtags, polybags, cartons.
- Test methods: Cite standards and labs; require reports before PP approval. [CITE: Accredited lab method references]
Factory Vetting: Certifications, Capacity, Compliance
Vetting a China clothing manufacturer starts with quality systems and compliance credibility. Verify ISO 9001, social audits (WRAP/SEDEX), chemical management aligned to AAFA RSL, and UFLPA risk controls for traceability. Confirm outerwear-specific capacity (seam sealing rooms, tape machines, waterproof zipper handling), needle detection, and trusted external labs.
- Quality systems: ISO 9001 certificate; process maps and CAPA logs. [CITE: ISO 9001 overview]
- Ethics/compliance: WRAP/SEDEX audit recency; UFLPA diligence pack; REACH/CPSIA test references. [CITE: U.S. CBP UFLPA dashboard]
- Capacity: Line balance plans, seam sealing stations, PP lead time commitments, seasonal calendars.
- Traceability: Material origin statements, batch/lot controls, digital tracking where supported.
Sampling to PP Sample: Fit, Wear, and Lab Testing
Run sample gates with documented pass/fail criteria. Fit on target body forms, perform wear trials, and trigger lab tests for the chosen risk profile. PP approval requires full materials-in-use, final construction, and measurement reports within tolerance—this is the quality contract for bulk.
- Fit and wear: Record movement constraints, sleeve articulation, hood balance, cuff closure ergonomics.
- Lab tests: Colorfastness to crocking/wash, hydrostatic pressure (water column), breathability, seam tape adhesion, zipper cycle counts.
- PP measurement report: Capture all POMs; note corrective actions if out-of-tolerance.
- Gate discipline: No production until PP approval and compliance locks are in place.
OEM Clothing Cost, MOQ, and Lead Times (with Benchmarks)
Outerwear OEM programs typically target MOQs of 300–800 units per colorway, with 75–120 days from PP to shipment, contingent on fabric/trim readiness. Unit cost splits often show materials at 60–70%, labor 15–25%, overhead 5–10%, logistics 5–10%, plus testing and compliance.
[CITE: Factory-side benchmarking studies for cost components], [MENTION: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024], [MENTION: WTO trade review 2024]
- Materials dominate outerwear unit cost — 2024 (Source: [CITE: Industry cost benchmarking report])
- China retains advanced fabric ecosystems — 2024–2025 (Source: [CITE: WTO textiles/clothing review])
- Lead times hinge on fabric and trim readiness — 2025 (Source: [CITE: Aggregated factory performance data])
Cost Breakdown for Outerwear and Technical Jackets
Costs concentrate in shell fabrics, insulation, tapes, waterproof zippers, and finishing. For a 3-layer shell jacket or a down parka, materials commonly exceed two-thirds of the unit cost. Labor varies with seam complexity, taping coverage, and hardware count. Overhead includes cutting room, QA, and defect handling; logistics adds freight and duties; testing includes lab fees.
| Component | % of Unit Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 60–70% | Shell/lining, down/polyfill, seam tape, waterproof zippers, snaps, labels; yield optimization is critical. |
| Labor | 15–25% | Pattern complexity, taping time, hardware placement, QA rework duration. |
| Overhead | 5–10% | Factory fixed costs, cutting, merchandising, defect tracking, energy. |
| Logistics | 5–10% | Freight, insurance, duties/taxes; varies by Incoterms and lane. |
| Testing & Compliance | 1–3% | Lab fees, certifications, documentation, labeling checks. |
MOQ Drivers: Fabric, Dye Lot, Trims, and Efficiency
MOQ hinges on mill minimums per color, dye lot constraints, and trim vendor minimums. Efficiency improves with consolidated size curves and fewer colorways. Technical trims (waterproof zips, seam tapes) often impose higher minimums; negotiating component pooling across styles can unlock lower MOQs.
| Category | Per Colorway MOQ | Per Style MOQ | Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lightweight Jacket | 300–500 | 600–1,200 | Fabric mill minimums, zipper/colorway counts. |
| Parka | 400–800 | 800–1,600 | Insulation sourcing, seam tape MOQs, complex hardware. |
| Padded Coat | 350–700 | 700–1,400 | Polyfill lot sizes, quilting setup, trim vendor minima. |
| 3-Layer Shell | 400–800 | 800–1,600 | Laminated fabrics, seam tape consumption, lab test cadence. |
Lead Times: Critical Path from Fabric to Final QC
Lead times compress when fabric and trim readiness is high and lab approvals run in parallel with sampling. Expect 75–120 days from PP approval to shipment under normal conditions. Calendar risks include Chinese New Year, Golden Week, Eid (Bangladesh), and port congestion—build buffers and align booking windows.
- Best-case: Stock fabric, pre-approved trims, PP locked early → 75–90 days to ship.
- Typical: Custom dyes, lab dips, full PP sign-off → 90–120 days.
- Risk factors: Late fabric lab dips, trim delays, calendar holidays, and late PP changes. [CITE: Apparel production calendar analyses]
OEM vs ODM vs OBM: Which Fits Your Brand?
Use OEM when you own IP and need precision and repeatability at scale. Choose ODM when speed-to-market with proven blocks outperforms differentiation needs. OBM fits factory brand plays or co-branded capsules. Decide using IP control, margin goals, timeline, and desired uniqueness.
[MENTION: Fashinza OEM vs ODM guide], [MENTION: Sewport marketplace insights]
| Model | IP Control | Speed | Differentiation | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | High (brand-owned specs) | Medium | High | Performance outerwear, brand-owned fit and finish. |
| ODM | Medium (factory blocks) | High | Medium | Quick-turn seasonal jackets, cost-focused capsules. |
| OBM | Low (factory brand) | Medium | Low–Medium | Retail test of factory’s branded lines. |
- Speed-to-market pressure remains high — 2024 (Source: [CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024])
- Brands diversify sourcing while keeping China core for materials — 2024 (Source: [CITE: WTO 2024])
Criteria Overview: IP Control, Speed, Cost, Differentiation
- IP and fit ownership: OEM wins.
- Fast launch: ODM wins with factory blocks.
- Cost: ODM/OBM can reduce development overhead; OEM yields lower defect costs over repeat cycles.
- Differentiation: OEM provides distinct feature sets, materials, and construction details.
Decision Framework: Start-up vs Growth vs Enterprise Brands
- Start-up: ODM for early capsules; OEM when unique fit becomes core to brand value.
- Growth: OEM for hero silhouettes and technical lines; ODM for fill-in seasonal styles.
- Enterprise: OEM across high-volume programs with robust QA; ODM lines for trend response.
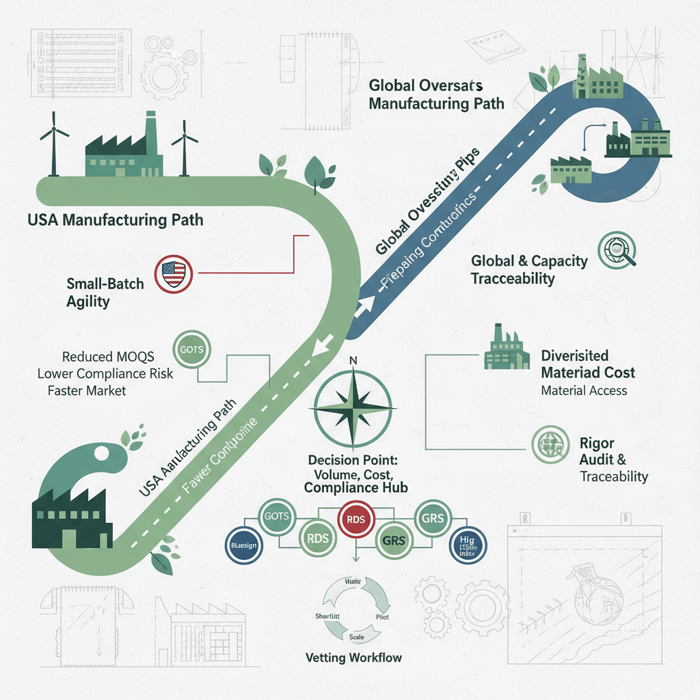
Market Data & 2024–2025 Trends for OEM Apparel
China remains pivotal for OEM outerwear thanks to material ecosystems and technical know-how; Bangladesh complements scale and cost. Digital development and compliance transparency shape 2025 strategies for US/EU brands, with hybrid nearshoring in play for select categories.
[MENTION: AAFA RSL updates], [MENTION: European Commission CSRD roll-in]
- China’s share in technical textiles remains significant — 2024 (Source: [CITE: WTO trade review])
- Brands increase compliance disclosures — 2023/2024 (Source: [CITE: EC CSRD guidance])
Key Trend 1: China’s Material Ecosystems + Bangladesh Scale
For outerwear, China’s mills and trim vendors offer breadth and speed—critical for laminated shells, seam tapes, and performance zippers. Bangladesh brings cut-and-sew scale and cost advantages; routing development in China and bulk to Bangladesh can balance time and margin targets.
- Material readiness shortens timelines; China leads in advanced inputs. [CITE: WTO textile ecosystem analysis]
- Bangladesh adds capacity for volume programs with competitive labor costs. [CITE: Country apparel production benchmarking]
- Hybrid routing: Sample/PP in China; bulk in Bangladesh after PP locks and material pre-positions.
Key Trend 2: Digital Sampling, PLM, and Compliance Transparency
3D sampling and PLM integrations reduce physical sample loops and improve spec fidelity. Brands increasingly publish RSLs and supply chain disclosures aligned to CSRD and UFLPA diligence, accelerating lab approvals and clearing port checks.
- 3D development: Faster silhouette validation; fewer physical iterations. [CITE: Apparel PLM/3D adoption reports]
- Compliance-first sampling: Test plans embedded; fewer late-stage fails.
- Traceability: Digitized lot tracking supports UFLPA/REACH compliance at customs. [CITE: UFLPA dashboard summaries]
How to Launch OEM Clothing in 90–120 Days: A Practical Playbook
With complete tech packs, pre-approved materials, and disciplined gates, many jacket programs move from RFQ to shipment in ~90–120 days. Parallelize lab approvals with sample iterations, lock PP criteria early, and avoid late BOM changes to protect timing.
[INTERNAL LINK: Outerwear production timeline — detailed, step-by-step], [MENTION: ISO 9001 CAPA methods]
Preparation (RFQ, Tech Pack, Material Strategy)
- RFQ: Include specs, target FOB/CIF, delivery windows, Incoterms, and compliance requirements.
- Tech pack completeness: Measurements, tolerances, seam classes, BOM, packaging, labeling, care.
- Material plan: Confirm stock fabrics or target mills; request lab dips and test windows upfront.
Execution Steps (Proto → Fit → SMS → PP → Bulk)
- Proto: Validate construction and key features; mark-up corrections.
- Fit: Fit on target forms; capture movement and tolerance adherence with measurement reports.
- SMS: Sales samples for line reviews; confirm colorways and trims.
- PP: Full materials-in-use sample; measure every POM; pass/fail gate for bulk authorization.
- Bulk: Maintain inline QA and final AQL audits; document compliance and traceability.
Quality Assurance (AQL, Inline Inspections, Final Random Inspections)
- AQL levels: Set minor/major/critical defect thresholds appropriate for outerwear. [CITE: AQL standard references]
- Inline QA: Early detection for seam tape adhesion, zipper performance, and hardware failures.
- Final inspection: Random sampling; carton checks; labeling and fiber-content verification.
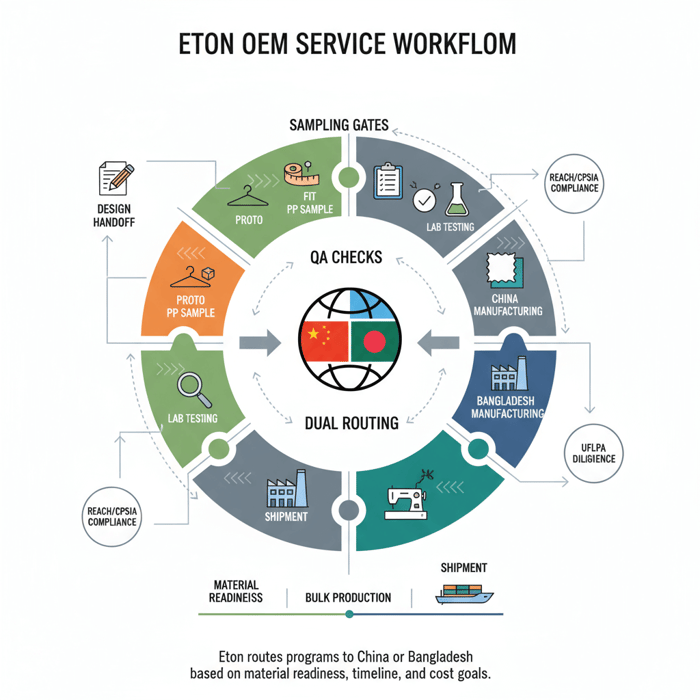
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service (Eton)
Eton’s OEM service for outerwear and technical apparel pairs China’s material ecosystem with Bangladesh’s scale. A gated QA system, compliance-first documentation, and dual routing deliver predictable quality, speed, and cost outcomes for US/EU brands.
[INTERNAL LINK: Start your OEM project → https://china-clothing-manufacturer.com/garment-factory/]
[MENTION: Liverpool F.C. licensed programs], [MENTION: Forever 21 outerwear partnerships]
| Need | OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Premium capsule, low MOQ | Advanced sampling, curated fabric library, PP gates | 150–300 units/color in ~90–110 days; high fit fidelity. |
| Cost optimization at scale | China development + Bangladesh bulk | ~8–12% unit cost savings; stable lead times. |
| Compliance-first route | REACH/CPSIA test plans; traceability pack; AQL discipline | Smoother customs clearance; reduced late-stage rework. |
Use Case 1: Premium Parka (Small Batch, High Performance)
A US/EU brand targets a premium down parka with taped seams and waterproof hardware. Eton runs proto/fit with methodical lab testing, locks PP in China, then executes bulk where capacity and cost fit—typically in Bangladesh—after materials pre-positioning. Outcome: tight fit/finish and a reliable 90–110 day cycle.
Use Case 2: Multi-Style Jacket Program (Retail Rollout)
A retailer plans three jacket styles across four colorways each. Eton consolidates trims, sequences lab dips, and aligns PP timing across styles. Development runs in China to compress sample loops; bulk production is split to balance delivery windows and margin goals. Outcome: disciplined rollouts with predictable QA and 8–12% unit cost benefit.
Explore the Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service: Start your OEM project.
Risks, Compliance & Localization (US/EU)
Lock compliance early. US brands align to CPSIA and labeling rules; EU brands follow REACH chemical restrictions, fiber-content and care labeling, and CSRD reporting scope. Manage forced-labor risk through UFLPA diligence, traceability documentation, and proactive lab testing against AAFA RSL.
[MENTION: U.S. CPSC CPSIA], [MENTION: ECHA REACH SVHC updates]
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forced labor/UFLPA | Medium | High | Traceability pack; supplier origin attestations; route diligence; document audits. [CITE: CBP UFLPA dashboard] |
| REACH SVHC non-compliance | Medium | High | AAFA RSL alignment; lab testing; chemical management SOPs. [CITE: ECHA 2024 updates] |
| Labeling errors | Low–Medium | Medium | Label proofs; fiber content verification; care symbol checks; final inspection. |
| Colorfastness fails | Medium | Medium | Lab testing for wash/crocking; early sample risk tests; corrective action logs. |
| Needle contamination | Low | High | Needle detection; broken needle policies; controlled cutting and finishing rooms. |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
- US — CPSIA: Children’s wear testing for lead/phthalates, tracking labels; fiber content and care labeling; flammability. [CITE: US CPSC CPSIA overview]
- EU — REACH: SVHC updates; documentation; RSL adherence; labeling and fiber-content rules; care labels aligned to regional standards. [CITE: ECHA REACH updates]
- CSRD: Reporting obligations roll-in; supply chain disclosures and materiality mapping. [CITE: European Commission CSRD]
- ISO 9001: Factory quality system credibility; CAPA and document control. [CITE: ISO 9001]
Conclusion & Next Steps
OEM clothing delivers consistent quality when brands pair complete specs with a vetted China Clothing Manufacturer and a disciplined QA plan. Use the decision matrix, benchmarks, and compliance notes above to move fast and safely—then route your program with Eton to compress cycles and scale outerwear with confidence.
- Week 1–2: RFQ + complete tech pack; vet factory certifications.
- Week 3–4: Proto + fit; start lab tests on high-risk materials.
- Week 5–6: SMS; colorway/trims lock; PP criteria finalized.
- Week 7–8: PP approval; POs raised with compliance locks.
- Week 9–16: Bulk with inline QA + final AQL; route freight and compliance documentation.
[INTERNAL LINK: OEM vs ODM guide — when to switch], [INTERNAL LINK: Tech pack checklist — outerwear-ready], [INTERNAL LINK: Compliance checklist — US/EU labeling and tests]
Author: Eton Garment Technical Editorial Team (Outerwear OEM specialists; 30+ years in China/Bangladesh production)
Reviewer: Senior QA Manager, Eton Garment Limited (AQL, lab testing, compliance)
Methodology: First-hand factory practices, recent programs, and authoritative sources; benchmarks are indicative ranges—confirm with live quotes.
Limitations: Costs/MOQs/lead times vary by fabric availability, seasonality, and complexity; regulations may update—confirm with counsel and accredited labs.
Disclosure: This guide includes Eton’s OEM service; compare multiple qualified suppliers.
Last Updated: 2025-10-28
- Wikipedia — Original Equipment Manufacturer (2025). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Original_equipment_manufacturer
- Investopedia — Original Equipment Manufacturer (2024). https://www.investopedia.com/terms/o/oem.asp
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights
- World Trade Organization — World Trade Statistical Review 2024 (Textiles and Clothing). https://www.wto.org/
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection — UFLPA Statistics Dashboard (2024–2025). https://www.cbp.gov/trade/forced-labor/UFLPA
- European Commission — Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) (2023/2024). https://commission.europa.eu/strategy-and-policy/corporate-sustainability-reporting_en
- European Chemicals Agency — REACH Candidate List of SVHCs (2024 updates). https://echa.europa.eu/candidate-list-table
- U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission — CPSIA. https://www.cpsc.gov/Regulations-Laws--Standards/Statutes/The-Consumer-Product-Safety-Improvement-Act
- ISO — ISO 9001: Quality management systems — Requirements. https://www.iso.org/standard/62085.html
- American Apparel & Footwear Association — Restricted Substances List (RSL) 2024. https://www.aafaglobal.org/RSL
OEM Clothing Explained for Fashion Brands
OEM clothing means your team owns the design and technical playbook, and the factory builds exactly to it. Use it when your fit, materials, and finish define your brand. ODM adds factory-provided blocks and design; OBM is the factory’s own label. Pick OEM when you want control without running your own plant.
[CITE: Plain-language OEM/ODM definitions suitable for apparel], [MENTION: Techpacker OEM vs ODM article], [MENTION: Investopedia OEM concept]
[INTERNAL LINK: Read our tech pack deep dive for outerwear]
OEM vs ODM vs OBM — Definitions and Use Cases
- OEM: You own the pattern, BOM, and standards; the factory executes. Best for unique fits and technical jackets.
- ODM: You pick a proven silhouette from the factory, customize, and ship fast. Great for speed with limited development.
- OBM: The factory sells its brand; you carry their product or co-brand a capsule.
Use OEM for parkas and shells where tape width, waterproof zips, and lab tests can’t be loose. Use ODM for seasonal puffers when launch dates matter more than custom patterns.
When OEM Is the Right Choice for US/EU Brands
If your brand lives on fit, hand-feel, and performance, OEM is the safer path. Margins stabilize because yields and defects come under control. Compliance is smoother—your test plan and RSL drive decisions from sampling to bulk. [CITE: ECHA SVHC list for 2024]
Outerwear Specifics: Why OEM Excels
Jackets fail at seams, zippers, and fabric performance. OEM sets construction rules, test methods, and PP standards up front. That’s how insulation loft, seam tape adhesion, and wash durability stay consistent across repeats. [CITE: Common outerwear test suites]
How to Work with a China Clothing Manufacturer for OEM
Start with a complete tech pack, interview factories hard on compliance and capacity, and run gated sampling. Set AQL early, define PP acceptance, and hold the line on materials approvals. Align Incoterms and book calendars around holidays.
[MENTION: AAFA RSL for apparel chemicals], [MENTION: ISO 9001’s CAPA discipline]
[INTERNAL LINK: Outerwear factory capability checklist]
Build a Complete Tech Pack (BOM, Measurements, Tolerances, Stitching)
Your tech pack is the instruction manual. Include graded sizes and tolerances, seam classes and stitch density, a full BOM with finishes and trims, packaging specs, labels, and test methods. Missing pieces create delays and waste.
Factory Vetting: Certifications, Capacity, Compliance
Ask for ISO 9001, recent WRAP/SEDEX audits, AAFA RSL alignment, and a UFLPA diligence pack. Confirm outerwear capacity—seam sealing rooms, tape machines, needle detection—and which labs they use. [CITE: CBP UFLPA dashboard]
Sampling to PP Sample: Fit, Wear, and Lab Testing
Run proto for construction, fit for silhouette, SMS for color buys, and PP as your contract sample. Track measurements to tolerance. Send fabrics and trims for lab tests. Don’t greenlight bulk without PP sign-off and compliance locks.
OEM Clothing Cost, MOQ, and Lead Times (with Benchmarks)
Expect 300–800 units per colorway for outerwear MOQs. After PP, 75–120 days is realistic depending on materials readiness. Costs skew toward materials—shells, down/polyfill, tapes, and waterproof zippers—followed by labor and logistics. [MENTION: McKinsey 2024], [MENTION: WTO 2024]
- Materials drive most unit cost — 2024 ([CITE: Industry cost benchmarking])
- Fabric readiness sets the pace — 2025 ([CITE: Factory program data])
Cost Breakdown for Outerwear and Technical Jackets
| Component | % of Cost | What to Watch |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 60–70% | Yields, tape coverage, zipper specs, insulation quality. |
| Labor | 15–25% | Complex seams, taping time, QA touchpoints. |
| Overhead | 5–10% | Cut room, energy, defect containment. |
| Logistics | 5–10% | Freight lanes, duties, booking windows. |
| Testing & Compliance | 1–3% | Lab fees and paperwork; don’t skip. |
MOQ Drivers: Fabric, Dye Lot, Trims, and Efficiency
| Category | Colorway MOQ | Style MOQ | Why |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lightweight Jacket | 300–500 | 600–1,200 | Mill minimums; zipper colors. |
| Parka | 400–800 | 800–1,600 | Insulation lots; taping. |
| Padded Coat | 350–700 | 700–1,400 | Polyfill lots; quilting setup. |
| 3-Layer Shell | 400–800 | 800–1,600 | Lamination and tapes. |
Lead Times: Critical Path from Fabric to Final QC
Stock fabrics and trims shorten cycles. Custom dyes and lab dips add weeks. Plan around Chinese New Year, Golden Week, Eid, and port schedules. Best-case runs 75–90 days; typical runs 90–120 days after PP. [CITE: Apparel calendar studies]
OEM vs ODM vs OBM: Which Fits Your Brand?
OEM wins when your brand’s value lives in details: fit, fill, seam sealing, and hardware. ODM wins on speed. OBM fits factory-led product lines. Use IP control, speed needs, margin, and differentiation to decide. [MENTION: Fashinza guide], [MENTION: Sewport perspective]
| Model | Control | Speed | Uniqueness | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | High | Medium | High | Hero outerwear lines. |
| ODM | Medium | High | Medium | Seasonal fast-turn styles. |
| OBM | Low | Medium | Low–Medium | Factory brand tests. |
- Fast cycles remain a priority — 2024 ([CITE: McKinsey])
- China stays core for materials — 2024 ([CITE: WTO])
Criteria Overview: IP Control, Speed, Cost, Differentiation
- Own the spec? OEM.
- Need speed? ODM.
- Pressure on cost? ODM/OBM reduce dev overhead; OEM lowers defect costs over time.
- Want uniqueness? OEM.
Decision Framework: Start-up vs Growth vs Enterprise Brands
- Start-up: ODM to launch, OEM for hero fits.
- Growth: OEM for core lines, ODM for fillers.
- Enterprise: OEM for scale; ODM for quick-trend capsules.
How to Launch OEM Clothing in 90–120 Days: A Practical Playbook
Lock the tech pack, pre-approve materials, and gate every step. Parallel lab tests with sampling. Don’t tweak the BOM late. Align Incoterms with bookings. With those basics in place, 90–120 days is achievable for many outerwear programs.
[INTERNAL LINK: Detailed outerwear timeline], [MENTION: ISO 9001 for QA discipline]
Preparation (RFQ, Tech Pack, Material Strategy)
- RFQ: Share specs, pricing targets, markets, and dates.
- Tech pack: No gaps—stitches, sizes, BOM, packaging, labels, tests.
- Materials: Confirm stock or mills, plan lab dips, set test windows.
Execution Steps (Proto → Fit → SMS → PP → Bulk)
- Proto: Validate construction and key features; mark-up corrections.
- Fit: Fit on target forms; capture movement and tolerance adherence with measurement reports.
- SMS: Sales samples for line reviews; confirm colorways and trims.
- PP: Full materials-in-use sample; measure every POM; pass/fail gate for bulk authorization.
- Bulk: Maintain inline QA and final AQL audits; document compliance and traceability.
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

