Made in China Apparel: How to Choose a China Clothing Manufacturer You Can Trust

 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
15 minute read
Made in China Apparel: How to Choose a China Clothing Manufacturer You Can Trust
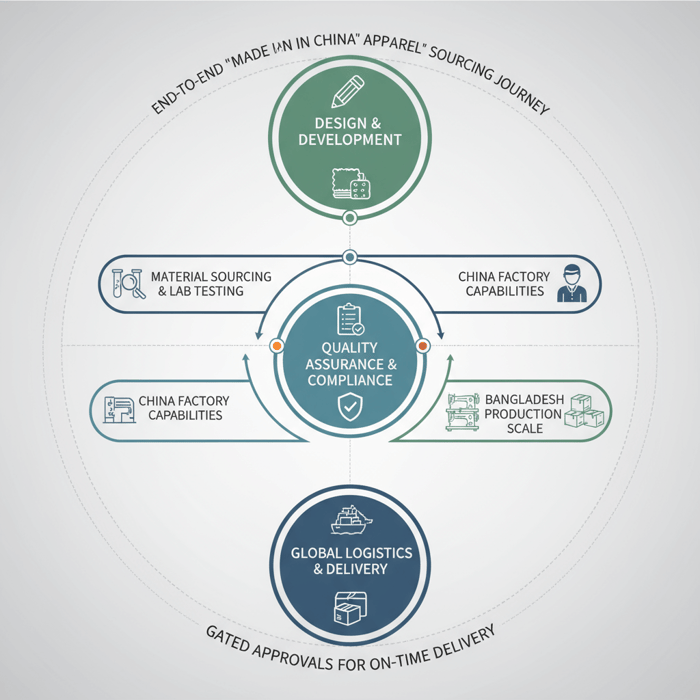
Made in China apparel is still a strong sourcing path for US and EU fashion brands when selection, testing, and documentation are handled with discipline. Working with a proven China Clothing Manufacturer lets teams move fast on technical outerwear, lock cost and lead-time targets, and maintain traceability for UFLPA and EU chemical rules. This guide gives you the exact steps, documents, and checkpoints that keep quality high and risk low.
For buyers weighing China against Bangladesh or Vietnam, the decision comes down to capability, compliance, and timeline. China offers deep access to technical fabrics, advanced bonding/taping lines, and quick-turn sampling; Bangladesh brings scale for cost-sensitive padded and down jackets with strong social compliance programs. Blending both can hit price, performance, and capacity. The following playbook shows how brands move from vendor vetting to on-time delivery with clear gates and visible accountability.
Made in China apparel delivers high quality, speed, and value when brands vet factories, lock technical specs early, and run a compliance-first plan. Use audited suppliers, set test matrices, manage AQL inspections, and maintain UFLPA/EU documentation from yarn to finished goods to hit timelines without surprises.
What “Made in China Apparel” Means in 2025—Perception vs. Reality
Made in China apparel spans mass basics and high-performance outerwear. Quality tracks to factory capability, materials, and process control—not the label alone. China remains strong for technical fabrics, trims, bonded seams, and speed-to-market when brands set clear specs and manage QA/QC with discipline. [CITE: WTO apparel export share and 2019–2024 trend] [MENTION: HKTDC Research 2024; McKinsey State of Fashion 2024] [INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on OEM vs. ODM for outerwear]

- Myth: “Made in China apparel equals low quality.” Reality: Capability varies by factory tier; audited lines with strong SOPs deliver premium outerwear. [CITE: Third-party audit pass rates and defect trends]
- Myth: “Technical jackets perform better outside China.” Reality: China holds dense ecosystems for membranes, seam tapes, and lab testing that favor speed and consistency. [CITE: Regional capability comparisons]
- Myth: “Country-of-origin labeling is simple.” Reality: Mixed supply chains require precise COO rules; development in China with production in Bangladesh needs accurate origin determination. [CITE: US/EU COO guidance]
Myths vs. Modern Capabilities
Today’s China garment factory network runs advanced processes: laser cutting for shell panels, multi-layer bonding, seam taping with calibrated parameters, and down-proof construction with baffle integrity. A well-run line manages water column targets (e.g., 10,000–20,000 mm) and breathability (e.g., 5,000–15,000 g/m²/24h) for rainwear and snow sports jackets. Brands that lock spec ranges, define lab tests, and gate approvals see fewer defects and lower rework. [CITE: Lab test benchmarks for hydrostatic head and MVTR] [MENTION: QIMA methodology; SGS textile testing] [INTERNAL LINK: Audit & QC Templates for apparel]
Where China Excels Today
Strengths include access to membranes and films, seam tapes, coated zippers, reflective trims, and specialized mills for down-proof fabrics. Sampling cycles are quick; proto rounds can move in 10–15 working days when BOMs are complete and color-trim constraints are handled up front. Integrated development teams—pattern, sample room, and test lab—shorten feedback loops. That ecosystem helps US and EU brands hit seasonal windows for technical lines. [CITE: Lead-time benchmarks by category from 2024–2025 buyer surveys] [MENTION: HKTDC; McKinsey State of Fashion]
When “China + Bangladesh” Beats Single-Country Sourcing
Use China for rapid design, proto, and PP sample approvals; shift bulk padded or down jackets to Bangladesh for scale and labor efficiency while keeping trims and testing aligned. You gain price leverage without losing speed. This blended model keeps development close to technical inputs and preserves consistency across factories through shared SOPs. [CITE: Regional cost comparisons for padded outerwear] [MENTION: BGMEA insights; QIMA audit trends]
How to Select a China Clothing Manufacturer for Made in China Apparel
Use a tiered checklist: capability match (category, materials), compliance (BSCI/WRAP, UFLPA risk controls), quality systems (AQL, lab testing), capacity and calendar fit, and transparent costing/MOQs. Run pilot sampling, factory audits, and reference checks before committing bulk. [MENTION: QIMA inspection frameworks; WRAP/BSCI recognition] [INTERNAL LINK: Factory audit checklist and supplier scorecard]
| Vetting Criteria | Questions to Ask | Evidence to Request |
|---|---|---|
| Category Capability | Which technical outerwear lines do you run? What seam sealing capacity per week? | Process photos, machine lists, sample references, defect logs |
| Compliance | Are you BSCI/WRAP certified? How do you manage UFLPA traceability? | Certificates, audit reports, chain-of-custody documentation |
| Quality Systems | What AQL levels do you apply? Which lab tests and testing partners? | SOPs, inspection reports, lab test results, corrective actions |
| Capacity & Calendar | What is monthly capacity by jacket type? Which blackout weeks? | Line plans, loading charts, seasonal calendars |
| Costing & MOQs | How are costs broken down? What MOQs for fabric and trims? | Open costing sheets, mill MOQ letters, trim vendor confirmations |
| Transparency | Can we review subcontractors and critical process partners? | Approved subcontractor list, NDA/IPA policy, escalation paths |
Capability & Compliance Screening
Start with category fit: down jackets, parkas, seam-sealed shells, and padded styles require different equipment and skill. Validate audits (BSCI, WRAP) and check whether OEKO-TEX 100 or facility-level STeP supports chemical safety. For cotton-rich goods shipped to the US, demand UFLPA traceability: yarn origin, spinning mill data, and transaction documents. [CITE: CBP UFLPA enforcement guidance 2024] [MENTION: CBP; OEKO-TEX] [INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability & Compliance Hub]
Sampling-to-Production Gates
Define gated progress: proto approval with measurement tolerances; size set fit; lab testing (hydrostatic head, seam strength, down-proofing, colorfastness); PP sample sign-off with trim boards; pilot run (50–200 pcs) to validate line balance and defect triggers; inline AQL inspections; final AQL and sealed carton checks. Missed gates warrant pause and corrective actions. [CITE: AQL 2.5/4.0 defect standards] [MENTION: QIMA; Intertek]
Supplier Scoring & Decision
Score on five criteria with weights: capability (30), compliance (20), quality systems (20), capacity/calendar (15), costing/transparency (15). Benchmark suppliers across the same spec and calendar. Pick two finalists; run PP + pilot to validate real performance before bulk. Document all decisions in a scorecard stored with audit/test artifacts. [CITE: Supplier scoring model examples] [MENTION: ISO 9001 frameworks; retailer sourcing scorecards]
Costs, MOQs & Lead Times for Made in China Apparel
Costs flex with fabric tech, membrane and seam sealing complexity, trim packages, and workmanship; MOQs track to mill and accessory constraints; lead times reflect calendar, lab testing, and logistics. Lock tech packs early, consolidate colorways, and line up testing to reduce volatility. [CITE: 2024 price movement reports for outerwear inputs] [MENTION: HKTDC; McKinsey]
| Category | Primary Cost Drivers | Typical MOQ | Lead-Time Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Shell (Seam-Sealed) | Membrane cost, seam tape usage, coated zippers, multi-layer bonding | Fabric 1,000–2,000 m; tape 5,000–10,000 m | 75–120 days (proto → bulk) |
| Down Jacket | Fill power, down-proof fabric, baffle construction, RDS down pricing | Shell fabric 1,000–2,500 m; down 300–800 kg | 85–130 days |
| Padded Jacket | Insulation grade, quilting lines, trim density, shell finish | Fabric 1,000–2,000 m; insulation 3,000–6,000 m | 70–110 days |
| Knitted Tops | Yarn count, dyeing/finishing, print/embellishments | Yarn 500–1,000 kg; fabric 1,000–2,000 m | 55–90 days |
- China remains a leading textile/apparel exporter — 2024 (Source: WTO) [CITE: WTO, World Trade Statistical Review 2024]
- Audit findings show chemical compliance gaps concentrate in finishing — 2024 (Source: QIMA) [CITE: QIMA Supply Chain Insights 2024]
- Brands maintain multi-country sourcing to balance risk and speed — 2024 (Source: McKinsey) [CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024]
Key Cost Drivers in Technical Apparel
Seam sealing adds time and consumables; membranes (PU, PTFE) shift pricing and performance; coated zippers and taped pockets raise material cost and handling. Down fill power (e.g., 650–800) drives price and thermal output; higher fill powers need stricter down-proof fabrics. Open costing should separate fabric, trims, labor, overhead, and margin for clarity. [CITE: Cost driver analysis for outerwear components] [MENTION: YKK zippers; OEKO-TEX chemical standards]
MOQ Strategies with Mills & Trim Suppliers
Consolidate colorways across styles, negotiate greige stock reservations, and select trims with flexible MOQs. Early BOM finalization helps mills align loom schedules and dye plans without long waits. Shared components across a capsule reduce purchase risk. Document vendor MOQ commitments in writing with roll-over clauses where possible. [CITE: Mill MOQ negotiation case studies] [MENTION: Major Asia mills; Hohenstein testing]
Lead-Time Compression Tactics
Parallelize lab testing with proto rounds, slot PP approval windows, and pre-book materials once lab “go” is reached. Run a pilot lot to catch defects while lines are fresh. Ship part-cargo by air for market-critical drops, balance with ocean for cost control. Reserve testing slots at external labs during sampling to avoid bottlenecks. [CITE: Logistics mode impact on lead times and cost] [MENTION: Maersk schedules; SGS labs] [INTERNAL LINK: Tech Pack & Calendar for outerwear]
Compliance Essentials for US & EU: UFLPA, REACH, PFAS, OEKO-TEX
Map origins and material inputs, maintain traceability records, and align chemical compliance to EU REACH and PFAS proposals with OEKO-TEX support. For US, apply UFLPA due diligence on cotton-rich goods. Build a testing plan and retain documentation before shipment. Requirements shift; confirm current notices with regulators. [CITE: CBP UFLPA enforcement updates 2024; ECHA PFAS proposal] [MENTION: CBP; ECHA]
| Regulation | Scope | Required Evidence | Responsible Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| UFLPA (US) | Cotton, yarn, textiles, any input with forced labor risk | Supply chain mapping, mill origin, transaction docs, affidavits | Sourcing Lead + Compliance Manager |
| EU REACH | SVHCs; Annex XVII restricted substances | Lab test reports, RSL compliance, SDS, supplier declarations | Compliance Manager |
| PFAS Proposal (EU) | Fluorinated DWRs and related chemistries | PFAS screening, finish declarations, alternative finish proof | R&D + Compliance |
| OEKO-TEX (Voluntary) | Product safety certification, facility STeP program | Certificates, test reports, audit summaries | Supplier + QA |
UFLPA Due Diligence for US Imports
Build chain-of-custody from cotton origin through yarn, fabric, and garment. Collect purchase orders, invoices, packing lists, bills of lading, mill certificates, and verifiable origin details. Maintain third-party verification where feasible. Keep a dossier per style to answer CBP queries. Pre-check suppliers for higher-risk inputs and switch materials where needed. [CITE: CBP Withhold Release guidance and documentation expectations] [MENTION: CBP; AAFA compliance notes]
EU REACH & PFAS Risks for Textiles
Screen against SVHC lists and Annex XVII. Plan for PFAS curbs by migrating to C0 or silicone-based DWR finishes and adjusting spec targets to realistic water repellency without persistent chemicals. Update RSLs and lab panels per season; retain certificates and SDS linked to BOMs. [CITE: ECHA PFAS restriction proposal and timeline] [MENTION: ECHA; OEKO-TEX Standard 100 updates]
OEKO-TEX & Voluntary Standards
OEKO-TEX 100 supports retailer acceptance and reduces re-test cycles. Facility-level STeP indicates structured chemical and environmental management. Pair certifications with your own test matrix to cover performance demands in technical outerwear beyond basic safety thresholds. [CITE: OEKO-TEX 2024 standard updates] [MENTION: OEKO-TEX; Hohenstein] [INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability & Compliance Hub]
How to Execute: From Tech Pack to On-Time Delivery
Build a calendar with gated steps: tech pack finalization, proto rounds, lab tests, PP sign-off, pilot run, bulk production, inline inspections, and shipment. Tie each step to inputs, outputs, and dates; define pause criteria to keep quality and timing on track. [CITE: Production calendar best practices in apparel] [MENTION: QIMA; ISO 9001]
- Finalize tech pack: BOM, measurement charts, tolerances, stitch/seam specs, test plan.
- Run proto and fit: capture comments with photos and confirmed changes.
- Book labs: design test matrix aligned to materials and category targets.
- Approve PP sample: trim board sign-off, labeling, country-of-origin tagging.
- Pilot run: validate line balance, seam sealing parameters, and defect thresholds.
- Bulk: inline AQL and corrective actions tracked to a shared register.
- Final AQL and sealed carton checks: confirm measurements and labeling.
- Ship with documentation: test reports, audit artifacts, and compliance dossiers.
Preparation: Tech Pack & Material Booking
Complete BOMs with material codes, finish declarations, zipper specs, tape types, and labeling. Define measurement tolerances per point-of-measure. Book greige and trims once lab “go” is reached. Document every change with version control to avoid mismatch between samples and bulk. [CITE: Impact of tech pack completeness on defect rates] [MENTION: PLM systems; YKK]
Execution Steps: Samples, Tests, PP & Pilot Run
Target lab tests for hydrostatic head, MVTR, seam strength, seam tape adhesion, down-proof tests, colorfastness, and pilling/abrasion where relevant. Approve PP with sealed trims and labels. Pilot run exposes real-world defects before full loading. Record settings for seam sealing—temperature, pressure, dwell time—to maintain consistency. [CITE: Apparel lab test protocols and method references] [MENTION: SGS; Intertek]
Quality Assurance: Inline & Final AQL
Use AQL 2.5 for major defects and AQL 4.0 for minor unless brand policy differs. Inline inspections at 10–20% completion catch issues early; final inspection validates measurement and labeling. Keep defect triggers and corrective actions visible across teams. [CITE: AQL sampling tables and acceptance criteria] [MENTION: QIMA; ISO 2859]
Market Data & Sourcing Trends (2024–2025)
China remains a leading textile exporter with demand for quick-turn technical categories. Brands diversify across China, Bangladesh, and Vietnam, using China for development and trims while balancing production regionally. Compliance and chemical rules shape material choices and timelines. [CITE: WTO export statistics 2024; QIMA audit trends; McKinsey sourcing insights] [MENTION: WTO; HKTDC]
Export & Demand Signals
Export values show consistent leadership with shifts toward performance categories. Retailers adjust model counts and colorways to align with inventory targets and compliance needs. Outerwear remains resilient where functionality matters. Brands that lock development in China keep calendar speed, then scale production where capacity and price favor the assortment. [CITE: WTO and HKTDC Research 2024] [MENTION: HKTDC; McKinsey]
Sourcing Diversification & Nearshoring
Diversification mitigates regulatory and logistics risk. US brands weigh UFLPA exposure on cotton inputs and switch blends or origin as needed. EU buyers model PFAS timelines and update finishes. Nearshoring helps basics; technical jackets stay anchored to regions with skill and materials. [CITE: Regional nearshoring case studies 2024] [MENTION: AAFA; ECHA]
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service links design development, lab testing, and compliant production across China and Bangladesh. The workflow maps buyer needs to factory steps with gated approvals so outerwear hits performance and schedule targets. Get started with OEM/ODM. [MENTION: Eton Garment Limited case experience] [INTERNAL LINK: Contact Eton — book a sourcing consult]
| Buyer Need | OEM/ODM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Fast technical parka development | Rapid proto rounds, lab test booking, PP sign-off gates | Calendar speed with performance validated |
| Scale padded jackets across seasons | China dev + Bangladesh bulk; shared SOPs | Price leverage with consistent quality |
| Compliance-first documentation | UFLPA dossiers, REACH/PFAS test mapping, OEKO-TEX support | Import-ready files with traceability |
| Transparent costing | Open cost sheets, MOQ plans, trim consolidation | Predictable budgets and fewer surprises |
Use Case 1: Technical Parka—Speed with Compliance
Brand brief: 15K mm water column, 8K g/m²/24h breathability, seam-sealed construction, PFAS-free DWR, US and EU rollout. Eton runs two proto rounds, books labs early, calibrates seam tape parameters, and locks PP within three weeks. Compliance files include test reports and labeling proof, ready before shipment. [CITE: Performance targets and lab method references] [MENTION: ECHA PFAS context; OEKO-TEX]
Use Case 2: Padded Jackets—Scale Across Seasons
Assortment spans entry price points and mid-tier designs. Development sits in China to finalize shell finish and trims. Bulk moves to Bangladesh for volume runs under shared AQL and SOPs. Inline inspection data flows to one dashboard; final AQL, labeling, and documentation ship with cartons. [CITE: Regional capacity and cost data] [MENTION: BGMEA; QIMA]
Risks, Compliance & Localization for US & EU
Identify risks—forced labor, chemical restrictions, IP, labeling—and rank likelihood and impact. Tie mitigations to documentation, testing, and calendar gates for both US and EU markets. Maintain a living risk register that updates with regulatory changes. [CITE: Retail risk management studies 2024] [MENTION: CBP; ECHA]
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| UFLPA documentation gaps | Medium–High | High (detentions, delays) | Dossier per style; chain-of-custody mapping; third-party verification |
| PFAS finish non-compliance | Medium | Medium–High | Switch to PFAS-free DWR; lab screening; update RSLs |
| AQL quality failures | Medium | Medium | Inline inspections; pilot runs; corrective action tracking |
| Labeling/COO errors | Low–Medium | Medium | Labeling SOP; PP label sign-off; COO rules review |
| IP leakage | Low–Medium | Medium | NDA/IPA controls; approved subcontractor lists; restricted access |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
US: Prepare UFLPA evidence with full transaction chains for cotton-rich goods; confirm care labeling and fiber content rules. EU: Align REACH Annex XVII and SVHC checks; plan PFAS changes; validate labeling rules including language and fiber declarations. Keep all certifications and lab reports ready for audits. [CITE: EU REACH and care labeling rules; US fiber content labeling]
Conclusion & Next Steps
Made in China apparel delivers when vendor selection is strict, compliance is documented, and QA/testing gates are respected. Use the checklist, lock your calendar, and blend China development with Bangladesh scale where it fits your line. To move, align a pilot program, validate SOPs, and confirm documentation before booking bulk. [INTERNAL LINK: Contact Eton — book a sourcing consult]

Author: Senior Sourcing & Production Lead, 15+ years in outerwear; China/Bangladesh factory experience.
Reviewer: Compliance & QA Manager, Eton Garment Limited.
Methodology: Combined Eton first-hand SOPs with authoritative sources and 2024–2025 industry data.
Limitations: Cost/MOQ/lead-time ranges vary by design, season, and supplier; regulations update frequently—confirm latest agency guidance.
Disclosure: Eton provides OEM/ODM services referenced herein.
Last Updated: 2025-10-28

- WTO — World Trade Statistical Review 2024 (2024). https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/statis_e/wts2024_e/wts24_toc_e.htm
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024 (2024). https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights/state-of-fashion
- QIMA — Supply Chain Insights/Barometer 2024 (2024). https://www.qima.com/quality-control-insights
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection — Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) (2024). https://www.cbp.gov/trade/forced-labor/UFLPA
- European Chemicals Agency — PFAS Restriction Proposal (2023–2024). https://echa.europa.eu/registry-of-clh-intentions-reach
- OEKO-TEX — Standard 100 Updates (2024). https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/news/press-releases
- HKTDC Research — Textiles and Clothing Industry in China (2024). https://research.hktdc.com/
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

