Knitwear Suppliers: How to Source Quality with a China Clothing Manufacturer
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
15 minute read
Knitwear Suppliers: How to Source Quality with a China Clothing Manufacturer
Knitwear suppliers shape quality, cost, and speed for sweaters, cardigans, knit dresses, and performance layers. Brands seeking a China Clothing Manufacturer can move from concept to production by locking yarn specs, verifying gauge and finishing, mapping US/EU compliance, and working with OEM/ODM partners that scale pilots into dependable volume without losing handfeel or silhouette.
Knitwear suppliers convert yarn into garments through knitting, linking, and finishing with tight QC. Define yarn, gauge, fit, and tests up front, compare regions, validate samples to AQL, and choose an OEM/ODM China Clothing Manufacturer with yarn lot control, linking quality, compliance credentials, and transparent lead times for US/EU programs.
What a Knitwear Supplier Actually Does (and Why It Matters)
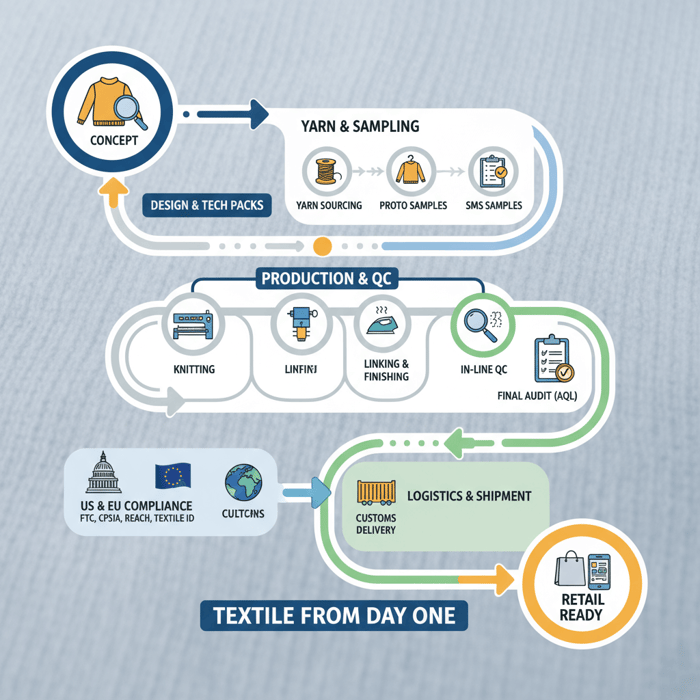
A knitwear supplier turns yarn into finished garments through knitting, linking, washing, finishing, and quality control. The supplier’s capabilities determine silhouette accuracy, handfeel, durability, and consistency across colorways and lots. Align the product type—fully-fashioned, cut-and-sew, or seamless—with the brand’s fit intent, price point, and delivery window.
Types of Knitwear (Fully-Fashioned, Cut-and-Sew, Seamless)
Fully-fashioned knitwear shapes panels on the machine, minimizing seams and improving drape. Linking joins panels at the stitch level for cleaner lines and better comfort. Cost sits above cut-and-sew but below premium seamless routes. Cut-and-sew relies on yardage knitted in rolls, then cut with patterns and sewn; it suits relaxed silhouettes and value tiers with simpler construction. Seamless knitting uses specialized machinery to create near-complete garments in one run, reducing cut waste and some linking work, often appealing for premium or performance layers where smooth interior lines matter.
Fit, cost, and lead time shift with each type. Fully-fashioned balances silhouette control and price. Cut-and-sew moves quicker where knitting yardage is abundant but may need more finishing to achieve target handfeel. Seamless adds machinery constraints and learning curves; sampling rounds can run longer and MOQs trend higher with select machines.
Yarns, Gauges, and Machinery
Yarn choice drives handfeel, warmth, and pilling resistance. Common fibers include cotton, wool, cashmere, viscose, modal, nylon, polyester, and blends with recycled content. Gauge defines stitches per inch and governs fabric density and drape. 3–5 gg deliver chunky sweaters; 7–12 gg sit in midweight territory; 12–16 gg push toward finer fashion or performance layers. Yarn count, twist, and ply influence stability, shrinkage, and fuzzing. Machinery spans flatbed knitting for fully-fashioned, circular knitting for yardage, and seamless machines for integral garments.
Align gauge with silhouette: oversized fishermen looks need coarse gauge; tailored cardigans suit mid-fine gauge; performance first layers often sit closer to fine gauge with stable blends. Shift yarn finishes—enzyme, softener, steam relax—to reach target handfeel without oversoftening that risks growth or shrink anomalies.
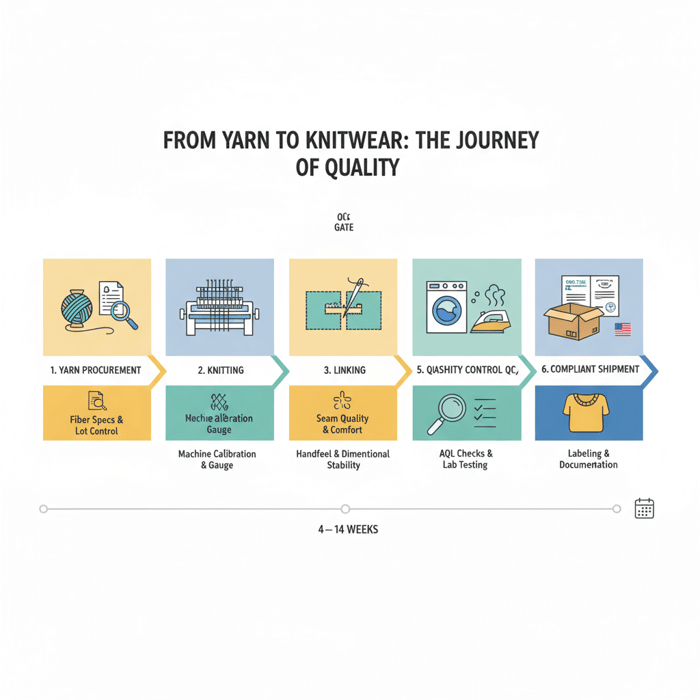
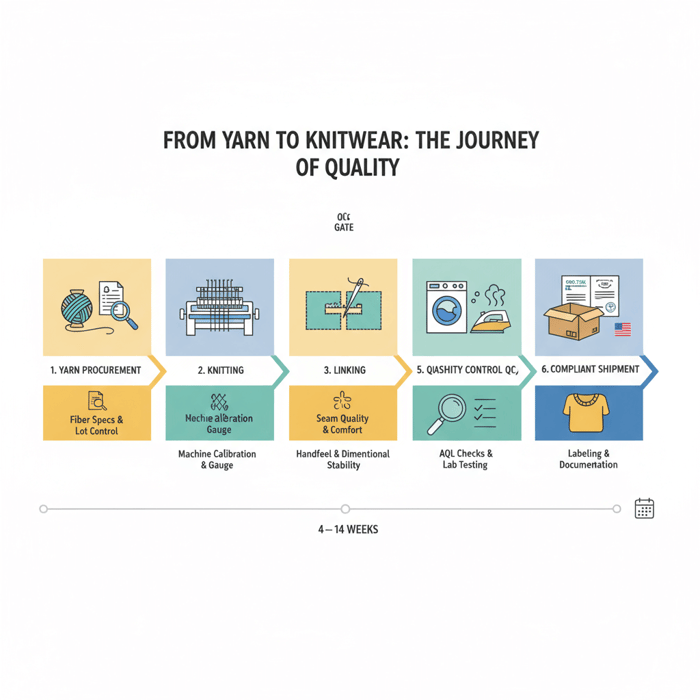
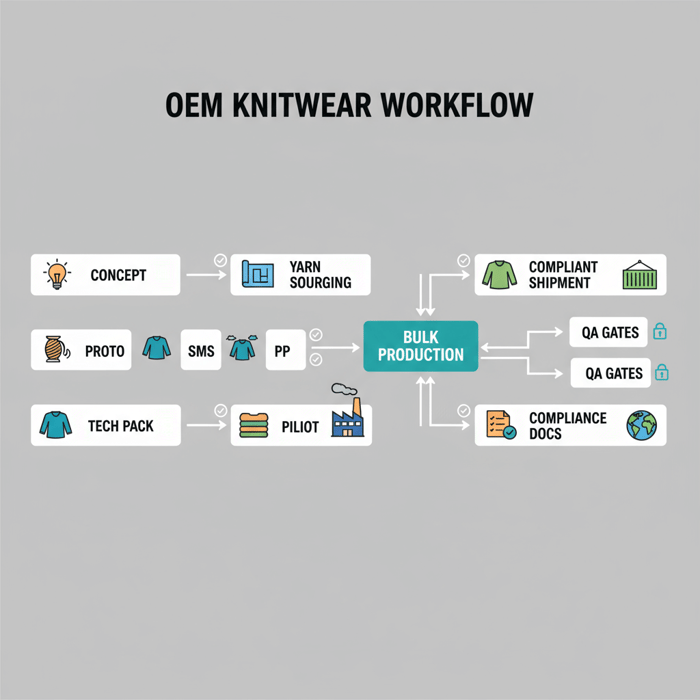
How to Source Knitwear Suppliers: A Step-by-Step Framework
Use a six-step workflow to move from concepts to reliable capacity: define specs, shortlist regions, vet compliance, request samples, run QC, pilot, then lock capacity. Track cost, lead time, and quality thresholds at each gate. Include buffers for yarn procurement and finishing slots to avoid calendar slip.
Preparation (Tech Packs, Yarn Specs, Fit Blocks)
Tech packs should lock silhouettes, measurements, tolerances, construction details, and finishing targets. Document yarn decisions with fiber content, count, ply, twist, dye method, finish, and performance expectations. Add gauge targets and measurement diagrams for key points of measure. Establish fit blocks and grade rules with size charts aligned to US or EU standards; track separate blocks for men, women, and kids. State test protocols—AATCC and ISO references for colorfastness, shrinkage, pilling, dimensional stability, and seam strength—so the supplier plans yarn and finishing accordingly. [MENTION: AATCC testing methods], [MENTION: ISO textile test standards].
Define packaging and labeling early to avoid rework. For US, plan FTC Textile Rules and CPSIA if children’s wear applies. For EU, plan Textile Labelling Regulation (EU No 1007/2011) and REACH documents. Include fiber disclosure, care labels, and tracking labels for kids’ products with batch references. [CITE: FTC Textile Labeling Rules (2023)], [CITE: EU No 1007/2011 labeling text], [CITE: CPSIA for children’s apparel], [CITE: REACH SVHC guidance].
Execution Steps (Shortlisting, Sampling, Pilot, PO)
- Shortlist regions: align price, speed, and capability across China, Bangladesh, Turkey, Italy. Add knitwear suppliers that match yarn and gauge plans.
- Compliance vetting: request certificates (OEKO-TEX, BSCI, WRAP, GRS), audit summaries, and testing lab reports. [MENTION: OEKO-TEX], [MENTION: amfori BSCI], [MENTION: WRAP], [MENTION: GRS].
- Sample request: ask for two rounds—proto for silhouette and handfeel, then SMS for final construction. Set pass criteria for measurements, shrinkage, pilling, and colorfastness.
- Costing and lead time: lock yarn sourcing timelines, knitting schedules, and finishing windows; capture trims and packaging.
- Pilot: approve PP samples, track first-article inspections, and tighten tolerances on shrinkage and growth.
- PO and capacity lock: confirm knit slots and finishing lines; secure booking for rolling drops if the program spans multiple delivery windows.
Plan a yarn buffer. Spun-dyed or specialty blends may require longer procurement windows and color approval cycles. Add lab dips, handfeel targets, and bulk verification steps to keep SMS and PP aligned to production realities.
Quality Assurance (AQL, Test Protocols, Colorfastness)
Create an AQL plan with sampling levels that match product risk. Define tests: colorfastness to washing and crocking under AATCC or ISO methods, dimensional stability and skew, pilling resistance (Martindale or ICI), seam and linking strength, and appearance after laundering. Align shrinkage tolerances with care label claims; avoid mismatch between lab results and washing instructions. [CITE: AATCC test method suite], [CITE: ISO textile testing references].
QC checkpoints: incoming yarn lot checks for count and twist consistency; in-line knitting reviews for gauge and tension; linking audits for seam neatness; finishing room checks for wash, steam, or tumble routines; final inspection for measurements and visual defects; carton checks for labeling accuracy. Record each gate with pass/fail outcomes. Quality control in apparel manufacturing overview.
Evaluating Knitwear Suppliers: Scorecard, Questions, and Red Flags
Use a weighted scorecard to compare knitwear suppliers across yarn control, gauge consistency, linking and finishing quality, QA systems, compliance maturity, capacity, lead time, and communication. Ask targeted questions during audits and screening. Block suppliers that show opaque costs, inconsistent shrinkage tests, or incomplete documentation.
Supplier Scorecard (Criteria + Weights)
| Criterion | Weight | What Good Looks Like | Pass Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yarn lot control | 15% | Lot tracking, tests for count/twist, shade variance limits | ≥80/100 |
| Gauge and tension consistency | 12% | Machine calibration logs, stable handfeel across sizes | ≥80/100 |
| Linking quality | 10% | Clean seams, no needle marks, even stitch density | ≥75/100 |
| Finishing control | 10% | Defined wash/steam routines; shrinkage within spec | ≥80/100 |
| QA/QC system | 12% | AQL plans; lab test integration; inline audits | ≥80/100 |
| Compliance maturity | 12% | OEKO-TEX, BSCI/WRAP, GRS; US/EU labeling fluency | ≥80/100 |
| Capacity and lead time | 12% | Realistic slots; transparent yarn procurement timelines | ≥75/100 |
| Communication and documentation | 9% | Clear tech pack feedback; test reports; route maps | ≥75/100 |
| Cost transparency | 8% | Breakdown: yarn, knitting, linking, washing, trims | ≥75/100 |
Use a go/no-go threshold at 78–82 average. Run a pilot before scaling any supplier above the threshold so you validate line stability with real production conditions.
Due Diligence Questions & Red Flags
- How do you manage yarn lots across multiple POs? Show shade band and count/twist logs.
- What gauges and machines cover our silhouettes? Provide calibration records and daily tension checks.
- Which finishing routines achieve our handfeel and shrink targets? Share SOPs and bulk test data.
- What AATCC/ISO tests are standard? Name the labs and provide recent reports.
- Which certifications are current? Send OEKO-TEX, BSCI/WRAP, GRS, and REACH declarations. [CITE: OEKO-TEX registry], [CITE: amfori BSCI], [CITE: WRAP], [CITE: GRS program].
- What is your typical MOQ and lead time for our yarns and gauges? Split yarn procurement vs. production windows.
- Red flag: inconsistent shrinkage tests between SMS and bulk.
- Red flag: no lab dips or shade control when dyeing varies by mill.
- Red flag: incomplete labeling knowledge for US FTC or EU No 1007/2011.
- Red flag: opaque costing where yarn and finishing are bundled without detail.
Knitwear sourcing toolkit with audit templates. Include a simple email template for screening: request gauges, yarn experience, lead-time ranges, MOQ bands, certifications, lab partners, and three client references aligned to US/EU retail calendars.
Sample & Pilot Validation
Acceptance criteria should track measurements, shrinkage, growth, pilling, colorfastness, seam/linking strength, and appearance after wash. Record each test with target values and tolerances, then approve PP and pilot lots only when SMS and PP echo the bulk plan. Capture production notes to inform care labels and customer claims. Quality control in apparel manufacturing.
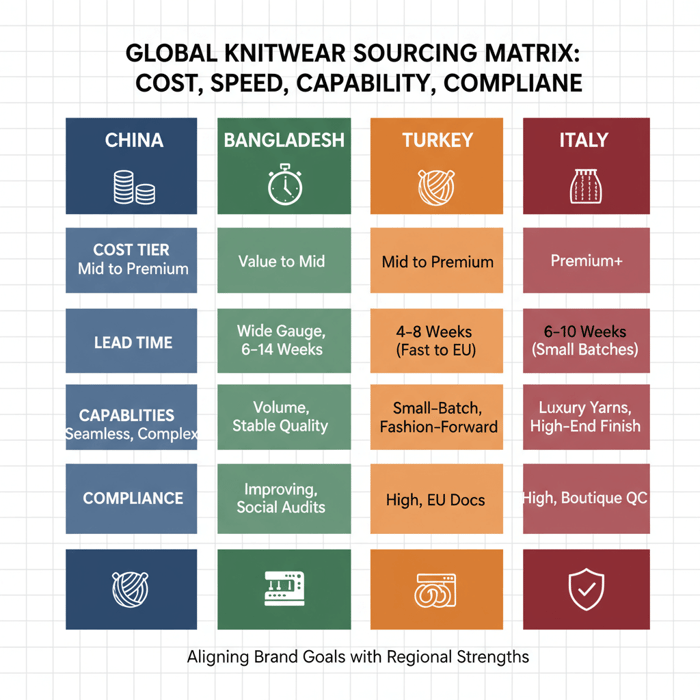
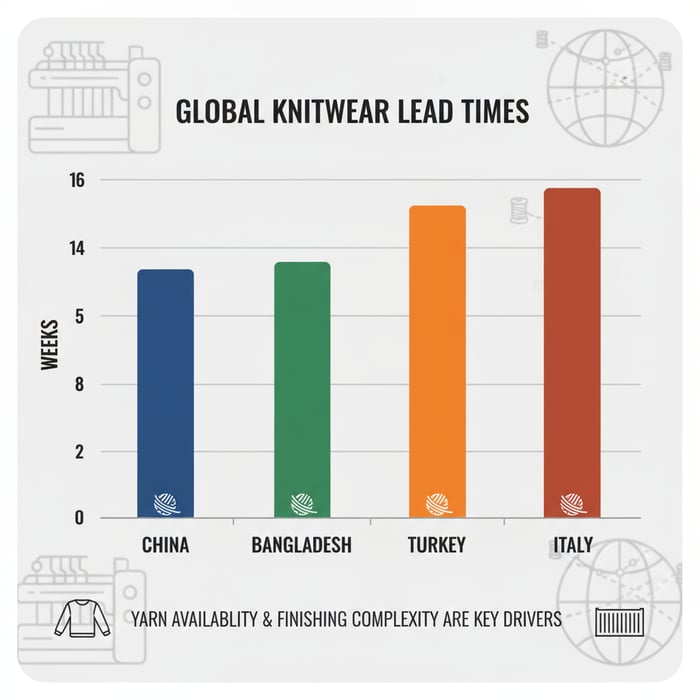
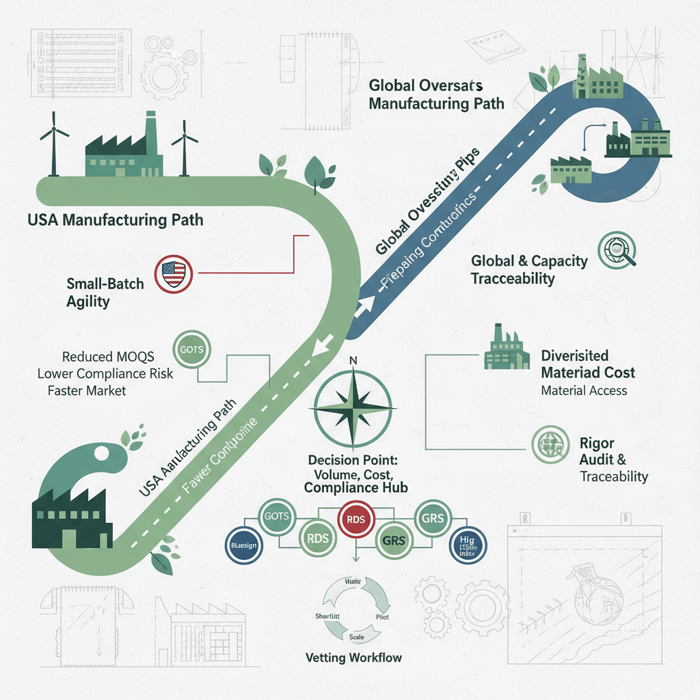
Knitwear Suppliers by Region: China vs. Bangladesh vs. Turkey vs. Italy
Regions differ on capability, cost, lead time, and compliance maturity. China delivers scale and technical breadth. Bangladesh provides strong value and volume. Turkey offers speed to Europe with flexible MOQs. Italy focuses on premium craftsmanship and sophisticated yarns. Choose the region that matches price architecture and calendar demands.
Criteria Overview (Cost, Lead-Time, Capabilities, Compliance)
| Region | Cost Tier | Typical Lead Time | Capabilities | Compliance Maturity | MOQ Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Mid to Premium | 6–12 weeks (yarn-dependent) | Wide gauge coverage, complex linking, seamless options | High, broad certifications | 300–1,000+ per style |
| Bangladesh | Value to Mid | 8–14 weeks | Volume programs, stable quality with clear SOPs | Improving, strong social audit adoption | 600–2,000+ per style |
| Turkey | Mid to Premium | 4–8 weeks (fast to EU) | Small-batch agility, fashion-forward details | High, strong EU documentation fluency | 150–600 per style |
| Italy | Premium+ | 6–10 weeks (small batches common) | Luxury yarns, high-end finishing, seamless expertise | High, boutique-quality controls | 50–300 per style |
- China remains the largest exporter of textiles/clothing — 2024 (Source: WTO) [CITE: WTO World Trade Statistical Review 2024].
- Brands pursue resilient sourcing and nearshoring for speed — 2024 (Source: McKinsey) [CITE: The State of Fashion 2024].
Decision Framework (Brand Goals → Best-Fit Region)
| Brand Goal | Recommended Region | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Premium handfeel, fine gauges | Italy or China | Access to luxury yarns and advanced finishing |
| Fast turn to EU | Turkey | Proximity, flexible MOQs, rapid knitting and finishing |
| Value volume | Bangladesh | Competitive cost with growing compliance frameworks |
| Balanced cost, complex construction | China | Technical breadth, stable finishing, integrated testing |
US & EU Compliance for Knitwear Suppliers: What to Require up Front
Require labeling compliance for US and EU, chemical and product safety documentation, and factory standards. Bake tests and paperwork into contracts. Track lab partners and certificate validity windows to keep approvals moving.
Labeling Rules (US FTC; EU Textile Labelling)
- US FTC Textile Rules: fiber content, manufacturer identity, country of origin, care instructions. Keep labels durable and legible, with kids’ items tracking per CPSIA. [CITE: FTC Textile Labeling Rules (2023)].
- EU Textile Labelling Regulation (EU No 1007/2011): standardized fiber names, tolerance, and language requirements. Ensure labels match component content and sizes. [CITE: EU No 1007/2011].
- Country of origin guidance: coordinate with customs brokers for US and EU import declarations. [CITE: Official customs guidance].
Chemical & Safety (REACH, CPSIA, Prop 65)
- REACH: SVHC disclosure and restricted substance management; set supplier declarations and test plans per article type. [CITE: ECHA SVHC list 2024].
- CPSIA: children’s knitwear needs tracking labels, small parts rules, and lead and phthalate limits. [CITE: CPSC CPSIA site].
- Prop 65: California warning requirements when listed chemicals exceed thresholds. [CITE: OEHHA Prop 65 list].
Use labeled citations in contracts: “Test to AATCC/ISO for colorfastness and dimensional stability; provide REACH declarations; CPSIA documents for kids’ styles.” Keep renewal schedules for certificates and rerun key tests before peak seasons.
Social & Environmental (OEKO-TEX, BSCI, WRAP, GRS)
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100: material-level safety coverage; confirm scope and article classes. It does not replace REACH but signals safer inputs. [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 overview].
- BSCI and WRAP: social audit frameworks; request full reports and corrective action visibility. [CITE: amfori BSCI], [CITE: WRAP].
- GRS: recycled content chain-of-custody; match claims on labels and marketing with certified inputs. [CITE: Textile Exchange GRS].
Place compliance mapping in onboarding checklists and supplier scorecards. Build a documentation vault with certificates, test reports, and labeling proofs so US/EU customs clearance stays smooth.
Data & Trends: Knitwear Demand, Sustainability, and Digital Product Passport
Knitwear holds demand as comfort and performance converge, while recycled fibers and traceability grow in share. EU policy work on Digital Product Passport raises documentation and transparency needs, adding data capture and label considerations for future compliance.
- EU strategies emphasize transparency and circularity — 2022–2024 (Source: European Commission) [CITE: EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles; CSRD guidance].
- US enforcement reminders for textile labeling — 2023 (Source: FTC) [CITE: FTC enforcement notes].
Key Trend 1: Comfort/Performance and Recycled Fibers
Collections blend soft handfeels with stability for sweaters and layers that travel from office to outdoors. Recycled polyester, nylon, and cotton enter more ranges with chain-of-custody claims backed by certifications. Pilling and shrink controls become more central for these blends. Align yarn choices with pilling targets and lab test repeatability to keep customer returns low. [CITE: Industry report on recycled fiber adoption], [MENTION: Textile Exchange guidance].
Key Trend 2: Traceability, DPP, and Documentation
DPP initiatives push brands to capture product-level data across inputs, processing, and finishing. Knitwear suppliers that manage yarn lot records, testing logs, and label proofs prepare brands for rising transparency demands. Build templates for data fields and batch IDs so product records flow into future digital passports without manual scrambles. [CITE: EU DPP policy notes], [MENTION: GS1 application in apparel traceability].
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service converts knitwear concepts into production with design support, yarn sourcing, sample development, pilot, compliance testing, and scalable manufacturing in China and Bangladesh. Programs move from proto to SMS, PP, pilot, and bulk with documented QA and compliance gates that match US/EU needs.
| Brand Need | OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Yarn consistency | Lot management and incoming tests | Stable handfeel across sizes and colors |
| Compliance documents | Integrated testing pack and certificate tracking | Faster approvals and smoother customs |
| Fit precision | Pattern alignment and gauge calibration | Fewer revisions; cleaner silhouettes |
| Cost clarity | Open costing: yarn, knitting, linking, finishing, trims | Transparency for margin planning |
| Speed to market | China/Bangladesh capacity planning and booking | On-time delivery against retail calendars |
Use Case 1: Small-Batch Capsule → Fast Turn
For a capsule of 150–400 units per style, define fine or mid gauges with compact trims, then slot production in China or Turkey partners through Eton’s network. SMS and PP pass with tight shrink tolerances and colorfastness to washing and crocking. DPP-ready documentation collects yarn lot IDs and testing logs. OEM/ODM apparel development services.
Use Case 2: Volume Program → Cost & Compliance
For 600–2,000+ units per style, shift volume to Bangladesh with clear linking and finishing SOPs. Costing captures yarn price volatility and buffer windows for dyeing. Compliance packages include REACH declarations, CPSIA for kids, and OEKO-TEX Standard 100 on inputs. Pilot runs stabilize line outputs before committing rollouts. Anchor the program with Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service for controlled execution.
Risks, Compliance & Localization
Top risks include yarn variability, shrinkage or growth beyond tolerance, pilling, labeling errors, and scheduling slips. Mitigate with pre-approved yarns, test plans, buffered lead times, and region-specific compliance checks for US and EU. Keep records per PO and style to support audits and future DPP needs.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yarn lot shade variance | Medium | High | Shade bands, lab dips, lot tracking, sample pulls |
| Shrinkage outside tolerance | Medium | High | Finish SOPs, pre-wash protocols, AATCC/ISO testing |
| Pilling above target | Medium | Medium | Fiber blend selection, twist/ply controls, pilling tests |
| Label noncompliance | Low–Medium | High | US FTC and EU label reviews, care validation, CPSIA tracking |
| Schedule slips | Medium | High | Yarn buffer, finishing slot reservations, pilot timing |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
US programs need correct fiber disclosure, care labels aligned to performance claims, and CPSIA requirements when applicable. EU programs need Textile Labelling compliance and REACH paperwork. Track Prop 65 warnings for California sales. Keep logs for testing and certificates so customs clearance aligns with documents. [CITE: FTC Textile Rules], [CITE: CPSIA], [CITE: Prop 65], [CITE: REACH].
Conclusion & Next Steps
Define yarn and gauge specs, validate finishing, map US/EU compliance, and choose knitwear suppliers that pass scorecard thresholds with controlled pilots. Use the regional matrix to pick China, Bangladesh, Turkey, or Italy based on price and speed. Move concepts into volume through Eton’s OEM pathway for fit, handfeel, and compliance that hold in real production.
Knitwear sourcing toolkit, Compliance checklist, Supplier scorecard template. For author credibility and factory notes, see Eton Yip — Founder & CEO — Author bio page.
- World Trade Organization — World Trade Statistical Review (2024). https://www.wto.org/ [CITE: WTO 2024 trade data].
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion (2024). https://www.mckinsey.com/ [CITE: Sourcing resilience and nearshoring trends].
- US Federal Trade Commission — Textile Labeling Rules & Guides (2023). https://www.ftc.gov/ [CITE: US labeling requirements].
- European Commission — Textile Labelling Regulation (EU No 1007/2011) and CSRD guidance (2022–2024). https://ec.europa.eu/ [CITE: EU labeling and sustainability strategy].
- OEKO-TEX — Standard 100 program. https://www.oeko-tex.com/ [CITE: Input safety coverage and certificate scope].
- amfori BSCI — Social compliance framework. https://www.amfori.org/ [CITE: Audit guidance].
- WRAP — Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production. https://wrapcompliance.org/ [CITE: Factory compliance standards].
- Textile Exchange — Global Recycled Standard. https://textileexchange.org/ [CITE: Chain-of-custody for recycled content].
- AATCC — Textile test methods. https://www.aatcc.org/ [CITE: Colorfastness, pilling, dimensional stability tests].
- ISO — Textile testing standards. https://www.iso.org/ [CITE: International test protocols].
- CPSC — CPSIA guidance for children’s apparel. https://www.cpsc.gov/ [CITE: Lead, phthalates, tracking labels].
- ECHA — REACH SVHC list and guidance. https://echa.europa.eu/ [CITE: Chemical restrictions and declarations].
- OEHHA — Proposition 65 list. https://oehha.ca.gov/ [CITE: Warning requirements for California].
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

