Homemade Tee Shirts vs Pro Production: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Guide for Scaling Quality and Compliance

 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
17 minute read
Homemade Tee Shirts vs Pro Production: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Guide for Scaling Quality and Compliance
Homemade tee shirts help brands test ideas fast, but a China Clothing Manufacturer delivers repeatable quality, cost control, and compliance when scale arrives. Brands in the US and EU often begin with DIY t-shirt printing for micro-drops and move to OEM once demand stabilizes. This guide maps definitions, costs, standards, and a clear transition path, grounded in Eton’s factory experience across China and Bangladesh.
Homemade tee shirts suit prototypes and small drops. Professional OEM production suits retail-grade quality, predictable costs, and compliance at scale. As volumes pass 100–300 units per style, OEM typically wins on unit cost, durability, and traceability. Use DIY for validation; shift to a vetted China Clothing Manufacturer for bulk.

What “Homemade Tee Shirts” Really Mean for Fashion Brands
Homemade tee shirts are low-volume garments produced in-house or by micro-setups using heat transfer vinyl (HTV), direct-to-garment (DTG), sublimation, or basic screen printing. Brands use them to prototype fits and graphics, validate demand, and serve events or community releases. Retail programs need repeatability, stable specs, and compliance checks that home setups rarely cover.
For brands, “homemade” includes basement studios, small workshops, and print-on-demand services that ship one-off orders. POD is not always the same as homemade tee shirts; it sits between DIY and professional production, offering externalized printing with minimal control over fabric spec and testing. Many teams bring DIY samples to Eton for pro replication, and recurring gaps appear: variable fabric weight, uncontrolled shrinkage, and neck shape drift between batches.
[MENTION: Printful and Teespring POD offerings] address speed and simplicity, while traditional screen shops offer stronger hand-feel and color consistency. Neither guarantees full-chain compliance for US/EU retail unless materials and labels are specified and verified.

Core DIY Methods and What They Deliver
DIY t-shirt printing spans several practical methods:
- HTV (Heat Transfer Vinyl) — Pros: low setup cost, fast protos, easy personalization. Cons: thicker hand-feel, potential edge lift over washes, limited fine detail. Typical volumes: 1–50 units per design. Best for: event merch and names/numbers.
- DTG (Direct-to-Garment) — Pros: full-color prints without screens, good for complex artworks and small runs. Cons: pre-treatment and fabric quality sensitive, wash-fastness varies by ink/fabric pairing. Typical volumes: 1–200 units. Best for: photo prints and micro-drops.
- Sublimation — Pros: vibrant, permanent on polyester blends, no hand on the print. Cons: requires polyester-rich fabric, color shift risk on non-white bases. Typical volumes: 1–200 units. Best for: performance tees and all-over graphics.
- Home Screen Printing — Pros: durable when cured well, strong opacity, cost-effective beyond 50–100 units. Cons: setup time, requires space and repeatable process control. Typical volumes: 20–500 units depending on tooling. Best for: solid spot-color graphics.
Experienced DIY teams add finishing touches like neck taping, woven labels, and swing tags by hand. Consistency depends on operator skill, fixtures, and the stability of blanks. Good basics (ringspun cotton, pre-shrunk finishing) raise success rates even at home.
Where DIY Shines—and Where It Breaks
DIY shines when:
- Design validation matters more than unit margin.
- Lead time is one to five days.
- Personalization or hyper-local demand calls for tiny batches.
- Event merch or limited community drops need fast turn.
DIY breaks when:
- Unit costs must hold under wholesale pricing.
- Fit, fabric GSM, shrinkage, and color matching must repeat season to season.
- US/EU compliance requirements need labels, chemical tests, and flammability checks.
- MOQ efficiency and freight consolidation drive margins.
Retail acceptance builds on durable specs. Eton teams often see neck rib distortion, uneven shrinkage, and ink cracking under repeat washes in homemade tee shirts. These are solvable with better fabrics, pre-wash finishing, controlled curing, and standard wash tests.
[CITE: A lab protocol from an accredited testing body on colorfastness and shrinkage] helps brands set baselines that home methods cannot easily verify at volume.
[INTERNAL LINK: OEM vs ODM explained → Cluster guide page idea]
Homemade Tee Shirts vs Professional Production: Cost, Quality, and Risk
DIY wins at tiny volumes and speed. OEM wins on cost-per-unit, durability, and compliance past roughly 100–300 units per style, depending on spec and method. As volumes rise, repeatable QC and documented materials lift customer satisfaction and retailer acceptance.
- Brands face rising pressure for traceable supply chains — 2024 (Source: [CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024]).
- Certification adoption and material transparency are rising — 2024 (Source: [CITE: Textile Exchange Material Change Insights 2024]).
- US/EU marketplaces apply stricter product integrity rules — 2023–2025 (Source: [CITE: EU GPSR, CPSC guidance]).
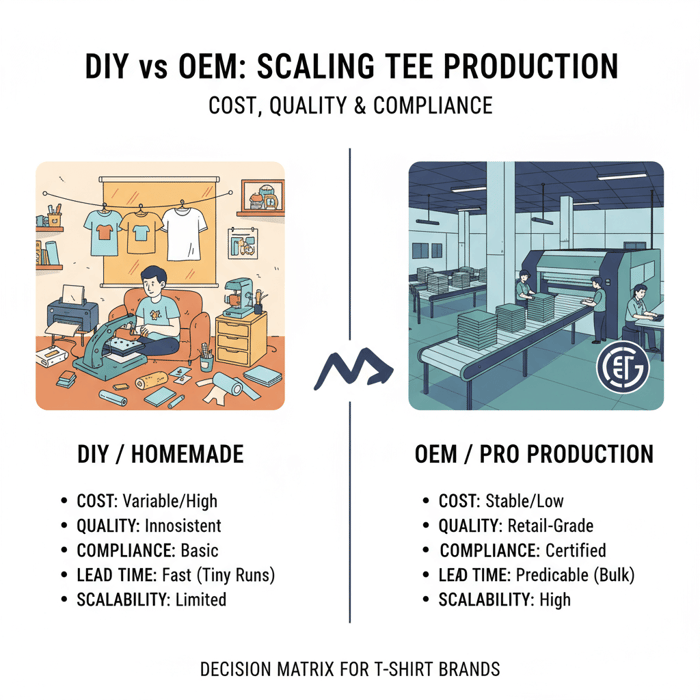
Cost & Volume Break-Even
Unit cost drivers include fabric, print method, labor time, wastage, packaging, shipping, and overhead. DIY bears higher labor minutes per unit, inconsistent wastage, and little freight efficiency. OEM amortizes setup, secures material pricing, and compresses QC time per unit.
- DIY at 1–50 units: higher total labor per shirt, retail blanks priced near consumer levels, limited economies of scale.
- DIY at 50–200 units: screen printing improves cost per unit but requires setup; DTG holds for complex art but ink costs accumulate.
- OEM at 100–300 units: fabric sourcing and finishing stabilize costs; print lines increase throughput; labels and packing standardize.
- OEM at 300–1000+ units: volume discounts compound; freight consolidation lowers per-unit shipping; QC scales with sampling plans.
Break-even moves with spec. Single-color screen prints with midweight cotton often cross at 150–200 units. Full-color DTG on premium ringspun cotton might cross closer to 100–150 units. All-over sublimation on polyester may stay with specialized vendors unless a factory line is set for that method.
[CITE: A comparative cost model from an apparel sourcing analysis, 2023–2024] can validate ranges by region. [MENTION: American Apparel & Footwear Association] offers context for cost structures and compliance tasks.
Quality & Compliance Implications
Quality lives in fit, fabric, and the print’s life across washes. Compliance lives in labels, chemical standards, and safety tests. Retail-grade tees specify GSM ranges, shrinkage percentages, and colorfastness tolerances with lab-backed methods.
- Shrinkage control: 3–5% max after standard wash cycles; pre-shrunk finishing improves outcomes. [CITE: ISO or AATCC test method reference].
- Colorfastness: wash, rubbing, and perspiration tests set minimum ratings to reduce returns. [CITE: AATCC methods].
- Seam strength: stitch density and rib recovery protect neckline shape. [CITE: ASTM seam strength method].
Compliance for US/EU includes fiber content and care labeling, REACH chemical safety, and flammability standards for textiles. Marketplace acceptance adds barcode rules and packaging restrictions. OEM programs document inputs and results to smooth customs and retail onboarding.
[INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on labeling and testing for apparel — pillar page]
| Program Attribute | DIY / Homemade | OEM / Eton-style |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Cost Predictability | Variable; labor minutes swing; ink/blanks priced at retail | Stable; fabric/print priced at volume; wastage controlled |
| Setup Time | Hours to days; instant for HTV/DTG | 2–6 weeks for sampling; line setup scheduled |
| Capacity | Limited by operator time and space | Scalable lines; multi-factory capacity |
| QA Repeatability | Operator-dependent; limited testing | Inline QC + lab tests; documented tolerances |
| Compliance Readiness | Basic labels; minimal documentation | Labels, REACH checks, flammability tests, COAs |
| Sustainability Proof | Citation rare; ad-hoc claims | OEKO-TEX/GRS sourcing; chain-of-custody |
| Lead Times | Ultra-fast for tiny runs; slow at volume | Predictable timelines; freight consolidation |
| Customization Breadth | Personalization strong; limited trims | Broad trims, packaging, labels; scalable variants |
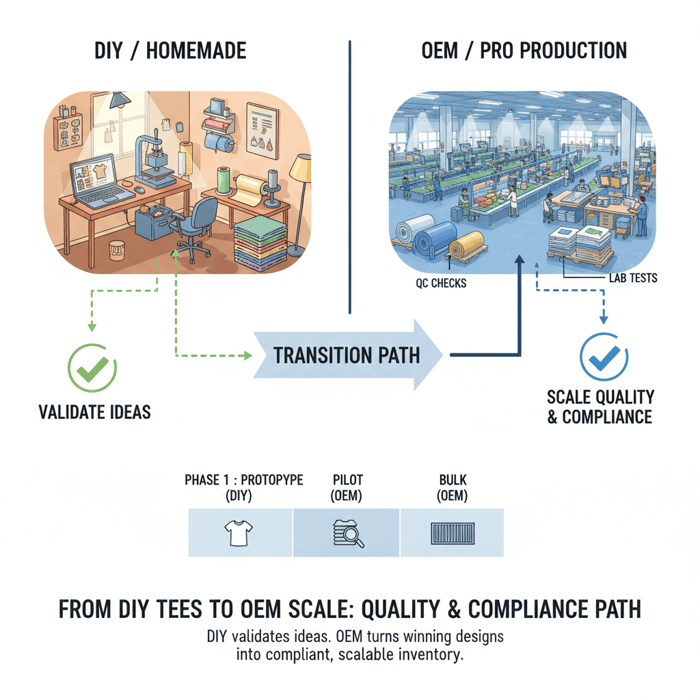
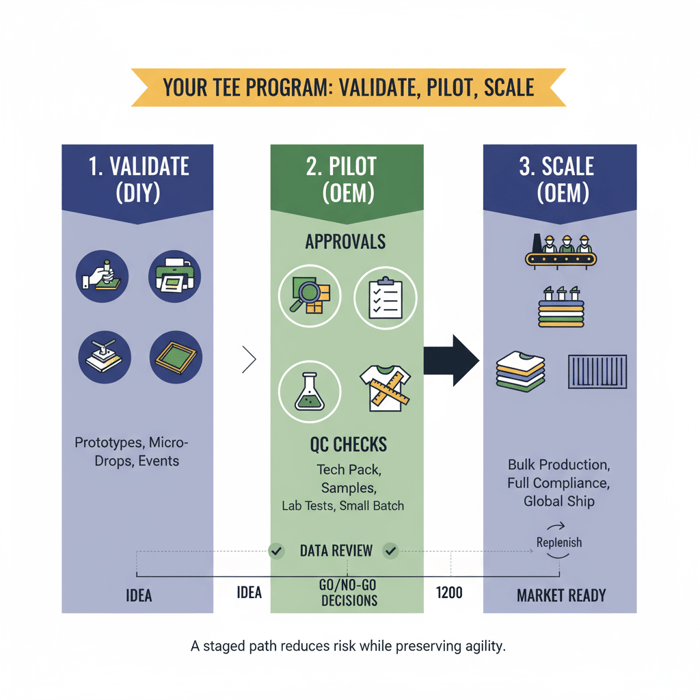
How to Transition from Homemade Tee Shirts to OEM Manufacturing
Move in three phases: specify the tech pack and standards, run samples and a pilot, then scale bulk with QC gates. Keep DIY micro-drops running while the pilot proves demand and fit. That sequence protects agility and reduces risk.
Preparation (Tech Pack + Materials)
A clear tech pack sets the program up for repeatable results. Include:
- Fabric: ringspun or combed cotton, GSM range (e.g., 160–220), finish (pre-shrunk, silicone softening), yarn details.
- Fit spec: graded measurements across sizes, neckline rib specs, stitch density, hem construction.
- Color and print: Pantone codes, print method (screen, DTG, discharge, water-based), artwork files with placement and scale.
- Wash tests: shrinkage target, colorfastness ratings, seam performance requirements.
- Trims and labels: woven or printed neck label, care label content per US/EU rules, swing tags, barcodes.
- Packaging: polybag spec or recycled alternative, carton markings, pack ratios, retail-ready folding.
- Compliance targets: REACH chemical limits, flammability references, OEKO-TEX or GRS inputs, document list and lab partners.
Eton advises a short materials list per drop to prevent drift. One cotton base across three colorways is easier to control than mixing multiple fabrics. Consistency raises yield and compresses approval cycles.
[INTERNAL LINK: T-shirt tech pack template — download page]
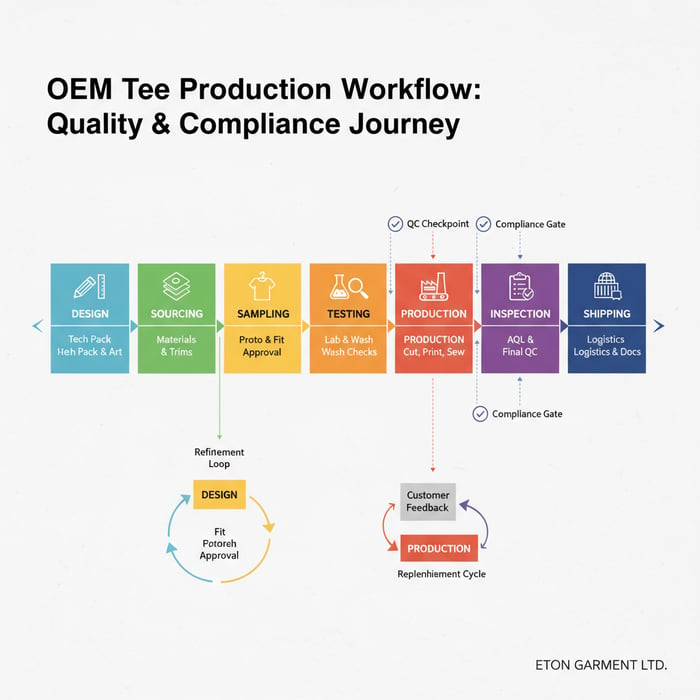
Execution Steps (Sampling → Pilot → Bulk)
- Kickoff: share tech pack, artwork, and timelines; confirm MOQ tiers and testing plan.
- Fabric strike-off: verify color, hand-feel, and finishing against GSM and shrinkage targets.
- Print test: run your chosen method on production fabric; validate opacity, hand, curing.
- Fit sample: assess neck shape recovery, shoulder seams, and sleeve hang; adjust graded specs.
- Pilot order: 50–150 units; run lab tests; collect customer feedback on wash cycles and fit.
- Bulk production: set inline QC gates; conduct final inspection (AQL); prepare shipping and documentation.
- Post-launch review: track returns and ratings by issue; refine specs for replenishment.
Time-boxing helps planning: sampling 2–4 weeks, pilot 3–5 weeks, bulk 6–9 weeks, transit by region. DTG-only programs may compress setup but still benefit from fabric and label control.
[CITE: Typical OEM lead time ranges from a trade association or sourcing marketplace, 2023–2024].
Quality Assurance (Inline + Final)
QA protects the brand and the customer. Use AQL sampling for incoming fabric, inline print checks, and final inspections. Add wash tests at pilot stage, then spot checks during bulk.
- Inline checks: print opacity, curing temperature, placement tolerances, stitch density, rib recovery.
- Final inspection: AQL sampling on defects, labels, packaging, and carton marking.
- Lab tests: shrinkage, colorfastness to wash and rubbing, fiber content verification.
Document the full set. Photos, measurements, and test reports ease retailer onboarding and customs clearance in the US and EU. Eton’s inspectors highlight recurring pitfalls: tape misplacement on labels, rib overstretch during handling, and under-cured prints that crack early.
[INTERNAL LINK: Quality control checklist — resource page]
Sourcing Fabrics, Prints, and Trims: From Home Setups to China Clothing Manufacturer Supply Chains
Durable, retail-ready tees start with consistent yarns, controlled knitting, and disciplined finishing. Pair the fabric to the print method and specify certified inputs. This raises wash life and meets US/EU expectations for material integrity.
Fabric & Finishing Choices
Common tee fabrics and finishes:
- Combed cotton: smoother, stronger yarns; cleaner prints; stable hand.
- Ringspun cotton: soft hand; good drape; popular for retail basics.
- Organic cotton: lower-impact cultivation; confirm certification and chain-of-custody.
- CVC (Chief Value Cotton) blends: cotton-poly balance for shape retention and lower shrink.
Finishing choices matter. Pre-shrunk finishing reduces returns. Enzyme or silicon softening adjusts hand-feel. Eton often targets 160–220 GSM for everyday tees, with rib specs that protect neckline shape over repeated wears.
GSM drives drape and perceived value. Heavier weights read premium but may warm quickly. Lighter weights breathe but can show print strike-through without careful ink selection.
[MENTION: Textile Exchange] publishes insights on preferred fibers, helping brands set material roadmaps that align with retailer expectations.
Print Methods at Scale
Method selection affects durability, hand-feel, and compliance tasks:
- Screen printing: strong opacity; long-lasting; ideal for spot colors and high volumes. Pair with ringspun cotton for a balanced hand.
- Water-based inks: soft hand; eco-claims possible; curing discipline and lab checks are essential.
- Plastisol: reliable coverage; more body on the print; check restricted substances for US/EU compliance.
- Discharge: removes dye for soft prints on cotton; color control and fabric compatibility must be tested.
- DTG: complex artworks and small batches; select fabrics with stable absorbency and pre-treatment routines.
[CITE: Comparative durability data from AATCC or a reputable lab] supports method selection for wash life claims.
Labels, Care, and Packaging
US/EU labeling requires fiber content, care instructions, and country of origin. Retailers add barcode formats and packaging rules. Build labels into the tech pack, proof the artwork, and confirm print durability on care tags.
- Neck labels: woven or printed; place and size for comfort; test wash readability.
- Care labels: symbols and text per US/EU norms; confirm fiber accuracy.
- Packaging: recycled poly alternatives, carton strength, pack ratios, and clear marks for DC processing.
Document label proofs before production. Label errors drive returns and marketplace takedowns. Eton’s teams run label checks during sample and pre-bulk approvals.
[INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability and compliance certifications — pillar page]
Data & Trends for T-Shirt Programs (US & EU)
Apparel basics remain resilient, design cycles tighten, and supply chain transparency rises. Brands that balance agility with documented compliance gain access to marketplaces and retailers with fewer friction points.
- Apparel basics show steady demand — 2024 (Source: [CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024]).
- Material certification and traceability adoption grow — 2024 (Source: [CITE: Textile Exchange Material Change Insights 2024]).
Agility With Accountability
Brands want speed and low inventories, yet retailers and platforms request labeling, testing, and documentation. Flexible MOQ tiers and pilot orders bridge the gap. Many US/EU teams keep homemade tee shirts active for idea testing while Eton runs pilots with lab checks to prepare bulk drops.
[MENTION: Amazon and Zalando] have raised product integrity expectations for listings, pushing better documentation and labeling accuracy. [CITE: Marketplace policy updates, 2023–2025].
Material Responsibility & Proof
Preferred materials rise in adoption, yet proof matters. OEKO-TEX STANDARD 100 signals restricted substances controls, and GRS supports recycled material claims. Chain-of-custody and certificates shift claims from marketing to evidence. This aids customs clearance and retailer onboarding.
[CITE: OEKO-TEX guidance, 2024] and [CITE: ECHA REACH summaries] help teams define specs and testing schedules.
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service scales winning tee designs with consistent quality, compliance documentation, and predictable costs. The service bridges rapid prototyping and retail-ready production, tying fabrics, prints, and labels to verified standards.
Start your OEM tee program with pilot orders and clear QC gates. Eton operates factories in China and Bangladesh with audited compliance and end-to-end inspection. That footprint supports seasonal core programs and replenishment models.
Use Case: Micro-Drop Validated → Pilot OEM
A team runs homemade tee shirts for three micro-drops. Orders hit 120 units on the third drop, and returns mention shrinkage and neck shape. Eton builds a tech pack with 180 GSM ringspun cotton, pre-shrunk finishing, and a two-color screen print. Pilot 100 units with wash and rub tests. Outcome: lower returns, cleaner color, stable necklines. Replenishment set at 300 units per colorway.
- Inputs: artwork files, Pantone codes, grading charts, compliance targets.
- Outputs: fabric swatch approval, print tests, fit samples, pilot run with lab reports.
- Timeline: 8–10 weeks to first pilot delivery excluding transit.
Use Case: Seasonal Core Tee Program
A retailer wants a core tee with three colorways and two graphic variants. MOQ set at 3×500 units. Eton sources OEKO-TEX certified cotton, runs screen prints and water-based variants, and sets a replenishment trigger at 60% sell-through. Packaging moves to recycled poly alternatives, with carton marking aligned to DC standards.
- Inputs: seasonal color palette, spec updates for fit and rib, label compliance list.
- Outputs: approved PPS (pre-production sample), confirmed barcodes, AQL plan, and freight schedule.
- Timeline: sampling 3 weeks; bulk 6–8 weeks; transit varies by region.
| Need | Eton OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Shrinkage Control | Pre-shrunk finishing + wash tests | Lower returns; size consistency |
| Compliance Proof | Labeling setup + REACH checks + flammability references | Marketplace acceptance; smoother customs |
| Cost Stability | Consolidated fabric and print sourcing | Predictable margins; scalable MOQ tiers |
| Speed With Accuracy | Pilot sampling and defined QC gates | Faster approvals; fewer production resets |
| Sustainability Signals | OEKO-TEX, GRS inputs; chain-of-custody docs | Credible claims; retailer alignment |
[INTERNAL LINK: Garment factory network overview — pillar page]
Sustainability & Materials Integrity
Pick standards that match brand goals and market expectations. Document inputs and chain-of-custody. State claims conservatively and back them with certificates and lab reports.
Selecting Standards That Fit Your Brand
Common pathways:
- OEKO-TEX STANDARD 100: tests for harmful substances on textiles, helpful for US/EU listings. [CITE: OEKO-TEX STANDARD 100 overview].
- GRS (Global Recycled Standard): supports recycled content claims with chain-of-custody. [CITE: Global Recycled Standard primer].
- BCI (Better Cotton): improves cotton farming practices; claims depend on system balance and traceability. [CITE: Better Cotton program notes].
Standard selection sets the testing plan. Agree on ink type, fabric inputs, and label claims with the factory before POs. Eton aligns the spec to available certified materials to prevent late-stage redesigns.
Documentation and Proof for Retailers
Build a simple sequence:
- Choose standard and scope (fabric, print, trims).
- Specify it in the PO and tech pack.
- Collect COAs, test results, and chain-of-custody certificates.
- Compile a retail-facing compliance pack.
Evidence protects listings and aids customs clearance. Without proof, claims may be removed and shipments delayed. Many buyers ask for test reports and certificates before final payment. Homemade tee shirts rarely have this documentation unless the brand sourced certified blanks and inks with traceable paperwork.
[INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability and compliance hub — pillar page]
Risks, Compliance & Localization (US & EU)
Align labeling, chemical, and safety requirements before production. Bake compliance into specs, then approve samples with labels and documentation. That approach avoids rework after the fact.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Label Errors | Medium | High returns; marketplace delisting | Pre-production label proof; sample verification; barcode test scans |
| High Shrinkage | Medium | Fit complaints; poor ratings | Fabric pre-wash; finishing; lab wash tests; inline checks |
| REACH Restricted Substance Exceedance | Low–Medium | Customs hold; rework costs | Supplier declarations; lab tests; certified inputs |
| Under-Cured Prints | Medium | Cracking; returns | Controlled curing; temperature logs; print method approval |
| Traceability Challenge (UFLPA) | Low–Medium | Shipment delays; documentation scrutiny | Chain-of-custody; supplier mapping; declarations |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
United States:
- FTC care and fiber labeling set content and care rules. (FTC guidance)
- CPSC flammability for clothing textiles applies to many apparel categories. (CPSC rules)
- UFLPA requires supply chain diligence to avoid forced labor links. (CBP guidance)
European Union:
- General Product Safety Regulation refreshes product safety expectations. (EU GPSR)
- REACH governs chemical safety; follow restricted substance lists and testing. (ECHA)
Plan labels and tests at the tech pack stage. Confirm final label artwork and content on samples. This avoids relabeling and holds at receiving centers. Eton’s teams maintain label checklists that slot into the approval sequence.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Use homemade tee shirts to learn. Shift to OEM when demand and standards call for repeatable quality, predictable costs, and compliance. Run a pilot with lab tests, then scale with clear QC gates and replenishment triggers. Keep micro-drops active for creative testing while the program matures.
- Clarify specs and materials; prepare the tech pack.
- Approve fabric and print tests; confirm labels and packaging.
- Run pilot; review lab reports and feedback.
- Scale bulk; lock AQL and documentation.
- Track returns and sell-through; refine for replenishment.
[INTERNAL LINK: MOQ and lead time planning — cluster page]
[INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability and compliance hub — pillar page]
Author & Review Notes (E-E-A-T)
Author: Senior Apparel Production Strategist, 12+ years in OEM/ODM, knitwear and outerwear programs in US/EU. Reviewer: Production Director, Eton Garment Limited; 20+ years across China and Bangladesh manufacturing lines. Methodology: Eton’s factory experience plus current industry and regulatory sources; structured for decision-making. Limitations: Costs vary by spec and season; regulations update — verify with accredited labs and counsel. Disclosure: Eton provides OEM manufacturing services described here. Last Updated: 2025-10-28.
[INTERNAL LINK: {{author_name}} — {{author_title}} {{author_bio_url}}]
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024 (2024). URL
- Textile Exchange — 2024 Material Change Insights (2024). URL
- FTC — Clothing & Textile Care Labeling (Year varies). URL
- European Commission — General Product Safety Regulation (EU) 2023/988 (2024). URL
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection — UFLPA Guidance (2023). URL
- OEKO-TEX — STANDARD 100 (Year varies). URL
- CPSC — Flammability of Clothing Textiles (16 CFR Part 1610) (Year varies). URL
- ECHA — Understanding REACH (Year varies). URL
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

