High Quality Fabric for Clothing: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Guide for US/EU Fashion Brands
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
16 minute read
High Quality Fabric for Clothing: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Guide for US/EU Fashion Brands
High quality fabric for clothing defines the success of performance lines, and the right China Clothing Manufacturer converts that intent into repeatable bulk outcomes. US/EU fashion brands need verified properties, credible certifications, and stable mill execution. This guide frames quality criteria, test methods, fiber choices, China sourcing workflows, MOQs and budgets, sustainability, and OEM integration for outerwear, sportswear, and fashion.
- Quality criteria linked to apparel performance and lab validation
- Fiber and construction comparisons for outerwear, sportswear, and fashion
- AATCC/ISO tests with report-reading tactics and certificate checks
- China sourcing: mill capacity, MOQs, lead times, shade continuity
- Cost drivers, trade-offs, and budgeting signals for US/EU launches
- Sustainability and compliance: OEKO-TEX, GOTS, RCS, Higg, EU/US regulations
- OEM integration: design → testing → approvals → bulk QC
High quality fabric for clothing pairs lab-verified performance with certification-backed safety and consistent bulk runs. Brands should specify end-use tests (AATCC/ISO), require recent OEKO-TEX or equivalent certificates, review mill capacity and MOQs, and run pilot approvals with a trusted China Clothing Manufacturer before committing bulk.
What Defines High Quality Fabric for Clothing (Criteria + Performance)
High quality fabric for clothing meets clear end-use targets through fiber choice, yarn engineering, construction, finishing, and lab validation. The anchor is performance matched to real use: abrasion, colorfastness, pilling, dimensional stability, waterproof/breathable ratings, and chemical safety—plus mill consistency across lots.
Start with the product brief. Specify end-use conditions, comfort priorities, visual targets, and risk tolerances. Translate these into measurable properties: abrasion resistance thresholds for urban jackets, colorfastness to washing for everyday wear, hydrostatic head for rain shells, breathability targets for active use, and pilling resistance for knit midlayers. Align each property to standardized tests so fabric selection moves from hand-feel preference to measurable compliance.
- Fiber and yarn: tensile strength, staple vs. filament, yarn count, twist, and blends that balance hand-feel with performance.
- Construction: weave (plain, twill, ripstop) and knit (jersey, interlock), density (GSM), and cover factor to tune durability and drape.
- Finishing: dyeing, heat-setting, sanforizing, brushing, calendaring, coatings, and membranes that deliver function without harming comfort.
- Testing: AATCC/ISO tests mapped to end-use performance for abrasion, colorfastness, pilling, water resistance, breathability, dimensional change.
- Certifications: hazardous substance control (OEKO-TEX Standard 100), recycled content claims (RCS), organic (GOTS), facility impact tools (Higg FEM).
- Consistency: shade continuity, width and skew stability, finishing repeatability, and batch documentation to stabilize bulk.
[CITE: A 2023–2025 standards body overview confirming typical apparel test protocols and thresholds] [MENTION: AATCC technical committees; ISO/TC 38 on textiles] [INTERNAL LINK: Fabric quality control checklist—create a resource page on {{websiteUrl}}]
Core Properties by End Use (Outerwear, Sportswear, Fashion)
Outerwear: durability and weather protection set the base. Abrasion (ISO 12947 Martindale), tear strength (ISO 13937), hydrostatic head for waterproofing (AATCC 127 or ISO 811), breathability via RET or MVTR (ISO 11092/ASTM E96), seam strength (ISO 13935), and low water pickup help maintain comfort. Active sportswear: stretch and recovery (ISO 20932), moisture management (AATCC 195), pilling resistance (ASTM D3512 or ISO 12945), colorfastness to perspiration (AATCC 15), wicking rate, and dimensional stability (ISO 6330 wash protocols) keep garments performing. Fashion and everyday: hand-feel and drape drive choice alongside colorfastness to washing and light (AATCC 61/16), pilling, skew stability, and print adhesion. Match thresholds to use cases and climate. [CITE: Technical report comparing hydrostatic head requirements for urban vs. alpine shells] [MENTION: Gore, Toray for membrane benchmarks] [INTERNAL LINK: Outerwear performance fabrics guide—pillar concept]
Consistency & Bulk Repeatability
Lab wins collapse without lot control. Shade continuity requires tight dye recipes, spectrophotometer targets (delta E tolerances), and retained counter-samples. Finishing stability depends on line capability and heat-setting discipline. Record batch IDs, finishing temperatures, and lab dip approval documents; hold reserve yardage for repairs. A preventive path: approve lab dips and hand-feel against master standards, run pilot bulk of one color, compare roll-to-roll shade, and keep retained swatches for dispute resolution. [CITE: Case note showing delta E control and first-bulk success rates in mill operations] [MENTION: Datacolor, X-Rite in shade management] [INTERNAL LINK: Our mill approval workflow—build a page explaining Eton’s QA checkpoints]
Types of High Quality Fabric for Clothing (Fiber & Construction Comparison)
Select fibers and constructions that meet the performance brief, sustainability targets, and tactile goals. Cotton, wool, nylon, polyester/rPET, blends, and laminates each carry strengths and trade-offs. Pair density and weave/knit choices with finishing and tests to fit outerwear, sportswear, and fashion lines.
| Material | Strengths | Considerations | Best Uses | Sustainability Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton / Organic Cotton | Comfort, breathability, natural hand, dye affinity | Pilling risk in low-twist yarns; slower drying | Fashion, casual wear, midlayers, lined jackets | Organic (GOTS) improves inputs; water footprint varies [CITE: Lifecycle analysis with irrigation data] |
| Wool | Insulation, moisture buffering, odor control | Care requirements; felting risk without finishing | Outerwear, premium fashion, base/midlayers | RWS and traceability programs support animal welfare [MENTION: Textile Exchange RWS] |
| Polyester / rPET | Strength, colorfastness, wrinkle resistance, cost | Lower moisture absorption; static without finishing | Sportswear, fashion, shell fabrics, insulation shells | Recycled (RCS) rising; microfiber concerns require design choices [CITE: PFMR 2024 trend line] |
| Nylon | High strength, abrasion resistance, soft hand | UV yellowing risk; cost premium over polyester | Technical outerwear, bags, high-wear zones | Recycled nylon adoption grows in performance sectors [MENTION: Aquafil ECONYL] |
| Blends | Balances hand, strength, recovery; cost tuning | Recycling complexity; blend ratio drives feel | All apparel segments; fashion knits and shells | Design for recyclability and durability targets |
| Laminates / Membranes | Waterproofing, windproofing, breathability control | Stiffness vs. comfort; edge sealing; seam tapes | Rain jackets, alpine shells, urban protection | PFAS-free finishes now adopted; verify claims [CITE: Industry shift to PFAS-free DWR] |
[INTERNAL LINK: Fiber and fabric matrix—expand as interactive on {{websiteUrl}}] [MENTION: bluesign for process safety; ZDHC MRSL for chemical inputs]
Natural vs. Synthetic vs. Blends
Natural fibers deliver tactile comfort and strong brand narratives. Synthetic fibers deliver strength, weather resistance, and fast-drying performance. Blends reconcile feel, durability, and cost. For midlayers, combed cotton-poly blends reduce pilling and maintain shape. For shells, nylon twills enhance abrasion resistance over polyester while recycled polyester holds shade and wide color ranges. Hand-feel and drape still matter: sueded finishes add warmth, calendaring sharpens visual depth, brushing elevates softness in knits without losing structure.
Laminates & Membranes (PU, TPU, PTFE)
Shells demand measured waterproofing and breathability. PU/TPU membranes offer flexible cost-performance balance; PTFE films drive high-end alpine needs. Waterproofing measured via hydrostatic head (AATCC 127/ISO 811) and breathability via RET or MVTR (ISO 11092/ASTM E96). Target urban rain jackets with 10,000–15,000 mm hydrostatic head and mid-tier MVTR, alpine shells with ≥20,000 mm and higher breathability metrics. Confirm seam tape compatibility, washing durability (ISO 6330), and delamination resistance before committing bulk. [CITE: Comparative MVTR/RET benchmarks for laminate choices] [MENTION: Toray Dermizax; ePTFE leaders]
How to Test and Verify High Quality Fabric for Clothing (Lab + Tactile)
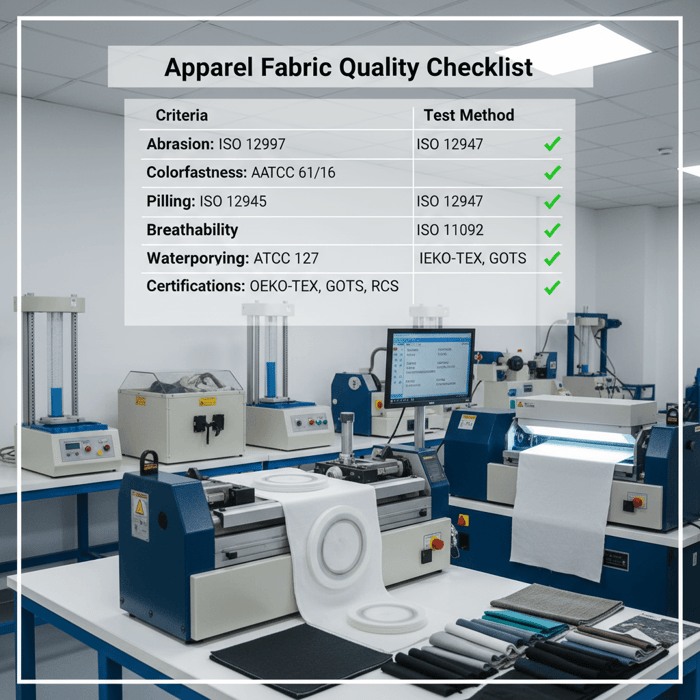
Verification starts with a spec, maps to tests, and ends with data literacy. Use AATCC/ISO methods for colorfastness, abrasion, pilling, waterproofing, breathability, and dimensional change; combine with tactile checks, pilot wash/wear trials, and certificate validation. Read reports closely, confirm dates and scopes, and watch for red flags.
- Define the end-use spec with thresholds for durability, comfort, and protection; state test methods and pass criteria.
- Select tests: AATCC colorfastness to laundering/light/perspiration; ISO abrasion; AATCC water resistance; ISO washing and drying protocols.
- Request Certificates of Analysis (COAs) with recent lab dates, batch references, and fabric ID clarity.
- Run tactile checks: hand-feel, drape, stretch and recovery, and surface integrity after light abrasion.
- Pilot wash/wear: apply ISO 6330 cycles and field wear to spot pilling, skew, or shade shifts.
- Review reports: compare results to spec; check methods and conditions; reconcile anomalies with retests.
- Approve: set master standards, retain counter-samples, and document agreed lab dips and finish settings.
- Brands have accelerated OEKO-TEX Standard 100 adoption since 2024 (Source: [CITE: OEKO-TEX annual certification update]).
- Recycled polyester (rPET) usage continues to rise across fashion segments (Source: [CITE: Textile Exchange PFMR 2024]).
[INTERNAL LINK: Fabric testing services overview—service page concept] [MENTION: Intertek, SGS for lab testing capacity]
Essential Tests & Why They Matter
Colorfastness: AATCC 61 for laundering and AATCC 16 for light keep garments looking right; add AATCC 15 for perspiration in activewear. Abrasion and pilling: ISO 12947 Martindale and ISO 12945 or ASTM D3512 safeguard surface integrity. Water resistance and repellency: AATCC 127 for hydrostatic head and spray tests reflect real rain; pair with breathability via ISO 11092 or ASTM E96. Dimensional stability: ISO 6330 verifies washing outcomes for shrinkage and skew. Stretch and recovery: ISO 20932 supports athletic fits. Every choice maps back to the product brief and climate.
Certificates & Data Integrity
Certificates vary widely in scope. For OEKO-TEX Standard 100, confirm the class relevant to the garment type, the certificate holder, fabric coverage, and expiration date. For recycled content claims (RCS/GRS), check the transaction certificates, batch IDs, and fiber percentages. For organic cotton (GOTS), confirm chain-of-custody and scope IDs. Red flags: mismatched fabric names, expired documents, incomplete test method descriptions, and missing lab accreditation details. Validate dates, link certificates to specific rolls, and retain master copies. [CITE: Guidance on reading OEKO-TEX and GOTS certificates] [MENTION: Higg Index FEM for facility impact transparency]
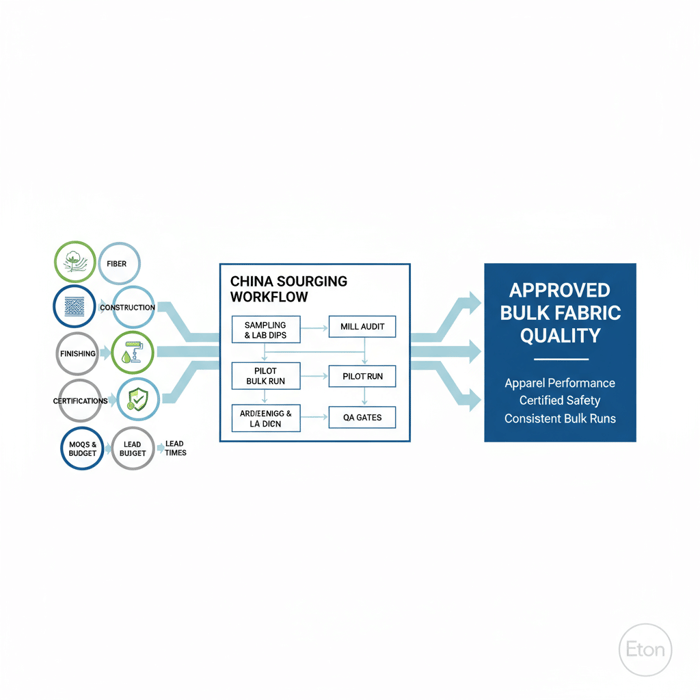
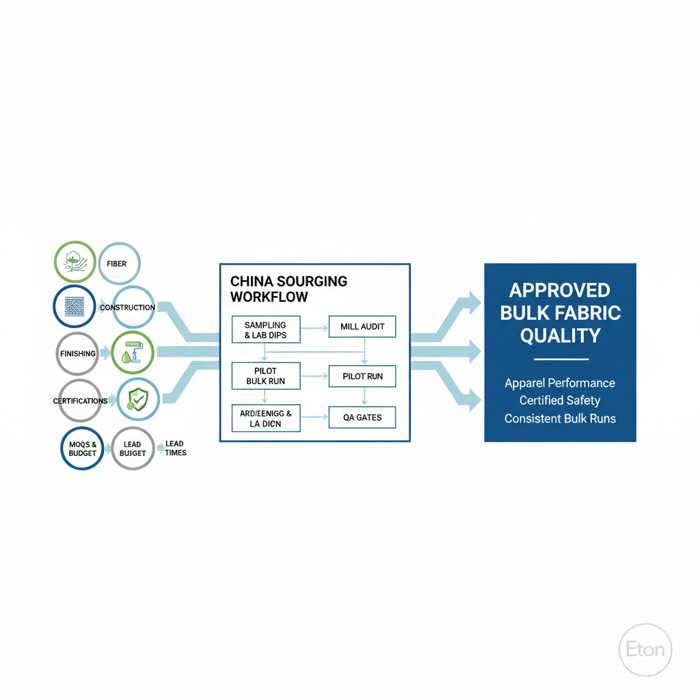
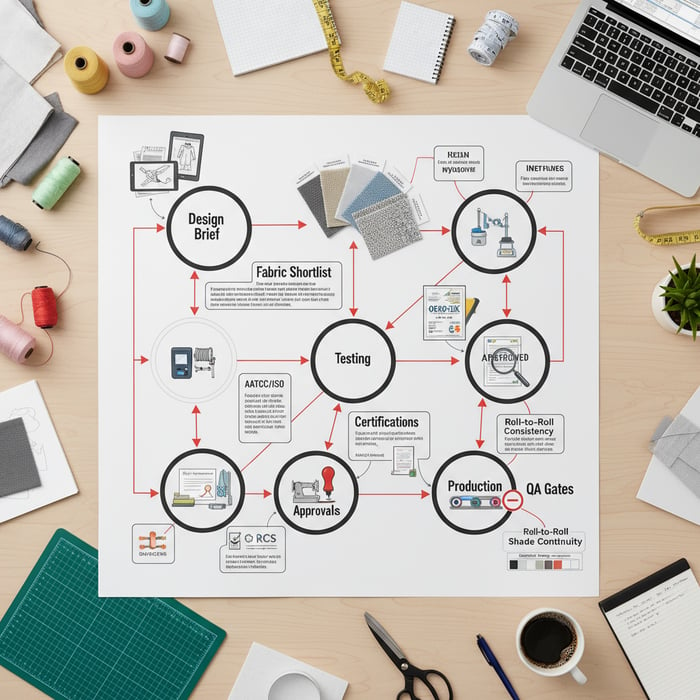
Sourcing High Quality Fabric from China (Mills, MOQs, Lead Times, Approvals)
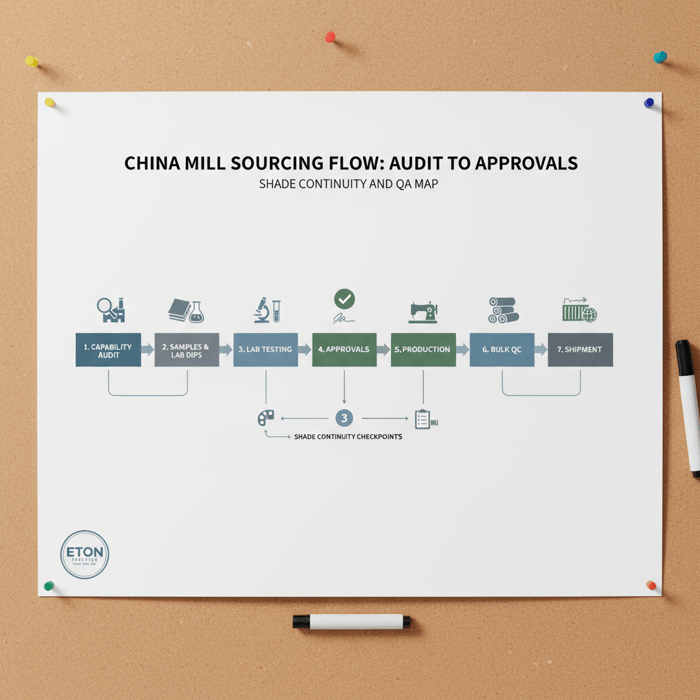
Reliable sourcing is a workflow: shortlist mills, confirm capacity, request samples and lab dips, secure test reports, run pilot bulk, and approve. Align dyeing, finishing, lamination, and color labs with your threshold needs. Document capability, shade targets, and counter-samples to stabilize bulk deliveries.
- Vendor shortlist: choose mills with proven outerwear/sportswear portfolios and recent certifications.
- Capability audit: verify dyeing/finishing lines, lab equipment, lamination suites, and seam tape resources.
- Samples & hand-feel: request multiple densities and constructions that match targets.
- Lab dips: set delta E tolerances and agree recipes; retain master standards.
- Test reports: require AATCC/ISO methods—dated, fabric-specific, and accredited.
- Pilot bulk: one color to test shade continuity, finishing stability, and roll-to-roll consistency.
- Bulk approvals: sign off specs, keep counter-samples, and record batch IDs and finishing settings.
Typical MOQs and lead times vary by construction and process complexity. Dyed woven fabrics often sit at 1,000–3,000 meters per color with 30–45 days; piece-dyed knits can be 800–2,000 meters with 20–35 days; laminated fabrics push MOQs to 1,500–5,000 meters with 45–60 days to accommodate film procurement and bonding windows. Small lots can move with surcharge or shared greige, if mill lines are flexible. [CITE: Trade data on MOQ ranges for China mills 2023–2025] [MENTION: regional mill clusters in Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Guangdong] [INTERNAL LINK: China garment factory network—pillar concept]
Capability & Capacity Checks
Capability review starts with the shop floor. Inspect dyeing ranges, heat-setting lines, singeing, sanforizing or compacting units, brushing and sueding tools, and calendaring. For laminates, confirm bonding equipment, clean rooms, and cured storage conditions; test seam tape compatibility. Ask for lab instruments: spectrophotometer for shade, tensile/tear testers, Martindale units, and spray test setups. Request batch documentation samples to see exact record-keeping. Capacity aligns with lead time and rush handling; verify weekly line throughput and maintenance cycles.
Shade & Lot Consistency
Shade stability depends on tight recipes and disciplined controls. Use spectrophotometer targets on lab dips; set clear delta E limits. Keep master submissions, lot-level counter-samples, and roll headers labeled with batch IDs. Approve one color pilot bulk first, review shade from roll to roll, and stress test finishing consistency with washing and abrasion checks. Adopt a dispute protocol with retained swatches, test reports, and clear sign-off history to protect timelines.
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Integration converts specifications into repeatable garments. Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service closes the loop: design brief, fabric development, lab testing, certification checks, bulk production, and quality control. The framework aligns end-use performance, compliance, and delivery speed for US/EU retail timelines.
| Brand Need | OEM Feature | Outcome | Indicative Timing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outerwear performance spec | Fabric shortlist + membrane matching | Measured waterproof/breathable shells | 2–3 weeks to shortlist and lab dips |
| US/EU test standards | AATCC/ISO test plan and report review | Clear pass/fail against thresholds | 1–2 weeks per round |
| Certification scope | OEKO-TEX/GOTS/RCS verification | Aligned compliance and claims | 1 week validation with labs |
| Shade continuity | Lab dip master + pilot bulk | Stable color in repeated lots | 3–4 weeks from dips to pilot |
| Bulk speed | China/Bangladesh line allocation | On-time first ship windows | 6–10 weeks fabric; garment lead aligned |
Eton Garment Limited has delivered outerwear, padded coats, parkas, and technical apparel for three decades across China and Bangladesh. Partners include Liverpool F.C., Forever 21, Babyshop, Max, Gloria Jeans, Jeep Apparel, and TFG Group. The OEM workflow stitches fabric choice to product performance with measurable QA checkpoints. [MENTION: Third-party labs auditing fabric performance] [INTERNAL LINK: Talk to Eton’s OEM team → {{productUrl}}]
Use Case 1: Technical Outerwear (Problem → Solution)
Brief: an EU retailer needs an urban rain shell with soft hand and solid waterproofing that survives daily commuting and intermittent washing. Solution: a nylon twill with PU/TPU membrane, hydrostatic head 15,000 mm (AATCC 127), MVTR suited to city movement (ASTM E96), spray rating at top tiers and seam tape validated. Shade controls set with delta E tolerances; dimensional change verified with ISO 6330; abrasion (ISO 12947) tuned via twill density. Pilot bulk confirms roll-to-roll stability and seam taping through full production.
Use Case 2: Fashion Retail (Problem → Solution)
Brief: a US brand wants a brushed polyester-cotton knit for a capsule line with premium hand-feel and consistent pastel shades. Solution: combed cotton-poly blend with controlled yarn twist for pilling resistance (ISO 12945), shade matched through lab dips with tight delta E, wash stability via ISO 6330, and soft brushing calibrated to avoid surface peeling. Pilot color run sets the master standard; bulk holds both hand-feel and shade window across multiple stores.
Costs, MOQs & Budgeting for High Quality Fabrics
Budgeting lands on fiber, finishing, certifications, MOQs, and lead times. Premium finishes and membranes lift unit costs; recycled content can shift price and MOQs; certifications add verification steps; laminated lines require longer windows. Balance spend on properties that matter to the end use and brand promise; trim extras that do not change real performance.
- Premium finishing boosts hand-feel and function but raises unit cost and lead time.
- Certified inputs simplify compliance reviews yet demand scope validation and document handling.
- Recycled content strengthens brand narratives while sometimes pushing MOQs or yield loss risks.
- Laminates deliver waterproofing and windproofing with higher MOQs and bonding line time.
| Driver | Impact | Indicative Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber choice | Unit cost, durability, dye response | Nylon > Polyester; Organic cotton premium | Check blend ratios and end-use fit |
| Finishing | Function and hand-feel | Basic finish → premium surcharge tier | Brushing, sueding, calendaring, coatings |
| Laminates | Waterproof/breathable function | Film cost + bonding operations | Seam tape and delamination tests needed |
| Certifications | Compliance confidence | Documentation and test fees | OEKO-TEX, RCS/GRS, GOTS scopes |
| MOQs & colors | Per-color commitment and inventory | 800–5,000 meters per color | Laminates and specialty dye lift MOQs |
| Lead times | Calendar fit and risk | 20–60+ days by process | Greige availability and line allocation |
MOQ & Lead Time Signals
Dyed vs. laminated fabrics follow different rhythms. Dyed wovens and knits can run 20–45 days with MOQs near 800–3,000 meters per color. Laminates pull in film procurement, bonding, and seam tape compatibility checks, stretching to 45–60+ days and raising MOQs to 1,500–5,000 meters. Color count increases complexity; pastel ranges require tighter shade control and may add re-dye time in case of mismatch.
Sustainability & Compliance for US & EU
Sustainability and compliance build trust. For fabric selection, align hazardous substance control, recycled content and organic claims, and facility impact frameworks. For US/EU retail, keep flammability rules in view and track EU chemicals policy evolution. Verify scopes, dates, and chain-of-custody to avoid audit friction.
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical non-compliance | Medium | High | OEKO-TEX, bluesign, ZDHC MRSL checks; recent lab reports |
| Expired certificates | Medium | Medium | Date validation; holder scope match; chain-of-custody audits |
| Flammability issues (US) | Low–Medium | High | Check 16 CFR Part 1610 applicability; confirm test results |
| PFAS usage in finishes | Medium | High | PFAS-free DWR sourcing; verify claims; review wash durability |
| Social compliance gaps | Medium | High | WRAP/BSCI audits; corrective action plans; transparent facility data |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
United States: flammability of clothing textiles (16 CFR Part 1610) applies to certain categories; check construction and fiber for risk. European Union: the EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles is reshaping material choices and reporting; watch chemicals policy updates and durability targets. Facility impact evaluation via the Higg Index remains standard for many global brands. [CITE: EU policy page update; CPSC guidance page] [MENTION: SAC Higg Index; European Commission announcements]
Conclusion & Next Steps
Quality starts with a spec and lands with data-backed approvals. Combine strong lab methods, precise certificate checks, and a disciplined China mill workflow. For outerwear and sportswear, match properties and thresholds to the climate and use case. Bring OEM integration into play to compress timelines and lock consistency from brief to bulk deliveries.
- Week 1: write the spec; set test methods and thresholds; name certifications.
- Weeks 2–3: shortlist mills; audit capacity; request samples and lab dips.
- Week 4: run tests; review reports; confirm certificates and scopes.
- Weeks 5–8: pilot bulk for one color; check shade, finishing, and wash stability.
- Ongoing: retain counter-samples; monitor lot consistency; refresh certificates before expiry.
Eton’s promise—“Textile From Day One.”—speaks to starting with fabric quality and carrying it through production. For US/EU brands building outerwear and sportswear lines, that path converts briefs into garments that meet performance and compliance with speed. Talk to Eton’s OEM team about integrating fabric selection, testing, and bulk QC. [INTERNAL LINK: Book a fabric quality consultation with Eton—conversion page idea] [INTERNAL LINK: {{companyName}} author bio—{{websiteUrl}}/about]

Explore our exclusive Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service to learn more.
- OEKO-TEX — Standard 100 (2024). https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/standards/oeko-tex-standard-100
- AATCC — Test Methods (2024). https://www.aatcc.org/testing/
- ISO — Textile Standards Index (2024). https://www.iso.org/ics/59.080.01/x/
- Textile Exchange — Preferred Fiber & Materials Market Report (2024). https://textileexchange.org/pfmr/
- Sustainable Apparel Coalition — Higg Index (2024). https://apparelcoalition.org/higgindex/
- European Commission — EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles (2024). https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/circular-economy/textiles_en
- U.S. CPSC — Flammability of Clothing Textiles, 16 CFR Part 1610 (2024). https://www.cpsc.gov/Regulations-Laws-Standards/Statutes/The-Consumer-Product-Safety-Act/Flammability-of-Clothing-Textiles
- WRAP — Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production (2024). https://wrapcompliance.org/
- amfori — BSCI Social Compliance (2024). https://www.amfori.org/content/amfori-bsci
- bluesign — System (2024). https://www.bluesign.com/en
- ZDHC — Manufacturing Restricted Substances List (MRSL) (2024). https://www.zdhc.org/mrsl
[CITE: Comparative study on laminate MVTR/RET values relevant to urban vs. alpine shells]
[MENTION: X-Rite shade management systems; Intertek textile labs]
[INTERNAL LINK: Author bio — Senior Apparel Sourcing Strategist on {{websiteUrl}}]
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

