High Quality Clothing: How to Choose a China Clothing Manufacturer You Can Trust
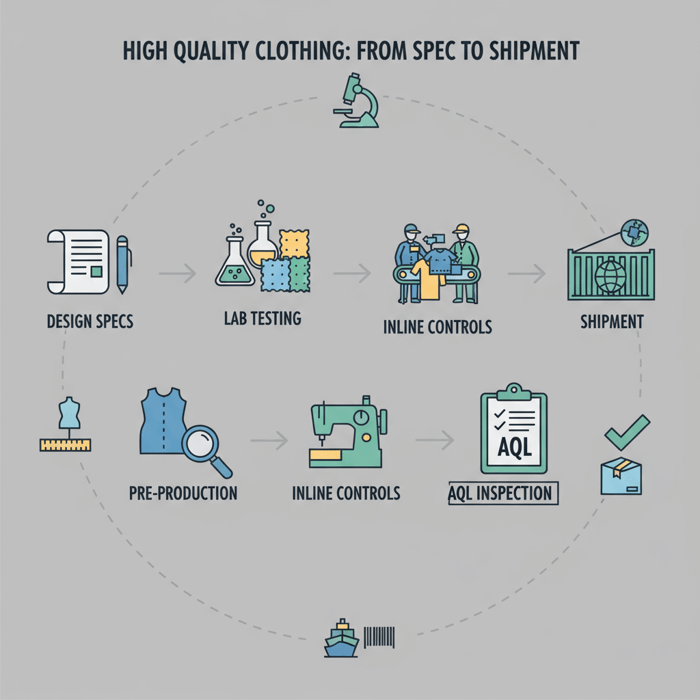
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 15th, 2025
20 minute read
High Quality Clothing: How to Choose a China Clothing Manufacturer You Can Trust
High quality clothing is engineered, not promised. For any China Clothing Manufacturer to deliver it consistently, brands need measurable specs, standards-based tests, and an inspection plan that works at production scale. This article translates “quality” into fit-for-purpose thresholds, AATCC/ASTM test plans, AQL-ready inspections, and China-specific vendor selection that meets US/EU compliance and sustainability expectations.
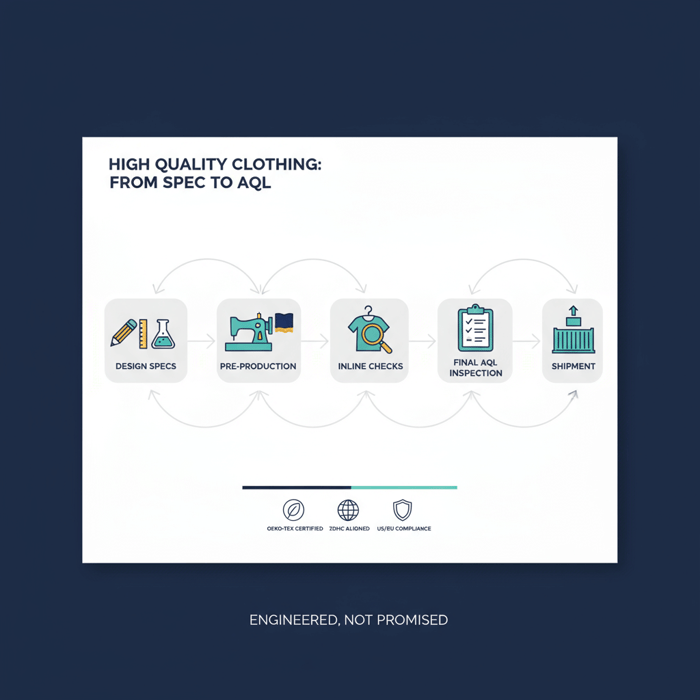
At Eton Garment Limited, we build high quality clothing by connecting design intent to factory-floor controls—tech packs with tolerances, disciplined pre-production, inline checks, and final AQL inspection—supported by OEKO-TEX-certified inputs and ZDHC-aligned chemical management. The result is consistent output, fewer returns, and proof of compliance when customs or customers ask for it.
High quality clothing means garments that meet defined performance specs, safety thresholds, and workmanship tolerances—validated by AATCC/ASTM lab tests, OEKO-TEX/ZDHC-compliant inputs, and AQL-driven inspections from proto through final. When sourcing from a China Clothing Manufacturer, request ISO 9001 systems, PP discipline, lab reports, and traceability aligned to US/EU regulations.
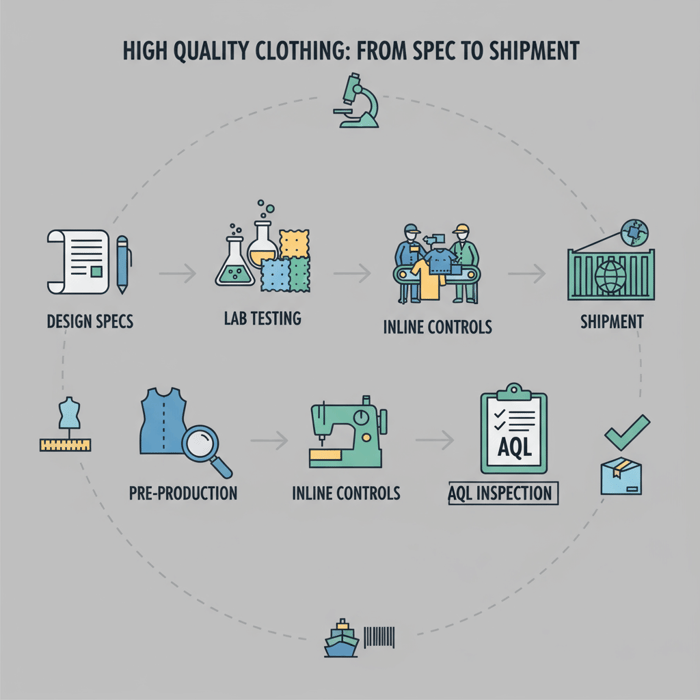
What “High Quality Clothing” Means in Manufacturing Terms
High quality clothing meets defined, measurable targets for performance, safety, and workmanship. The targets live in the tech pack and are verified by standards-based tests (AATCC/ASTM/ISO), while output consistency is controlled by AQL-based inspections across sampling, inline, and pre-shipment stages.
Build a definition you can buy against. List the garment’s end-use risks and translate them into attributes, test methods, thresholds, and tolerances. Then align inspections and acceptance criteria to those risks. This creates a common language for your brand, your China partner, and third-party labs.
- Fit and sizing: Block accuracy and graded measurements kept within tolerance bands.
- Durability and appearance: Seam strength, abrasion/pilling resistance, and colorfastness test passes.
- Dimensional stability: Shrinkage and skew within specified percentages after care cycles.
- Chemical and product safety: Inputs screened to OEKO-TEX Standard 100; MRSL alignment per ZDHC; CPSIA/REACH labeling and heavy metals limits met.
- Workmanship: Stitch density and seam construction match the tech pack; no critical defects; functional hardware cycles validated.
- Traceability and documentation: Lot-level traceability, bills of materials, lab reports, and audit history available on request.
[PAA MICRO-QUESTION] Which single KPI best predicts garment quality at scale? Short answer: “Rate of PP-validated lines starting production on time.” On-time PP correlates with frozen specs, finalized trims, and trained lines—upstream controls that lower inline defects. [CITE: A factory performance study linking PP readiness to defect rates] [MENTION: AAFA] [MENTION: SGS]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on 'Apparel Quality Control & AQL Guide'] [INTERNAL LINK: Eton’s Quality Control & Testing Center]
Performance & Safety Attributes
Durability: Specify seam strength (e.g., ASTM D1683), tear strength (ASTM D1424), abrasion (ASTM D4966 Martindale or ASTM D3884 Taber), and pilling (ASTM D4970 or ISO 12945). Set clear pass/fail thresholds linked to end-use. A commuter jacket might target ≥20,000 Martindale rubs; a premium parka might target ≥40,000.
Colorfastness: Control bleeding, crocking, and fading using AATCC 8 (crocking), 15 (perspiration), 61 (accelerated laundering), and 16 (light). Dark denim that fails AATCC 8 dry crocking can stain; aim for Grade 4–5 for premium outputs.
Dimensional stability: Combine AATCC 135/150 for home laundering shrinkage and skew with AATCC 179 or ISO 5077-based methods. Premium tees often target ≤3% shrinkage; knits may require tighter specs if a precise fit matters.
Chemical and product safety: Use OEKO-TEX Standard 100-certified inputs and ZDHC MRSL v3.1-aligned chemical inventories. For trims, screen for heavy metals and nickel release (EN 1811). For children’s wear, ensure CPSIA tracking labels and lead limits are met. [CITE: OEKO-TEX 2024 chemical scope updates] [MENTION: OEKO-TEX] [MENTION: ZDHC]
Workmanship & Tolerances
Workmanship is the visible face of quality. Define stitch density (e.g., 8–10 SPI for outerwear topstitch, 10–12 SPI for light wovens), seam allowances, and seam types (e.g., safety stitch + overlock on high-stress seams). Call out seam slippage testing (ISO 13936-2) where woven fabric stability is a risk.
- Measurements: Provide graded size charts with tolerances (e.g., chest ±1.0 cm, sleeve length ±0.7 cm). Tolerances must be tight enough to protect fit, yet realistic for the fabric and line capability.
- Functional hardware: Zipper cycle tests (e.g., 5,000–10,000 cycles), snap pull tests (ASTM D4846), corrosion resistance (ASTM B117 salt spray). For outerwear, verify slider locking and anti-corrosion finishes.
- Visual standards: Define critical/major/minor defect lists with swatch references for shade, puckering, pleating, and skipped stitches.
Documentation & Traceability
Documentation protects decisions. A complete tech pack must include BOM with supplier and certification IDs, trim cards with finish specs, and lab test plans. Keep lot-level traceability for fabrics, insulation, snaps, and zippers; maintain COOs and mill invoices to answer UFLPA or REACH queries.
Labeling and fiber content must follow US FTC rules and EU Regulation 1007/2011. Record care method validation (wash tests) to match care labels and reduce returns. [CITE: FTC Care Labeling Rule overview] [MENTION: U.S. FTC] [MENTION: European Commission DG GROW]
E-E-A-T note: This framework aligns with AATCC/ASTM methods, ISO 9001 systems, OEKO-TEX, and ZDHC MRSL. It is not a substitute for legal advice; consult compliance counsel and accredited labs.
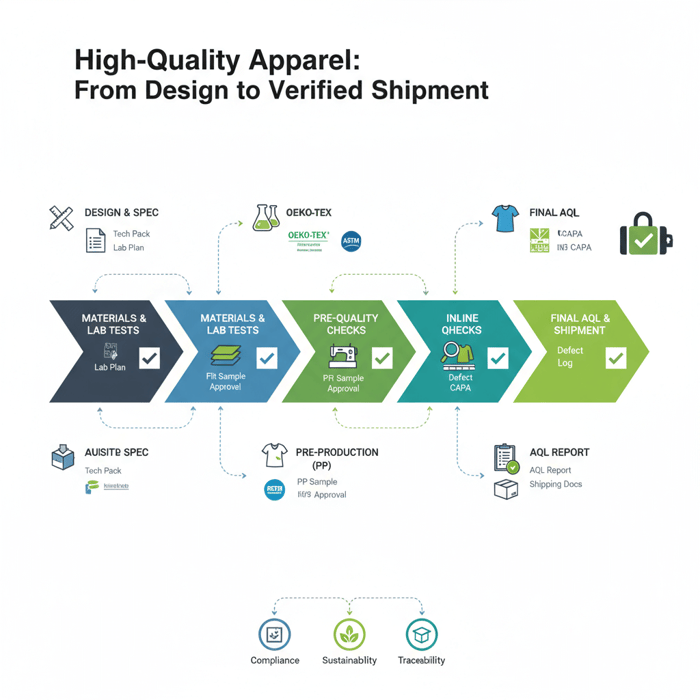
How to Manufacture High Quality Clothing: From Tech Pack to Final AQL
Quality is produced by process control. Tie every stage—tech pack, sampling, inline, and final inspection—to a clear input/output and approval gate. Use AQL-based inspections to accept or hold shipments against defined risks and business priorities.
Follow a sequence that prevents ambiguity from reaching the line. Confirm fabric and trims, freeze measurements via fit approvals, and validate construction before loading bulk. Add corrective actions early wherever data shows drift.
- Tech pack creation: Define specs, tolerances, and a lab test plan; pre-book lab slots.
- Proto → fit → size set → PP: Close fit issues, approve construction details, and freeze BOM.
- Pilot run and inline inspections: Validate the line’s first units and monitor drift with sampling.
- Final AQL inspection and CAPA: Inspect against AQL, implement corrective actions, and document results.
[PAA MICRO-QUESTION] What AQL level should premium brands use for outerwear? Many brands target AQL 2.5 for major defects and 4.0 for minor, with zero tolerance for criticals. High-risk programs lift rigor to AQL 1.5 for majors. Adjust by risk, price point, and customer expectations. [CITE: AQL acceptance sampling primer from a standards body] [MENTION: ANSI/ASQ Z1.4] [MENTION: Bureau Veritas]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on 'Apparel Quality Control & AQL Guide'] [INTERNAL LINK: Full-Service OEM/ODM for Brands]
The Bulletproof Tech Pack
Start with a tech pack that prevents guesswork. Include construction diagrams, seam types, topstitch patterns, SPI, and seam allowances. Add a tolerance table for each point of measure; flag “no tolerance” for critical measurements like jacket chest and inseam on tailored fits.
- Lab test plan: Attribute-to-test map with thresholds and batch cadence. Include colorfastness, abrasion/pilling, dimensional stability, seam strength, and—for outerwear—hydrostatic head and seam-seal adhesion.
- Materials and trims: BOM with mill names, lot IDs, certifications (OEKO-TEX, GRS, RDS where relevant), and finish specs (e.g., PFAS-free DWR type, coating weight).
- Fit blocks: Reference past approvals where relevant to reduce rounds. Require fit comments with photos and callouts.
Inline Control & CAPA
Inline checks catch drift. Use defect coding, sample by operation and bundle, and add targeted checks when risk rises (e.g., new fabric, new operator). Record defect Pareto, run root cause, and update work instructions the same shift.
- Sampling frequency: Start at 2–5% of output for new styles; reduce as Cpk shows stability. Increase frequency during style changes or after non-conformance.
- Measurement checks: Conduct size set verification on the line; spot-check key measures against tolerances every X bundles.
- CAPA loop: Define containment, root cause, corrective action, and verification. Track time-to-close; audit repeat rates monthly. [CITE: Manufacturing CAPA effectiveness benchmark] [MENTION: ISO 9001] [MENTION: Intertek]
Pre-Shipment Verification
Finalize with clear acceptance criteria. Set AQL sample sizes based on lot quantity, risk, and defect class definitions. Include carton audits, packaging checks, and PPK (package performance) checks where required for DC automation.
- Final AQL: Critical 0 acceptance; majors per AQL 2.5 unless escalated; minors per AQL 4.0. Record lot, sample size, failures by defect code, and disposition.
- Carton audit: Verify barcode symbology, carton crush strength, palletization, and carton weight variation.
- Labeling: Confirm fiber content, RN/EIN, country of origin, care symbols (ASTM D5489/ISO 3758), and any REACH/CPSIA statements. [CITE: CPSIA apparel labeling checklist] [MENTION: CPSC] [MENTION: AAFA]
High Quality Clothing Materials: Fabrics, Trims, and Lab Tests
Premium output starts with proven inputs. Select fabrics and trims with certifications and lab data that match end-use needs. Map risks to AATCC/ASTM/ISO tests and choose PFAS-free finishes that meet DWR needs while aligning with ZDHC and regional chemical rules.
| Attribute | Test Method | Example Threshold | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasion resistance | ASTM D4966 (Martindale) / ASTM D3884 (Taber) | ≥20,000 cycles (outerwear shell); ≥40,000 for premium | Urban commuter jackets, parkas |
| Pilling | ASTM D4970 / ISO 12945 | Grade 4–5 | Knit fleeces, brushed shells |
| Colorfastness to crocking | AATCC 8 | Grade 4–5 (dry/wet) | Dark denim, pigment-dyed cotton |
| Colorfastness to laundering | AATCC 61 | Color change/staining ≥4 | Everyday apparel |
| Lightfastness | AATCC 16 | ≥4 after specified exposure | Outdoor gear, activewear |
| Dimensional stability | AATCC 135/150 | ≤3% shrinkage/skew | Knits, tees, fleece |
| Seam strength | ASTM D1683 | Meets load target without failure | High-stress seams |
| Hydrostatic head | ISO 811 / AATCC 127 | ≥10,000 mm for waterproof shells | Rain jackets, snow gear |
| Air permeability | ASTM D737 | Specify cfm for breathability tier | Breathable laminates |
| Nickel release (EU) | EN 1811 | Compliant release rate | Snaps, trims on EU-bound goods |
[PAA MICRO-QUESTION] Which test best predicts color bleeding in dark denim? AATCC 8 (crocking) is the red flag test; pair with AATCC 61 (laundering) to catch dye loss in wash. [CITE: AATCC method overview] [MENTION: AATCC] [MENTION: Cotton Incorporated]
[INTERNAL LINK: Fabric & Trim Sourcing for Performance] [INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability & Compliance Hub]
Fabrics & Finishes
Nylon and polyester blends dominate performance outerwear for strength and weather resistance. Cotton and cotton-rich blends deliver comfort and breathability but need finishing to resist pilling and shrinkage. For weather protection, specify coatings/laminates with target hydrostatic head and MVTR. Tie DWR to PFAS-free chemistry (C0) where possible to meet emerging restrictions.
- PFAS-free DWR strategies: Silicone- or hydrocarbon-based finishes, paraffin emulsions, and hyperbranched polymer systems. Expect lower initial ratings than long-chain fluorocarbons; specify spray ratings and wash-down performance over X cycles. [CITE: Technical brief comparing PFAS-free DWR durability] [MENTION: bluesign] [MENTION: Hohenstein]
- Insulation: Down (specify fill power, RDS where applicable) or synthetics (CLO/TOG targets). Validate warmth retention after laundering.
- Laminates: Specify membrane type, layer construction (2L/2.5L/3L), and seam tape compatibility.
Trims & Hardware
Hardware drives user experience and returns. Standardize zipper brands and tape types across lines; define coatings for corrosion resistance. Validate function with cycle, pull, and salt spray tests.
- Zippers: Cycle testing (5,000–10,000), slider lock retention, tape adhesion. Thermal stress checks for seam sealing overlap zones.
- Snaps and buttons: Pull tests (ASTM D4846), nickel release (EN 1811), coating thickness, salt spray (ASTM B117) for coastal markets.
- Cords, stoppers, and toggles: Elongation, recovery, and break strength; stopper locking force.
Lab Testing Plan
Create a batch-level cadence keyed to risk. Color, print, and finish changes trigger new test runs. For outerwear, add seam-seal adhesion and foam tape compatibility checks on every material change.
- Colorfastness: AATCC 8/15/16/61 as relevant by color and end-use.
- Durability: ASTM D4966/D3884 abrasion, ASTM D4970 pilling, ASTM D1424 tear, ASTM D5034 grab tensile.
- Weatherproofing: ISO 811 or AATCC 127 hydrostatic head; seam-seal adhesion method; rainroom or spray tests (AATCC 22) for water repellency ratings.
- Chemical safety: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 certificates for inputs; ZDHC MRSL screening; REACH SVHC monitoring. [CITE: ZDHC MRSL v3.1 scope] [MENTION: ECHA] [MENTION: TUV SUD]
Choosing a China Clothing Manufacturer for High Quality Clothing
Look for ISO-backed systems, documented outerwear wins, OEKO-TEX/ZDHC-aligned inputs, lab access, and transparent traceability. Verify with audits, PP sample discipline, and a pilot run. Shortlist partners who publish procedures, share lab data, and welcome third-party inspections.
Sourcing in China offers breadth of capability, material range, and speed, but quality depends on the factory’s process maturity and compliance posture. Test their claims with documents and on-floor behavior, not a showroom tour.
| Criteria | Why it matters | How to verify | Red flags |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 QMS | Process discipline and CAPA culture | Valid certificate; on-floor SOPs; CAPA logs | Expired cert; no CAPA tracker |
| OEKO-TEX/ZDHC alignment | Chemical compliance and input safety | Certificates; MRSL inventory; SDS library | Gaps in SDS; unknown sub-suppliers |
| Lab access | Faster testing and validation | In-house lab scope; third-party partners | No test reports; slow turnarounds |
| Outerwear expertise | Seam taping, insulation control, DWR | PP samples; past clients; test data | Wrinkles, seam leaks, poor tape adhesion |
| Traceability/UFLPA readiness | Import risk control for US/EU | Lot mapping; COOs; transaction docs | Missing mill invoices; vague chains |
| AQL practice | Shipment acceptance discipline | AQL records; defect Pareto; rework logs | No sampling plans; ad hoc decisions |
- China pros: Diverse mills and trims, skilled outerwear operators, sampling speed, mature testing ecosystem. [CITE: Industry capacity overview] [MENTION: CNTAC] [MENTION: Intertek China]
- China cons: Varying chemical compliance maturity, PFAS transition learning curve, documentation gaps in complex tiers if not managed.
[PAA MICRO-QUESTION] What documents should I request before placing a PO? Tech pack vFinal, PP sample sign-off, lab test plan and pre-booking, BOM with certifications, supplier list with COOs, AQL plan, social/compliance audits, and pilot-run acceptance criteria.
[INTERNAL LINK: Garment factory capability overview — https://china-clothing-manufacturer.com/garment-factory/] [INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability & Compliance Hub]
Audit & Compliance Checklist
- Quality: ISO 9001; SOPs visible at lines; measurement stations equipped; CAPA logs reviewed monthly.
- Chemical: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 inputs; ZDHC MRSL 3.1 inventory; wastewater test results if dyehouse is in chain; PFAS-free DWR disclosure.
- Social: Amfori BSCI, SMETA, SA8000 where applicable; grievance mechanism; working hours tracking. [CITE: Social audit acceptance criteria trends] [MENTION: amfori] [MENTION: Sedex]
- DPP readiness (EU): Bill of materials, material composition, durability data storage, repair information plan.
- Lab partners: Current scope with AATCC/ASTM methods; sample lead times documented.
Outerwear-Specific Capabilities
- Seam taping: Calibrated machines, trained tape operators, adhesion tests per lot, compatibility with laminates and DWR.
- Baffle and quilting control: Uniform fill, migration prevention, stitch length controls, cold-spot inspection.
- Insulation management: Down fill power validation, synthetic CLO data, laundering retention tests.
- Weather tests: Hydrostatic head targets, rainroom validation, spray tests (AATCC 22), zipper garage and storm flap function.
Traceability & UFLPA Risk Management
US-bound goods face forced labor scrutiny. Map suppliers to fiber, yarn, fabric, and trim levels. Keep COOs, purchase contracts, invoices, transport documents, and production records. For cotton, maintain farm/ginning evidence or credible tracer program documentation. [CITE: UFLPA enforcement guidance] [MENTION: US CBP] [MENTION: AAFA Traceability Playbook]
Cost, MOQ, and Lead-Time Trade-offs for High Quality Clothing
Premium quality brings upfront costs—better materials, lab tests, and more inspections—but lowers returns and reputational risk. Tune cost by matching material grades to end-use, aligning MOQs with mill realities, and phasing tests to avoid late surprises.
| Cost driver | Unit cost impact | Risk impact | Tuning tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fabric grade | High (10–35% uplift) | Lower abrasion/pilling failures | Upgrade shell; keep lining basic if hidden |
| PFAS-free DWR | Moderate (3–10%) | Meets policy; early reproofing needed | Specify wash-down; set spray ratings per cycle |
| Test intensity | Low–moderate (lab fees) | Early defect discovery | Front-load tests; batch by color/lot |
| Inspection frequency | Low (service fees) | Fewer shipment holds | Increase on new lines; taper after stability |
| MOQ strategy | High on small runs | Small lots add variability | Consolidate colors; share greige where possible |
| Lead time buffer | None to moderate | Reduces freight upgrades and rework | Add a 1–2 week lab buffer around PP |
- Returns linked to quality drive margin erosion — 2024 (Source: [CITE: “State of Fashion 2024” or comparable industry report])
- Compliance documentation requests rising in EU pilots — 2025 (Source: [CITE: EU ESPR/DPP communications])
- PFAS restrictions expanding across US states — 2024–2026 (Source: [CITE: State-level PFAS policy tracker])
MOQ & Capacity Planning
Match MOQ to mill economics and line stability. Micro-lots raise variation and test cost per unit. When launching a new shell fabric, run a pilot to validate cutting, sewing, and finishing behavior, then scale. Maintain a capacity buffer for rework without breaking the calendar.
- Pilot runs: 50–100 units per color to validate construction and cycle times.
- Shared greige: Use common base fabric with different overdyes to lower MOQ pressure.
- Capacity buffers: Reserve 5–10% capacity for rework and changeovers.
Test & Inspection Budgeting
Concentrate spend where uncertainty is highest: new fabrics, new finish chemistries, and new lines. Batch tests by color and lot; maintain a core panel of performance tests across seasons for comparability.
- Color panels: Combine similar shades for AATCC 8/61 when appropriate.
- Outerwear: Always budget hydrostatic head and seam-seal adhesion verification per lot.
- Third-party inspections: Use inline checks in season’s first month; taper as defect rates stabilize. [CITE: Inspection ROI analysis] [MENTION: QIMA] [MENTION: SGS]
Returns & Reputation Economics
Prevention beats recovery. A fit miss or seam failure erodes reviews and compresses margin through returns and discounts. A fraction of the unit cost spent on upstream testing and approvals usually saves multiples in reverse logistics and salvage. [CITE: Returns cost study in apparel] [MENTION: NRF] [MENTION: McKinsey]
Data & Trends: Quality, Sustainability, and Compliance in US & EU
Quality is moving from claims to proof. Expect requests for lab data, digital product information, and supply chain documentation. EU ESPR/DPP pilots are building the template, and US import scrutiny around forced labor keeps documentation in focus.
- EU ESPR adopted framework for eco-design and DPP — 2024 (Source: [CITE: European Commission ESPR page])
- UFLPA detentions continue in apparel — 2023–2025 (Source: [CITE: US CBP enforcement updates])
- Consumer demand for durability claims climbing — 2024 (Source: [CITE: Market research on durability claims])
EU ESPR & Digital Product Passport
DPP will require data transparency: material composition, durability metrics, repair options, and end-of-life guidance. Store test results, care validation, and supplier identities in a retrievable format. Plan for QR-accessible data on-garment for EU launches. [CITE: ESPR/DPP explainer] [MENTION: European Commission] [MENTION: GS1]
US Import Controls & Safety
UFLPA asks importers to prove clean supply chains. Prepare supplier maps, transaction docs, and fiber origin evidence. For children’s wear, CPSIA tracking labels, lead testing, and small parts requirements remain table stakes. [CITE: UFLPA Operational Guidance] [CITE: CPSC CPSIA apparel guidance] [MENTION: US CBP] [MENTION: CPSC]
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service integrates design support, certified sourcing, standards-based testing, and AQL-driven QC across China and Bangladesh. We translate high quality clothing specs into production-ready controls and deliverables—on time and at scale.
| Brand need | OEM feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Durability and fit consistency | Tech pack creation, fit blocks, lab plan | Fewer returns; consistent size runs |
| Weather protection without PFAS | PFAS-free DWR sourcing, seam-tape validation | Regulatory alignment; reliable spray ratings |
| Compliance & traceability | OEKO-TEX/ZDHC inputs; documentation flow | Audit-ready files; faster customs clearance |
| Scale with lower risk | Inline inspection + CAPA; AQL final | Stable output; predictable launches |
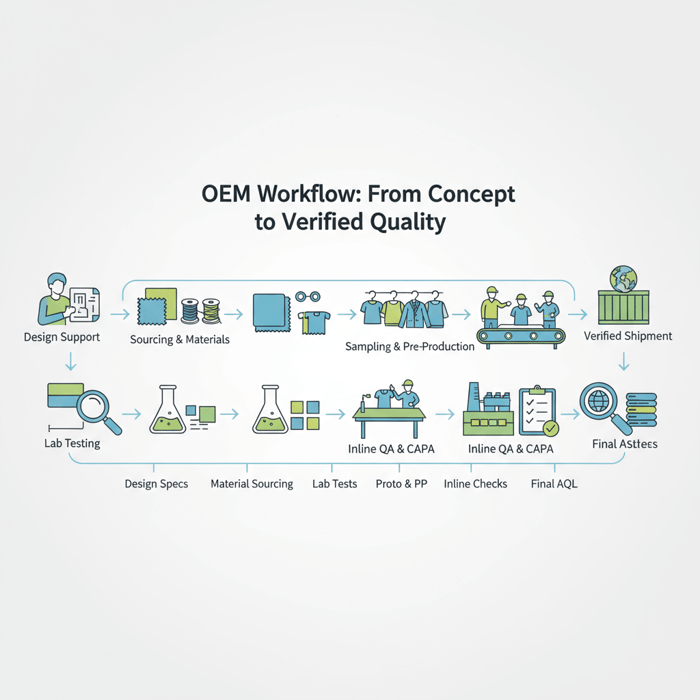
See our garment factory capability overview: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service. We run proto-to-PP-to-final with AQL levels commonly at 2.5 for majors and 4.0 for minors, adjusting per risk and price point. [MENTION: Eton Garment Limited] [INTERNAL LINK: Full-Service OEM/ODM for Brands]
Use Case 1: Premium Outerwear (Problem → Solution)
Problem: A waterproof-breathable jacket failed rain tests and experienced tape lift in shipment two. Solution: Switch to a compatible 3L laminate, tighten seam allowance windows, recalibrate tape temperature/pressure, add ISO 811 and adhesion tests per lot, upgrade to PFAS-free DWR with wash-down targets, and validate zippers with 10,000-cycle tests. Result: Stable performance across colors. [CITE: Case example format used by third-party labs] [MENTION: YKK] [MENTION: W.L. Gore & Associates]
Use Case 2: Branded Lifestyle Capsule (Problem → Solution)
Problem: Inconsistent fits across factories drove high returns. Solution: Create brand fit blocks, consolidate trims, load inline measurement stations, publish a tolerance table per POM, and run AQL majors at 1.5 for the first two drops. Result: Return rate dropped; reviews improved. [CITE: Fit consistency and returns correlation] [MENTION: Shopify research unit] [MENTION: Narvar]
Risks, Compliance & Localization
Define risks early—defects, chemical non-compliance, forced labor exposure—and mitigate with test plans, audits, and labeling/documentation aligned to destination markets. Keep disclosure honest: if a finish underperforms after washing, set care or product claims accordingly.
- Pros: Standards-first approach creates a common language across brand, factory, and lab; documentation speeds audits.
- Cons: Upfront testing and longer PP windows add to calendar; PFAS-free transitions may reduce initial water repellency ratings.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color crocking (dark shades) | Medium–high | High (returns, complaints) | AATCC 8/61; adjust dyeing; use cationic fixatives |
| Seam leakage | Medium | High | ISO 811/AATCC 127; seam tape calibration; PP rainroom |
| PFAS non-compliance | Rising | High (regulatory, brand) | PFAS-free DWR; supplier attestations; targeted lab screens |
| UFLPA documentation gaps | Medium | High (detention) | Supplier maps, COOs, farm-level evidence or tracer |
| Fit drift across sizes | Medium | Medium–high | Size set approvals; inline POM checks; tolerance enforcement |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
US: CPSIA labeling and children’s safety testing; FTC care and fiber labeling; UFLPA documentation for imports. EU: REACH SVHCs, Nickel directive (EN 1811), Textiles Regulation 1007/2011 for fiber names, ESPR/DPP trajectory for transparency. [CITE: REACH SVHC summary] [CITE: EU Textiles Regulation 1007/2011] [MENTION: ECHA] [MENTION: DG ENER]
Disclaimer: Compliance notes are guidance. Confirm requirements with counsel and accredited labs. Destination-specific rules may require additional testing and labeling.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Define “high quality clothing” as measurable performance and workmanship, choose a China partner with proof-backed systems, plan trade-offs early, and document compliance. Follow a gated path and you’ll scale consistency without mid-season surprises.
- Week 1–2 — Specs/tests: Finalize tech pack, tolerance tables, BOM, and lab plan. Pre-book tests.
- Week 3–6 — Sampling: Proto, fit, size set, PP; lock construction, tape settings, and trims.
- Week 7–12 — Pilot/inline: Run pilot, increase inline sampling; apply CAPA where defects appear.
- Pre-ship — Final AQL: Execute AQL by risk class; verify cartons, labels, and documents.
Ready to build on this framework? Explore Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service and connect with our manufacturing team. [INTERNAL LINK: Contact Manufacturing Team] [INTERNAL LINK: Performance Outerwear OEM/ODM pillar page]
References & Sources
- ISO — ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems (Current). [CITE: ISO 9001 overview page URL]
- OEKO-TEX — STANDARD 100 (2024). [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 URL]
- ZDHC — MRSL v3.1 (2023). [CITE: ZDHC MRSL page]
- European Commission — Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) & Digital Product Passport (2024). [CITE: ESPR/DPP page]
- U.S. CPSC — CPSIA Guidance for Apparel/Textiles (2023/2024). [CITE: CPSC apparel guidance page]
- U.S. CBP — UFLPA Operational Guidance for Importers (2023/2024). [CITE: CBP UFLPA page]
- AATCC — Test Methods (2023–2024). [CITE: AATCC test methods portal]
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024. [CITE: McKinsey report URL]
- Worldly (Higg) — Facility Modules & Methodology (2023–2024). [CITE: Worldly methodology page]
- FTC — Care Labeling Rule and Fiber Labeling (Current). [CITE: FTC labeling pages]
- ECHA — REACH SVHC and Nickel release guidance (Current). [CITE: ECHA pages]
- AAFA — Traceability and Forced Labor Resources (Current). [CITE: AAFA resource page]
FAQs
Related Articles

Chinese dress shop vs China clothing manufacturer: how brands move from retail inspiration to scalable OEM/ODM
10 minute read
October 15th, 2025
Chinese dress shop vs China clothing manufacturer: how brands move from retail inspiration to scalable... more »

Empowering Your Brand: The Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Company Logo Clothing as a Leading Clothing Manufacturer
15 minute read
October 15th, 2025
Empowering Your Brand: The Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Company Logo Clothing as a Leading Clothing Manufacturer... more »
Screenprint T Shirts: A Fashion Brand’s Guide to Sourcing at Scale with a China Clothing Manufacturer
19 minute read
October 15th, 2025
Screenprint T Shirts: A Fashion Brand’s Guide to Sourcing at Scale with a China Clothing... more »
Discover the World of Kinds of Hats: Essential Insights for Fashion Sourcing Managers Seeking Innovation and Excellence
8 minute read
October 15th, 2025
Discover the World of Kinds of Hats: Essential Insights for Fashion Sourcing Managers Seeking Innovation and... more »

