Garment Manufacture: How Fashion Brands Choose a China Clothing Manufacturer
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
6 minute read
Garment Manufacture: How Fashion Brands Choose a China Clothing Manufacturer
Garment manufacture for a China Clothing Manufacturer is the end-to-end path from a tech pack to shipment—spanning sampling, sourcing, cutting, sewing, finishing, QA, and compliance for US/EU markets. Brands moving from prototypes to scale need clear models (OEM vs ODM), transparent costs/MOQs, dependable timelines, and documented quality systems to avoid missed deadlines and non-compliance.
Garment manufacture converts tech packs into finished apparel through sampling, sourcing, cutting, sewing, finishing, quality checks, and shipment. When selecting a China clothing manufacturer, weigh category expertise, compliance for REACH/CPSIA, lead times, MOQs, and QC maturity—especially for technical outerwear. Favor transparent costs, AQL QA, and clear responsibilities across OEM/ODM models.
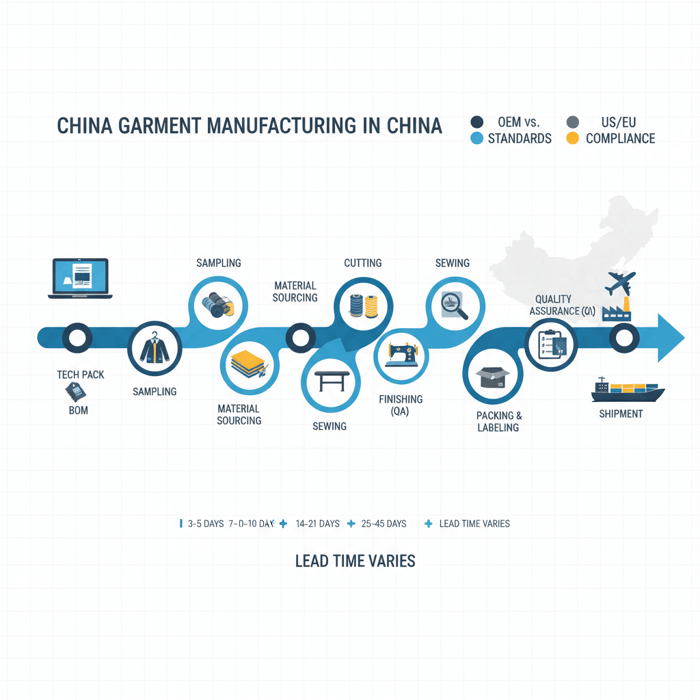
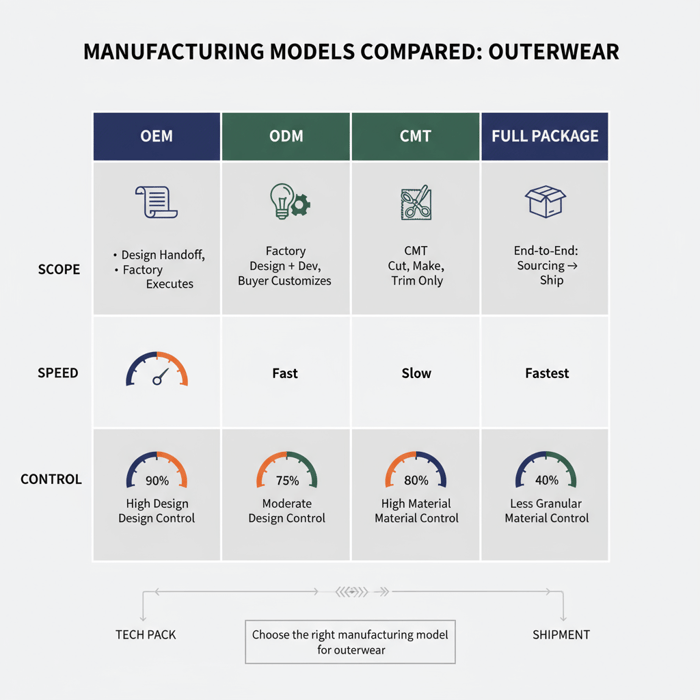
Garment Manufacture 101: OEM vs ODM, CMT vs Full Package
OEM delivers against your design and tech pack; ODM adds in-house design and development; CMT focuses on cut-make-trim only; full-package covers sourcing through delivery. For outerwear, model choice impacts speed, control of fit and performance, and total landed cost.
| Model | What it includes | Pros | Cons | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacture to buyer tech pack, BOM, and patterns; factory executes sampling and bulk. | Strong control over design; predictable fit blocks; easier brand IP protection. | Requires complete specs; more buyer-side development work. | Established brands with design teams; consistent outerwear blocks and standards. |
| ODM | Factory provides design concepts, patterns, and development; buyer customizes and approves. | Faster concepting; access to factory R&D; lower upfront development cost. | Less IP control; fit/feature compromises across shared blocks. | Private-label and speed-focused collections; smaller teams scaling category assortment. |
| CMT | Cut, make, trim labor only; buyer supplies fabric, trims, patterns, and markers. | Tight material control; potential cost savings on sourcing. | High buyer workload; coordination risks; multiple vendor interfaces. | Experienced sourcing teams; repeat styles with locked supply chain inputs. |
| Full Package | End-to-end: sourcing, sampling, production, QA, logistics support. | Single accountable partner; speed through material ecosystem. | Less granular material control unless specified; requires trust and audits. | Brands scaling fast with lean teams; complex outerwear needing integrated capabilities. |
The Roles of Tech Pack and BOM
A complete tech pack defines silhouette, graded measurements, construction details, stitch types, seam allowances, trim placements, and performance targets. Pair it with a BOM listing fabrics, insulation, linings, zippers/snaps, seam tape, labels, and packaging—down to color codes, finishes, and supplier references. For outerwear, specify water column/breathability ranges (e.g., 10,000 mm / 10,000 g/m²/24h), insulation CLO targets, seam sealing coverage, and functional tests (e.g., rain room, hydrostatic head). Attach reference photos or line drawings, fit comments, tolerance tables, and testing methods so the factory interprets requirements consistently.
Ownership of IP, Patterns, and Tooling
Define ownership of base patterns, graded sets, digital markers, and custom tools (e.g., quilting templates, seam tapes) in the contract. State whether vendor grading and CAD files are licensed to the brand, and clarify whether pattern changes are exclusive to your styles. If ODM concepts are used, specify design IP boundaries and co-ownership terms. Document file handover at project close, especially for multi-country splits where markers and QC specs must travel intact. Lock naming conventions and version control to prevent drift across sampling rounds.
[CITE: Industry contract templates for apparel sourcing covering IP and tooling ownership] [MENTION: YKK for closure systems; 3M Thinsulate insulation] [INTERNAL LINK: Our OEM vs ODM outerwear guide]
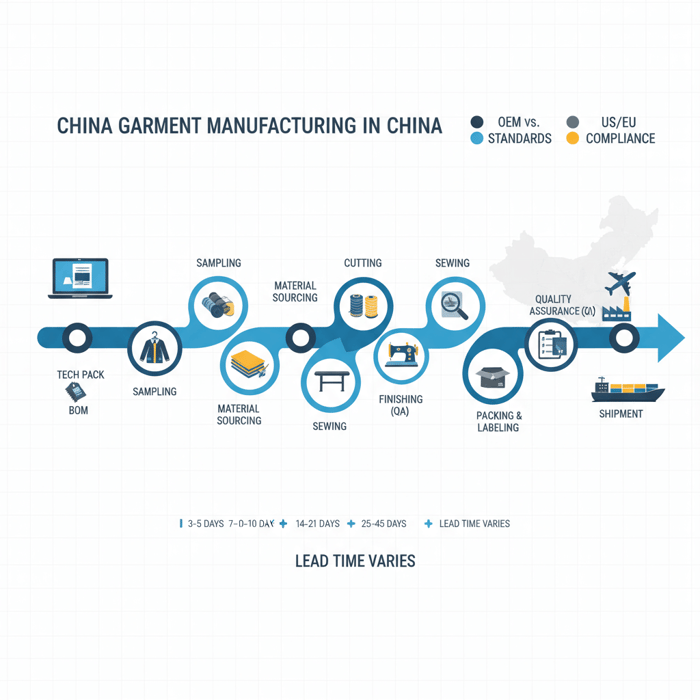
The Garment Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step with Lead Times
From design handoff to TOP approval and shipment, outerwear timelines in China typically span multiple sampling rounds, material buys, bulk production, QA, and logistics. Knowing inputs, outputs, ownership, and likely bottlenecks keeps projects on schedule.
- Kickoff: Confirm tech pack, BOM, size run, target AQL, compliance scope, and delivery window.
- Proto Sample (P1): Build from available stock fabrics to test silhouette, construction, and initial measurements.
- Fit Sample (F1/F2): Correct fit and balance; check grading logic; align measurement tolerances.
- Material Sourcing: Lock mills, insulation specs, seam tapes; issue POs aligned to MOQs and test plans.
- PP Sample: Produce with bulk materials and final construction; approve as the production blueprint.
- Bulk Production: Cutting, sewing, seam sealing, finishing, and inline QA.
- TOP (Top of Production): Pull finished units to confirm alignment with PP and QC criteria.
- Final QA + Packing: AQL inspection; carton and labeling per destination rules.
- Shipment: Book logistics; prepare compliance and customs documents.
| Stage | Inputs | Outputs | Timeframe | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kickoff | Tech pack, BOM, QA/Compliance scope | Confirmed spec, plan, milestones | 3–5 days | Brand + Factory |
| Proto (P1) | Base pattern, available materials | Prototype sample; issue list | 7–10 days | Factory |
| Fit (F1/F2) | P1 feedback; measurement targets | Adjusted pattern; fit signoff | 10–14 days | Brand + Factory |
| Material Sourcing | BOM; lab test plan | Bulk POs; test reports | 14–21 days | Factory |
| PP Sample | Bulk material; final spec | Approved PP sample | 7–10 days | Factory |
| Bulk Production | PP approval; cut plan | Finished units | 25–45 days | Factory |
| TOP | Finished garments | TOP approval record | 2–4 days | Brand + Factory |
| Final QA + Packing | AQL plan; labels/cartons | Inspection report; packed goods | 3–5 days | Factory |
| Shipment | Logistics booking | B/L; compliance docs | Lead time varies | Factory + Forwarder |
Sampling Phases: Proto → Fit → PP
Proto sample proves silhouette and construction. Fit rounds correct shoulder slopes, sleeve length, armhole ease, and grading across sizes. PP locks materials and manufacturing methods; it is the only sample that should proceed to bulk identical and without substitutions. Track change logs with versioned fit comments, and never merge changes without revalidation. For outerwear, include test panels for seam sealing and insulation loft so construction and thermal targets hold under real production conditions.
Inline, End-line, and Final QA
Apply AQL sampling plans with clear defect categories (critical, major, minor). Inline QA catches sewing and sealing issues early; end-line checks confirm finishing and measurements; final QA verifies presentation, labeling, and packaging. Record measurement tables for each size, and keep CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions) documentation if defect rates exceed thresholds. Align QA with ISO 9001 systems for traceability and continuous improvement. [CITE: ISO 9001 guidance for apparel factories] [MENTION: SGS, Intertek as accredited labs]
TOP Approval and Shipment Prep
TOP approval pulls finished units early in bulk to confirm alignment with the PP sample and QC criteria. Inspect construction, measurements, seam sealing, appearance, and labeling against AQL plans. Once approved, prepare shipment by booking logistics and assembling compliance documents (REACH/CPSIA test reports, GCC for US children’s products, packing list, commercial invoice, and bill of lading). Keep identical document versions between factory and brand to avoid customs delays.
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
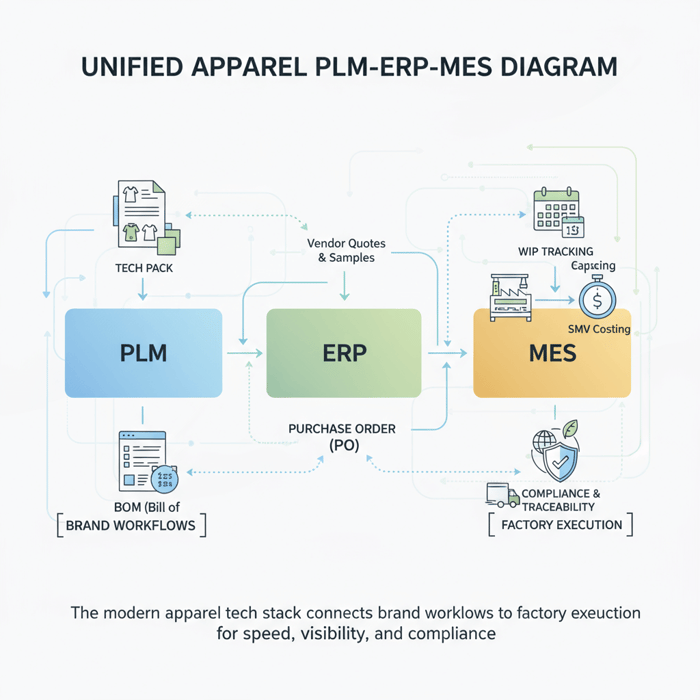
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

