Fashion Wholesale Marketplace: The China Clothing Manufacturer’s Guide for US & EU Brands
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
15 minute read
Fashion Wholesale Marketplace: The China Clothing Manufacturer’s Guide for US & EU Brands
Fashion wholesale marketplace choices shape margin, speed, and risk for US and EU fashion brands. For teams deciding between ready-to-ship wholesale and a China Clothing Manufacturer for OEM/ODM, this guide offers a compliant, margin-aware roadmap. It shows where wholesale fits, how to vet suppliers, what costs matter, and when to pivot to manufacturing for control and scale.
A fashion wholesale marketplace is a B2B platform where brands and retailers buy ready-made apparel from multiple suppliers. Use marketplaces to test trends and replenish basics with speed; shift to OEM/ODM with a China Clothing Manufacturer when repeat demand, margins, and compliance needs justify custom design, larger volumes, and tighter cost control.
Wholesale decisions now determine whether emerging labels grow with healthy margins and low risk. This guide blends marketplace selection with a manufacturer’s view to help US/EU teams decide when wholesale works, how to vet vendors for quality and compliance, and how OEM/ODM unlocks uniqueness and better unit economics at scale. You’ll get a category-fit comparison of major platforms, a compliance-first workflow aligned to REACH/CPSIA/UFLPA, margin math including Incoterms and landed-cost modeling, and a practical transition plan into manufacturing with Eton Garment Limited. Expect a step-by-step sourcing process, document checklists, and risk controls used in real outerwear projects. Move from small tests to confident production without quality surprises or regulatory setbacks.
Fashion Wholesale Marketplace: Definition & How It Works
A fashion wholesale marketplace aggregates multiple apparel suppliers so brands can browse catalogs, request samples, place purchase orders, and manage payments in one place. It accelerates trend tests and replenishment, but limits design control and uniqueness compared with OEM/ODM manufacturing where you own specs, trims, and fit.
- What it is: A digital B2B platform listing wholesale-ready apparel with prices, MOQs, lead times, and returns/policies.
- How buying works: Browse or filter by category, request samples, confirm MOQs, set terms and Incoterms, place a PO, and track fulfillment.
- Common fees: Platform commissions, payment processing, shipping or logistics fees, and returns/restocking policies. [CITE: “Platform fee schedules from leading B2B marketplaces, 2024 updates”]
- Lead times: From ready-to-ship in 3–7 days for in-stock to 2–8 weeks for made-to-order wholesale lines.
- Compliance touchpoints: Collect material and chemical declarations, labeling templates, CPSIA/REACH test reports, and forced-labor due diligence statements early. [CITE: “ECHA REACH scope and restricted substances list (updated)”] [CITE: “CPSC CPSIA apparel testing & tracking label guidance, current year”]
PAA: What’s the difference between a wholesale marketplace and a supplier directory? A marketplace handles listings and transactions and often payment and returns; a directory lists suppliers but leaves due diligence, negotiation, and contracting to you.
[MENTION: Faire marketplace overview (company).] [MENTION: Alibaba platform B2B model (company).] Our foundational guide on OEM vs. ODM explained.
Marketplace Mechanics (Discovery → Vetting → Sample → PO → Delivery)
Discovery: Filter by category (outerwear, streetwear, kids), material, MOQ, and location. Save shortlists and request line sheets. [MENTION: JOOR and NuORDER as B2B wholesale showrooms.]
Vetting: Review store ratings, complaint history, and return rates on-platform. Request brand lists, social proof, and compliance documents (REACH/CPSIA test reports, fabric specs, fiber content declarations). Add a forced-labor risk questionnaire aligned with UFLPA import screening for US-bound goods. [CITE: “CBP UFLPA Operational Guidance for Importers, 2024”]
Sampling: Define pass/fail criteria (fabric GSM and composition verified by lab, color fastness, seam strength, fit). Use the same lighting and size chart used in shoots. Retain counter-signed samples.
PO: Fix Incoterms 2020 (EXW/FOB/DDP), payment terms, AQL sampling level, and rework/returns clauses in writing. Align HS codes and duty estimates for US/EU lanes. [CITE: “ICC Incoterms 2020 official overview”]
Delivery: Book logistics to match Incoterms. Inspect on arrival with a receiving checklist (carton integrity, barcode scans, size ratio, hangtags, fiber labels).
When Marketplaces Fit vs. Don’t Fit
- Fits: Capsule tests (50–300 units/style), replenishment of evergreen basics, limited-time drops, fast trend reads, and budget-constrained seasons.
- Doesn’t fit: Proprietary fits, unique trims/branding, technical outerwear with strict testing, performance gear with lab certifications, or volumes beyond 2,000–5,000 units per style where OEM/ODM brings better margin.
- Risk tolerance: Marketplaces reduce minimum commitment and lead time but cap differentiation and control. If reliability, IP protection, and detailed compliance are non-negotiable, OEM/ODM is the better path.
Our primer on Sustainability & compliance for apparel. [MENTION: SGS and Bureau Veritas testing services.]
Best Fashion Wholesale Marketplaces: Comparison & Fit
Different platforms serve different use cases: contemporary boutiques (Faire), LA trend-driven assortments (FashionGo/LA Showroom), enterprise B2B (JOOR, NuORDER), and global sourcing (Alibaba). Choose by category fit, MOQs, compliance support, payment terms, and logistics options.
| Platform | Category Fit | Typical MOQ | Lead Time | Compliance Support | Fees/Terms | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faire | Contemporary, boutique edits | 6–24 units/style | In-stock or 2–6 weeks | Basic policies; vendor-provided docs | Platform commission; net terms options | Independent retailers, capsule tests |
| FashionGo | Trend, streetwear, LA-driven | Pre-pack ratios | In-stock or 1–4 weeks | Limited; rely on supplier | Listing/transaction fees vary | Fast trend reads, value tiers |
| LA Showroom | LA brands, occasion, basics | Pre-pack ratios | In-stock or 1–4 weeks | Limited; rely on supplier | Platform + payment fees | US boutiques needing speed |
| JOOR | Premium/enterprise showrooms | Varies by brand | Seasonal order cycles | Brand-driven standards | SaaS + transaction models | Established labels, B2B wholesale |
| NuORDER | Enterprise linesheets & B2B | Varies by brand | Seasonal order cycles | Brand-driven standards | SaaS + services | Growth brands scaling wholesale |
| Alibaba | Global sourcing, breadth | Varies; many 100–300+ | Made-to-order 3–8 weeks | Supplier-provided; verify rigorously | Listing + escrow-style options | Supplier discovery, FOB pricing |
| Handshake | US-focused wholesale | Low to medium | In-stock or 2–4 weeks | Basic guardrails | Platform commission | SMB retailers on Shopify |
- Pros: Speed to market, breadth of selection, low initial capital outlay, easier returns or cancellations on some platforms.
- Cons: Limited control over fit and branding, variable compliance documentation, inconsistent quality, and capped margins at scale.
- Wholesale volatility and inventory risk remain elevated after 2023; speed-to-shelf remains a priority for brands (Source: [CITE: “McKinsey State of Fashion 2024/2025”]).
- Private-label growth outpaces multi-brand wholesale in several categories, pushing brands toward OEM/ODM for margin (Source: [CITE: “Industry analysis on private-label expansion, 2024–2025”]).
[MENTION: JOOR case studies on digital wholesale.] [MENTION: Alibaba trade assurance references.]
Criteria Overview (Category, MOQ, Compliance, Logistics, Fees)
- Category fit: Match your core assortment (outerwear vs. dresses vs. kidswear). Ask for production histories and return rates by category.
- MOQs: Check pre-pack ratios vs. open-size runs. Confirm replenishment rules and closeout policies.
- Compliance: Require test reports for restricted substances, flammability (where applicable), and labeling. Validate lab names (SGS, Intertek, Bureau Veritas). [CITE: “Global apparel test protocols, 2023–2025 updates”]
- Logistics: Confirm shipping options (domestic vs. international), Incoterms, and duty/tax handling for US/EU.
- Fees/terms: Model platform commissions, payment processing, and returns against expected sell-through and markdowns.
Decision Framework (Pilot, Replenish, Scale, Transition)
- Pilot: 50–150 units/style; sample fast; verify compliance; monitor return rates.
- Replenish: Repeat POs for styles with 60–70% sell-through in 4–8 weeks; tighten QC and packaging controls.
- Scale: Negotiate better pricing or net terms; formalize AQL and carton specs; consider multi-source risk hedging.
- Transition: Move proven styles to OEM/ODM once monthly volume exceeds 500–2,000 units and customization or margin gains justify it.
Our Outerwear development hub.
Fashion Wholesale Marketplace vs OEM/ODM Manufacturing
Marketplaces win on speed and low initial commitment. OEM/ODM wins on control, brand uniqueness, and unit costs at scale. Pivot once repeat demand stabilizes, margins are capped by wholesale pricing, or compliance/customization needs exceed platform offerings.
| Dimension | Marketplace | OEM/ODM with a China Clothing Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast (in-stock 3–7 days) | Slower upfront (sampling/dev), faster at scale |
| MOQ | Low to mid; pre-packs | Higher per style initially; negotiable with volume |
| Unit Cost | Fixed wholesale; limited negotiation | Lower with volume and material leverage |
| Branding | Limited customization | Full control over trims, fit, and packaging |
| IP & Design | Shared styles risk sameness | Original patterns and protected fits |
| Compliance | Supplier-provided; variable rigor | Programmatic testing and documentation |
| Scale | Limited by supplier stock and policies | Built for 1,000–10,000+ units per style |
Transition Triggers (Volume, Margin, Differentiation, Compliance)
- Volume: 500–2,000+ units per style per month or multi-season repeats.
- Margin: Wholesale pricing caps gross margin; OEM/ODM can unlock 10–25 percentage points depending on material and process control. [CITE: “Gross margin benchmarks for private label vs wholesale, 2024 report”]
- Differentiation: Fit, trims, and exclusive fabrics required to stand apart.
- Compliance: Need for recurring lab testing, factory audits, and traceability beyond what platforms provide.
Common Pitfalls When Switching
- Underestimating development time: Plan 6–12 weeks for sampling on technical outerwear.
- Incomplete tech packs: Ambiguity raises unit cost and delays approvals.
- Skipping pre-production samples: Approve PP samples before bulk to avoid spec drift.
- Ignoring Incoterms: EXW vs. DDP shifts risk and cost; misalignment hurts margin.
- Insufficient compliance evidence: Keep lab reports, fiber tests, and origin documents audit-ready. [CITE: “EU Textile Regulation 1007/2011 labeling requirements”]
[MENTION: Intertek performance testing.] Our foundational guide on OEM vs. ODM explained.
How to Source on Fashion Wholesale Marketplaces (Step-by-Step)
Use a structured workflow: define a requirement, shortlist vendors, sample against test criteria, run AQL checks, verify compliance, and stage POs with clear QC gates and logistics plans. This mirrors onboarding and QC steps Eton runs in China and Bangladesh for outerwear and technical apparel.
Preparation (Tech Pack, Compliance Requirements, Target Landed Cost)
- Define assortment intent: trend capsule, evergreen basics, or seasonal story. Lock size curves and colorways.
- Set compliance bar: US (CPSIA/CPSC), EU (REACH), country of origin, fiber content, care labels, and any performance claims. [CITE: “CPSC CPSIA guide for apparel labeling”] [CITE: “ECHA SVHC updates, latest list”]
- Budget landed cost: Build a target cost with Incoterms, freight, duties, insurance, testing, and returns allowance.
- Create sampling checklist: Fabric GSM, composition, trims, stitching SPI, zipper spec, seam strength, color fastness.
- Receiving standards: Carton marks, barcode placement, folding/packing method, hangtag placement, polybag warnings.
Execution Steps (Shortlist → Sample → Test → Negotiate → PO → QC → Ship)
- Shortlist: 5–8 vendors across 2–3 platforms. Check ratings, disputes, and MOQ fit.
- Sample: Order samples; test against checklist; record pass/fail with photos.
- Lab test: Send critical items to an accredited lab (SGS, Bureau Veritas, Intertek) for chemical and performance tests. [CITE: “Recognized apparel testing labs directory, 2024”]
- Negotiate: Confirm price breaks, replenishment windows, pre-pack flexibility, and returns. Lock Incoterms and transit times.
- PO: Attach spec sheets, AQL level, defect classification (minor/major/critical), and rework/chargeback rules.
- QC: Pre-shipment inspection with ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 (ISO 2859-1) sampling plan. [CITE: “ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 / ISO 2859-1 overview, 2023”]
- Ship: Align labels, HTS codes, and documents. For US: prepare UFLPA origin/traceability files; for EU: REACH documentation binder.
Quality Assurance (AQL Sampling, Testing Labs, Packaging Checks)
- AQL: Choose General Inspection Level II, AQL 2.5–4.0 for major defects depending on category risk.
- Testing cadence: Pre-production verification for high-risk materials; random checks each shipment for color fastness, seam strength.
- Packaging: Verify carton burst strength, poly thickness, warning labels, barcode scannability, and size ratio accuracy.
[MENTION: ISO 2859-1 sampling standard.] Our Outerwear development hub.
Costs, MOQs & Margin Math
Model margin with clear Incoterms, MOQs, and payment terms. Landed cost equals product, freight, duties, insurance, testing, compliance, handling, and returns allowance. Use staged buys to reduce risk and renegotiate after demand validation.
| Scenario | Cost Components | Who Controls Freight/Duties | Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| EXW (Ex Works) | Unit price + inland pickup + export clearance + international freight + insurance + duties/taxes + drayage + delivery + testing/compliance | Buyer | Max control; higher admin load and risk |
| FOB (Free on Board) | Unit price to port + international freight + insurance + duties/taxes + drayage + delivery + testing/compliance | Buyer from origin port | Balanced control and complexity |
| DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) | Unit price + logistics bundled + duties/taxes included + testing/compliance may be separate | Seller | Low admin; validate hidden margins |
Incoterms & Landed Cost
- Pick Incoterms 2020 deliberately. FOB suits brands with freight partners; DDP can speed pilots but obscures cost drivers. [CITE: “ICC Incoterms 2020 reference”]
- Duty planning: Assign correct HS codes; check USITC HTS and EU TARIC. [CITE: “USITC HTS search, 2024”] [CITE: “EU TARIC database, 2024”]
- Testing and compliance: Budget $50–$300 per style for lab checks depending on scope.
- Returns allowance: Add 1–3% of cost for potential rework/returns in pilots; refine as you stabilize quality.
MOQ Strategy and Renegotiation Points
- Start small: 50–150 units to validate; expand to 300–600 units with price breaks.
- Negotiate: Price ladders at 200/500/1,000 units; lock validity periods and raw material volatility clauses.
- Switch levers: Move to OEM/ODM once price ladders flatten and differentiation needs rise.
- Incoterms define cost and risk allocation in cross-border trade (Source: [CITE: “ICC Incoterms 2020 summary”]).
- Apparel duties vary widely by HS code and fiber content—check before setting retail (Source: [CITE: “USITC HTS / EU TARIC official sites”]).
Garment factory capabilities for outerwear.
Risks, Compliance & Localization
US/EU compliance must be built into sourcing. For the EU, align with REACH restrictions and documentation. For the US, meet CPSIA labeling/testing and prepare for UFLPA origin and traceability screening. Require test reports, supplier declarations, and audit-ready files for every shipment.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forced-labor flags (UFLPA) | Medium | Severe | Traceability docs, supplier screening, CBP-ready files, alternative sources. [CITE: “CBP UFLPA guidance, 2024”] |
| REACH chemical non-compliance | Low–Medium | Severe | Lab tests per material; supplier declarations; substance monitoring. [CITE: “ECHA REACH guidance”] |
| CPSIA labeling/testing gaps | Low–Medium | High | Tracking labels; flammability tests where applicable; certificates of conformity. [CITE: “CPSC CPSIA apparel guidance”] |
| Quality variation | Medium | High | AQL 2.5–4.0; PP sample approval; defect chargebacks. |
| IP/design overlap | Medium | Medium | Move proven styles to OEM; NDAs; unique trims/patterns. |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
- US: CPSIA requires tracking labels and test certificates for certain categories; retain lab reports and supplier attestations. UFLPA requires heightened due diligence on origin and inputs. [CITE: “CPSC CPSIA overview”] [CITE: “CBP UFLPA Operational Guidance”]
- EU: REACH restricts chemicals and imposes documentation duties. Maintain safety data, test results, and supplier declarations. [CITE: “ECHA REACH regulation portal”]
[MENTION: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 as a voluntary chemical safety label.]
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Use marketplaces to validate demand and timing; switch to Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service to improve margin, control design, and scale with documented compliance—especially for jackets, padded coats, and technical apparel.
| Brand Need | OEM/ODM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Better margin on repeat styles | Material leverage, tiered price ladders | Lower unit cost at 500–10,000+ units |
| Unique fit and trims | Patternmaking, lab dips, trim sourcing | Exclusive look and brand alignment |
| Compliance at scale | Programmatic testing (REACH/CPSIA), audits | Audit-ready shipments and documentation |
| Technical outerwear | Taped seams, performance lab tests, field trials | Reliable results in demanding use-cases |
Eton Garment Limited operates modern facilities in China and Bangladesh and supports OEM/ODM from design and fabric sourcing to production and QC, backed by international compliance. Learn more about our Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service.
Use Case 1: Trend Capsule → OEM for Margin and Brand Control
A US boutique validated a quilted bomber on a fashion wholesale marketplace at 300 units across two drops. Gross margin plateaued at wholesale price floors. Eton replicated the aesthetic through OEM, optimized pattern and fill weight, sourced a down-proof fabric with lab-backed color fastness, and secured a 15–20 point margin lift at 1,500 units per reorder. Documentation included REACH test reports and CPSIA labeling kits. [CITE: “Color fastness test methods (AATCC/ISO) reference”]
Use Case 2: Technical Outerwear with Strict QC
A European brand needed a waterproof parka meeting hydrostatic head and seam sealing requirements. Marketplace options lacked verified testing. Eton’s ODM team delivered fabric development, seam taping, PP sample approvals, and third-party lab tests for water resistance and seam slippage. The project used AQL 2.5, carton drop tests, and barcoded packaging, with full REACH documentation and factory audit records ready for EU import. [CITE: “Hydrostatic pressure testing standards, ISO/AATCC”]

Garment factory capabilities for outerwear. [MENTION: AATCC and ISO test standards.]
Conclusion & Next Steps
Pick a marketplace by category fit, MOQ flexibility, and compliance readiness. Pilot with samples, set QC gates, and document every shipment. Once styles repeat and margins cap out, move to OEM/ODM with a trusted China Clothing Manufacturer to regain control over fit, branding, and cost.
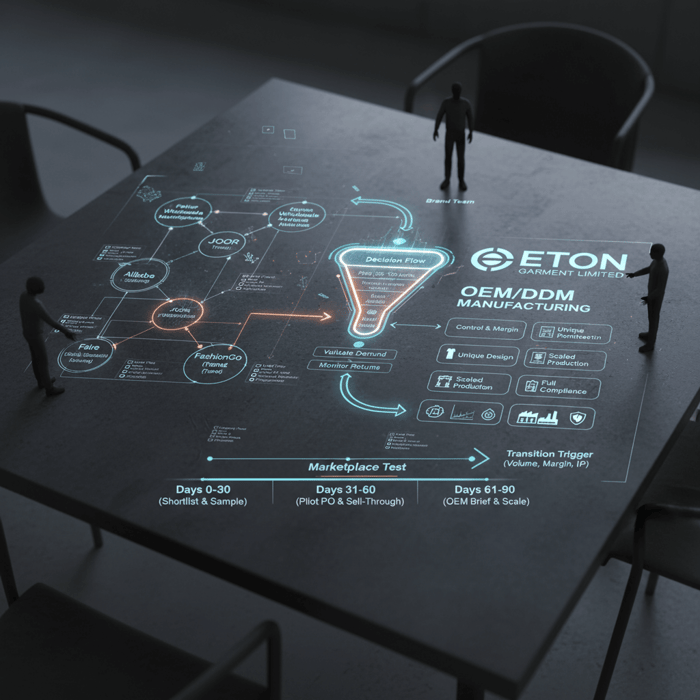
- Days 0–30: Shortlist platforms and suppliers; lock compliance criteria; sample and lab test.
- Days 31–60: Place a pilot PO with AQL and Incoterms set; monitor sell-through and returns.
- Days 61–90: Negotiate replenishment; prepare OEM brief for winning styles; request costed BOM and PP sample with Eton.
Ready to shift proven winners to OEM/ODM? Share a brief and target landed cost. Eton will map sampling, testing, and QC to your category and market.


Author: Senior Apparel Sourcing Strategist (10+ years in OEM/ODM, US/EU compliance). Reviewer: Eton Technical Director, Outerwear (15+ years). Methodology: Marketplace best practices blended with Eton’s OEM workflows; aligned with CBP, ECHA, CPSC guidance. Limitations: Platform fees, MOQs, and regulations evolve; validate at time of sourcing. Disclosure: Eton provides OEM/ODM manufacturing; no paid endorsements for marketplaces.
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024/2025 (2024). [CITE: “McKinsey State of Fashion”]
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection — Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) Guidance (2024). [CITE: “CBP UFLPA guidance”]
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) — REACH Regulation Guidance (2024). [CITE: “ECHA REACH portal”]
- U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) — CPSIA Guidance for Apparel (2024). [CITE: “CPSC CPSIA portal”]
- International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) — Incoterms 2020 (2020). [CITE: “ICC Incoterms site”]
- USITC — Harmonized Tariff Schedule (2024). [CITE: “USITC HTS online”]
- EU — TARIC Consultation (2024). [CITE: “EU TARIC”]
- ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 / ISO 2859-1 — Sampling Procedures for Inspection by Attributes (2023). [CITE: “ISO 2859-1 overview”]
- OEKO-TEX — Standard 100 (2024). [CITE: “OEKO-TEX Standard 100”]
- AATCC/ISO — Color Fastness & Hydrostatic Pressure Test Methods (2023–2024). [CITE: “AATCC/ISO standards”]
[MENTION: Faire.] [MENTION: JOOR.] [MENTION: NuORDER.] [MENTION: Alibaba.] Our foundational guide on OEM vs. ODM explained. Garment factory capabilities for outerwear.
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
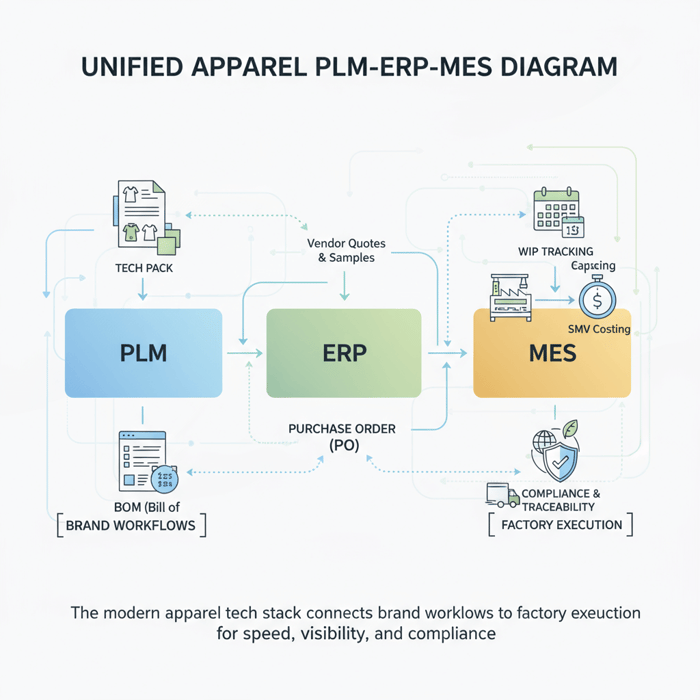
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

