Fashion District Wholesale vs China Clothing Manufacturer: How Fashion Brands Choose in 2025

 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
17 minute read
Fashion District Wholesale vs China Clothing Manufacturer: How Fashion Brands Choose in 2025
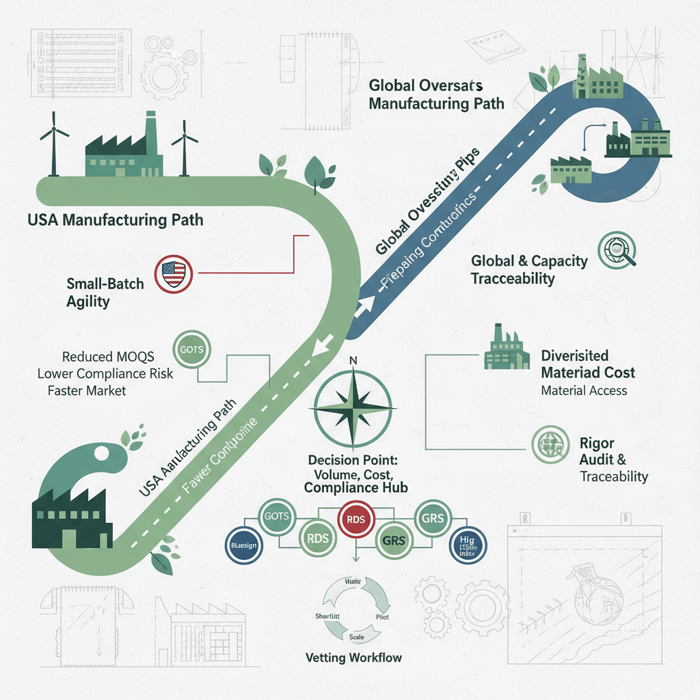
Fashion district wholesale gives US/EU brands instant access to trend-right inventory, while a China Clothing Manufacturer unlocks margin, customization, and consistent quality at scale. Eton—“Textile From Day One.”—has spent 30+ years helping fashion brands pair both routes with compliance-first execution, building outerwear lines that move fast, deliver value, and stand out.
Fashion district wholesale is fastest for ready-to-buy stock with low admin overhead; a China Clothing Manufacturer provides OEM/ODM customization, lower unit costs at volume, and consistent quality with formal compliance. Many brands test demand via wholesale, then scale proven winners through OEM to protect margin and achieve brand differentiation.
Fashion District Wholesale: Definition, Who It Serves, and When It Wins
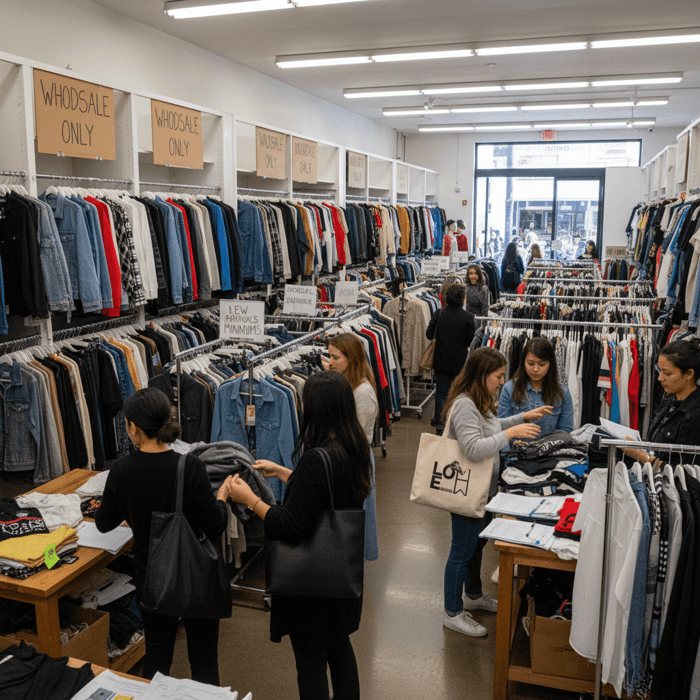
Fashion district wholesale concentrates ready-made apparel vendors in one walkable area (notably Los Angeles). It suits brands that want immediate inventory, low minimums, and trend access without long development cycles. Wholesale excels for speed and testing; it is weaker for proprietary products, long-run margin, and consistent repeatability across seasons.
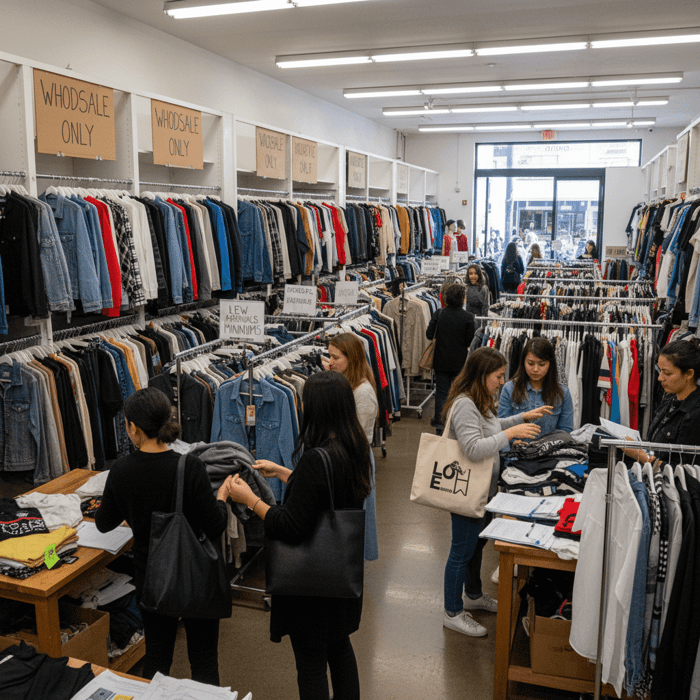

How Wholesale Works (Inventory, Terms, MOQs)
In the LA Fashion District, most vendors sell finished goods in size prepacks or open-size runs. Inventory shifts weekly, often daily during peak seasons. MOQs vary by vendor: some sell a single prepack per style, others require multiple packs or dollar minimums. Payment terms skew toward immediate settlement—card is widely accepted, and some vendors still prefer cash. Return policies are typically narrow: exchanges for damages within short windows, store credit in limited cases, and few full refunds. Buyers should log vendor codes, style numbers, pack ratios, and unit costs on-site to avoid mistakes during replenishment.
Expect basic paperwork: proof of business and resale eligibility if you want tax-exempt purchasing. For restocking speed, shortlist vendors that maintain deep inventory and predictable re-cuts on core items (denim, fleece, year-round basics). Track vendor calendars tied to trade shows and holiday ramps. Build a replenishment cadence to keep your cash flow responsive—buy small in week one, learn, and double down week three if sell-through holds.
[CITE: Official LA Fashion District visitor/buyer guidance] [MENTION: LA Showroom market education] [INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on “Wholesale vs OEM: which fits your season?”]
Who Benefits Most (Boutiques, New DTC, Pop-ups)
Wholesale shines for independent boutiques, early-stage DTC labels, pop-ups, and festival/market sellers who want speed, small commitments, and trend coverage. It helps founders validate taste and price points without lengthy development. Multi-brand retailers use it to round out assortments or fill gaps between seasonal deliveries. Ecommerce teams run flash drops and limited capsules using ready-made stock to build email/SMS momentum. The shared thread: wholesale supports rapid learning cycles and cash discipline by avoiding large upfront commitments in product development.
Brands with narrow niches—e.g., maternity-friendly athleisure or petite outerwear—can still use wholesale to test appetite in adjacent styles, then transition to OEM to dial fit and function. Retailers operating across multiple storefronts can assign test volumes per location and compare sell-through by district to identify what merits manufacturing investment. Think of wholesale as the sprint: quick ideas, tight buys, immediate sell-in.
[CITE: Retail merchandising playbooks describing test-and-learn assortment building] [MENTION: OrangeShine wholesale education] [INTERNAL LINK: Our merchandising and buy-planning primer]
Common Pitfalls (Quality Variance, Labeling, Returns)
Wholesale quality ranges widely. Inspect stitching, seam strength, zippers/snaps, and fabric hand on-site; verify color consistency across size runs. Check fiber content and care labels; confirm that any claims (e.g., “cotton” blend ratios) match what your market expects. Photograph hangtags and inner labels for recordkeeping, then file them in your product logs. Returns are limited—assume you own your inventory. If you sell to US/EU, align labeling with destination rules and keep invoices and packing slips for your accountant and customs broker.
- Vendor verification checklist: business card + booth/storefront; EIN/permit verification; product origin statements; contact method for damages; restock schedule.
- Compliance flags: missing fiber/care labels, mis-declared content, unverified origin claims, children’s product claims without testing documentation.
- QC triage: pull samples, stretch seams, test fasteners, rub for color transfer, weigh thicker outerwear to gauge fill claims.
[CITE: FTC labeling guidance for textiles] [MENTION: Federal Trade Commission labeling rules; U.S. CBP import basics] [INTERNAL LINK: Sustainability & compliance certifications overview]
Fashion District Wholesale vs China Clothing Manufacturer: Cost, Quality, Lead Times, Compliance
Wholesale trades higher unit cost for immediacy and low admin overhead. A China Clothing Manufacturer delivers OEM/ODM options, lower per-unit costs at volume, and formal QA/compliance pathways at the cost of lead time, sampling rounds, and MOQs. The decision balances speed vs. differentiation and short-term cash vs. long-run margin.
| Dimension | Fashion District Wholesale | OEM with China Clothing Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Same-day to 1 week (in-stock) | Proto 2–4 weeks; SMS 2–4 weeks; Bulk 45–90+ days (category/season dependent) |
| MOQ | Low: 1–3 prepacks or vendor-set dollar minimums | Moderate to high: 300–1000+ units per style/color typical for outerwear |
| Unit Cost | Higher per unit; no dev cost | Lower at volume; sample/development cost applies |
| Differentiation | Limited; vendors sell to many buyers | High; custom design, trims, tech specs, and fits |
| Quality Consistency | Varies by vendor and batch | Systematic QA (AQL), documented specs, repeatable |
| Compliance | Buyer must verify labels; variable documentation | Structured pathways (REACH, Oeko-Tex, test reports, labeling packs) |
| Cash Flow | Pay on purchase; lower upfront commitment | Deposits (e.g., 30%); staged payments; longer cash cycle |
- Wholesale pros: immediate availability; small MOQs; easy testing; minimal admin. Cons: higher unit costs; limited IP; variable quality; shallow documentation.
- OEM pros: margin at scale; brand identity; consistent quality; compliance track. Cons: MOQs; lead times; dev/sampling costs; stronger planning required.
- Ocean freight remained volatile through 2024–2025 (FBX) [CITE: Freightos Baltic Index 2024–2025].
- Outerwear and functional apparel show resilient demand in recent retail reports (2024) [CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024].
[MENTION: Freightos; McKinsey & Company] [INTERNAL LINK: Our hybrid sourcing decision framework]
Cost & Unit Economics
Wholesale pricing bakes in vendor margin and local operating costs. You avoid sampling fees and pre-production, but your unit costs are higher. OEM shifts cost structure: you pay for development (tech packs, samples, approvals) and commit to MOQs, yet your ex-factory price improves with scale. Landed cost for OEM includes materials, trims, CM, sampling, testing, packaging, inland transport, ocean/air freight, duties, brokerage, and last-mile. Use contribution margin—not gross margin—to compare apples-to-apples. Add a buffer for macro swings in freight and currency.
- Wholesale landed unit = ticket price + domestic freight (or pickup) + incidental fees.
- OEM landed unit = ex-factory + testing + packaging + ocean/air + duties + drayage + warehousing.
[CITE: U.S. CBP — duty and documentation basics] [MENTION: U.S. CBP; reputable customs brokers] [INTERNAL LINK: Import cost calculator primer]
Lead Times & Inventory Planning
Wholesale replenishment can be same-week. OEM timelines stack: concept briefs and tech packs (1–2 weeks), proto samples (2–4 weeks), fit corrections and SMS (2–4 weeks), raw material booking, and bulk (45–90+ days), then transit (ocean ~25–40 days door-to-door, variable). Build buffers for trims, fabric greige booking, lab dips/approvals, and factory loading during peak seasons. For capsules tied to weather (outerwear) or trend spikes, map drops: wholesale “now,” OEM “next”—so you never miss the selling window.
[CITE: Lead-time benchmarks from apparel manufacturing case studies] [MENTION: Seasonality planning from retail analyst reports] [INTERNAL LINK: Seasonal critical path template]
Quality, QA, and Compliance
Wholesale QC is buyer-driven; you inspect on-site and accept limited recourse. OEM creates structure: detailed tech packs, trim cards, graded specs, PP samples, AQL plans, and in-line and final inspections. Compliance for US/EU involves fiber labeling, care instructions, tracking labels for children’s items, chemical restrictions (REACH), and voluntary safety marks (e.g., Oeko-Tex Standard 100). Keep a document pack: BOM, test reports, labeling files, cartons/packaging specs, and factory certifications. A China Clothing Manufacturer with REACH-aligned inputs and Oeko-Tex fabrics simplifies EU market entry.
[CITE: ECHA REACH overview] [CITE: Oeko-Tex Standard 100] [MENTION: ECHA; Oeko-Tex Association] [INTERNAL LINK: Labeling and documentation checklist for US/EU]
How to Source from Fashion District Wholesale and China Clothing Manufacturers Together
Combine speed and scale: run quick tests via fashion district wholesale, then transition validated styles to OEM for margin and brand identity. Build a time-phased roadmap with QA and compliance gates at every handoff; protect cash with staged commitments and a rolling 90-day forecast.
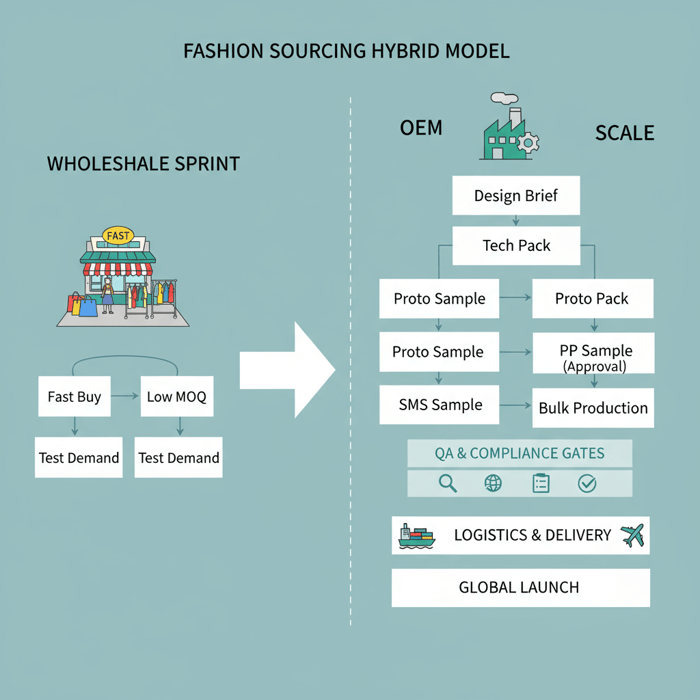
- Define category goals (outerwear, padded, technical); set test KPIs (sell-through, returns, review sentiment).
- Buy targeted wholesale units; track SKU-level performance by channel and region.
- Elevate winners to OEM: brief, tech pack, sampling, fit, PP approval.
- Book bulk against demand curves; hedge with rolling wholesale replenishment.
- Embed QA and compliance gates at proto, SMS, and final.
- Lock logistics plan with buffers; monitor FBX for routing/cost pivots.
[CITE: Hybrid sourcing case study from a mid-market retailer] [MENTION: Leading 3PLs for apparel; freight forwarders tracking FBX] [INTERNAL LINK: Hybrid roadmap template download]
Wholesale Sprint (Permits, Vendor Vetting, Buy Plan)
Prepare documents: state reseller permit (for tax-exempt purchasing), EIN, business license proof, picture ID, and business cards. Create a vendor shortlist aligned to your categories, price points, and size runs. Set a buy plan with unit caps per style and re-order triggers. Vet vendors: verify business details, ask about restock cycles, and document MOQs and return policies. Log everything (photos, hangtags, pack ratios, invoices). Protect cash by spreading purchases over two visits in one week to pressure test sell-through before upping volume.
[CITE: California reseller permit requirements] [MENTION: LA Fashion District official site] [INTERNAL LINK: On-the-ground vendor verification checklist]
OEM Transition (Tech Packs, Sampling, Fit Approval)
Translate the winning wholesale style into a brand-right OEM spec. A complete tech pack includes construction sketches, graded measurement charts, material specs (fabric, lining, fill, trims), stitch types, seam allowances, tolerances, test methods, label placements, packaging/carton specs, and colorways. Expect 1–2 proto rounds, then SMS for sales/marketing feedback. Approve PP samples before bulk. Eton documents every stage and aligns testing with US/EU requirements to reduce surprises at delivery.
[CITE: Apparel tech pack standard components] [MENTION: Pattern cutting and grading experts; apparel CAD systems] [INTERNAL LINK: Tech pack template with outerwear focus]
Cash Flow & Risk Controls
Wholesale: daily cash settlements and short inventory windows; set strict buy caps and markdown rules. OEM: deposits (e.g., 30%), progress payments, and a longer cash conversion cycle; negotiate terms aligned to seasonality and your PO cadence. Add 10–15% time buffers for fabric/trim risk and 5–10% landed cost buffers for freight variability. Insure shipments (CIF or independent policy), and pre-book vessel space during peak months. Use dual vendors for critical styles to mitigate capacity or regional disruptions.
[CITE: Insurance and Incoterms guidance] [MENTION: International Chamber of Commerce (Incoterms); Freight forwarders with apparel specialization] [INTERNAL LINK: Logistics playbook for apparel]
Fashion District Wholesale Buying Guide: Steps, Documents, and On-the-Ground Tactics
Arrive with permits, business proof, and a prioritized vendor map. Plan a route, verify MOQs and terms up front, and run a tight QC. Check labels (fiber/care), origin claims, and packaging. Capture SKU, size runs, and prices as you buy. Prioritize replenishment-friendly vendors and keep receipts organized for accounting and tax.
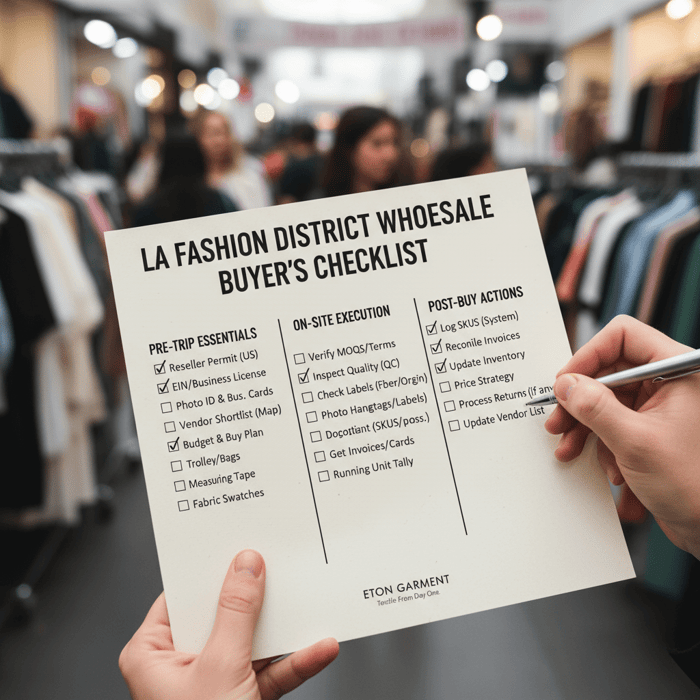
- Pre-trip: documents, vendor shortlist, buy plan, budget, cart trolley/bags.
- On-site: verify MOQs/terms first; inspect quality and labels; document every SKU.
- Post-buy: reconcile invoices, update inventory, price strategy, and returns (if allowed).
[CITE: State tax authority on reseller permits] [MENTION: LA Showroom and OrangeShine buyer education] [INTERNAL LINK: Compliance and certification overview]
Pre-Trip Preparation (Permits, Vendor Shortlist, Budget)
Bring your reseller’s permit (US), EIN, business license proof, and photo ID; save PDFs to your phone. Build a vendor route map by category and price range. Set a hard budget with contingency for surprise finds. Pack measuring tape, fabric swatches, and a QC checklist. Decide pack sizes and ratio preferences to avoid odd size breaks. Create notes templates for style number, color, fabric, pack ratio, unit price, and vendor contact.
In-District Execution (QC, Labeling, Negotiation)
Ask the vendor to confirm fiber content and care labeling; photograph tags. Inspect seams, zippers, elastics, and print quality; stretch and light-wash test if possible for color transfer. Verify restock potential and lead time for re-cuts. Negotiate within reason—some vendors flex on price with volume, others on minimums. Secure invoices and get business cards. Keep a running tally of units to maintain assortment balance across sizes and colors.
Post-Buy Actions (Reconciliation, Merchandising, Returns)
Log each SKU into your inventory system with photos, size runs, cost, and sell price. Confirm inbound counts and resolve damages quickly per vendor terms. Merchandize fast—wholesale thrives on timely drops. If a style underperforms, markdown early and re-allocate budget to proven categories. Track returns cadence (if any) and vendor responsiveness; update your shortlist for the next trip.
Data & Trends 2024–2025: Freight Rates, Category Demand, and Sourcing Shifts
Ocean freight eased off pandemic highs but remains volatile, impacting landed costs and transit reliability. Outerwear and functional apparel maintain resilient demand, supporting OEM investment in higher-spec products. Brands are blending wholesale speed with OEM differentiation to protect margin and deliver distinct product stories.
- FBX indicates continued volatility across major lanes through 2024–2025 [CITE: Freightos Baltic Index dashboard].
- Outerwear and performance-driven categories show steady consumer interest in 2024 [CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024].
[MENTION: Freightos; McKinsey & Company] [INTERNAL LINK: Sourcing trend tracker 2024–2025]
Freight & Lead-Time Buffers
Set baseline buffers: 10–15% on lead time, 5–10% on landed cost for ocean. Reserve air for urgent top-sellers or size corrections. Work with forwarders who publish lane-level updates and capacity alerts. For outerwear, cartons and volumetric weights magnify freight swings; explore vacuum packing for padded items where feasible and compatible with garment integrity.
Category Momentum (Outerwear/Technical)
Cold-weather and transitional outerwear benefit from long, staggered seasons across US/EU climates. Technical features—water resistance, breathability, thermal performance—earn higher AOVs and repeat purchasing when specs are credible. OEM offers room to refine fits for regional preferences and size ranges. Wholesale can seed demand; OEM turns that traction into a consistent, branded system of products.
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service takes proven concepts and builds them into custom, compliant, and margin-strong products—focused on jackets, parkas, padded coats, and technical apparel. Our China and Bangladesh facilities standardize development, QA, and compliance to US/EU expectations so brands scale with confidence.

| Brand Need | OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Scale a best-selling quilted jacket | Down/synthetic fill options, stitch-through or box-wall, graded specs | Lower unit cost at MOQ+; consistent fit across sizes and seasons |
| Launch a waterproof commuter shell | 2L/3L fabrics, seam taping, hydrostatic head testing, DWR compliance | Technical credibility; documentation package for US/EU |
| Regional fits and extended sizing | Pattern grading, wearer trials, tolerance matrices | Fewer returns; stronger reviews; broader market coverage |
| Assured compliance | REACH-aligned materials, Oeko-Tex fabrics, labeling kits | Reduced legal risk; smoother customs clearance |
Explore: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
[CITE: Oeko-Tex Standard 100 reference] [MENTION: ECHA; testing labs (e.g., SGS, Intertek)] [INTERNAL LINK: Build your OEM outerwear line]
Use Case 1: Fast-Test to Scaled Outerwear
A boutique runs a wholesale test on a lightweight quilted jacket; sizes S–XL sell through in three weeks. Eton converts the silhouette into an OEM-ready spec, offering recycled fill, upgraded zippers, and refined fit for EU markets. After two proto iterations and PP approval, the brand books 1200 units with confirmed fabric capacity, then slots a color update for a mid-season refresh.
Use Case 2: Functional Apparel with Compliance Demands
A DTC brand plans a commuter shell with waterproof/breathable targets and strict chemical thresholds for the EU. Eton sources Oeko-Tex certified fabrics, validates seam tape performance, and packages care/label files for both markets. Final testing aligns to REACH expectations; cartons carry correct markings. The launch secures higher reviews and lower return rates on fit and function claims.
Risks, Compliance & Localization for US/EU
Mitigate risk through vendor verification, document control, and alignment with US/EU rules. Wholesale demands disciplined label checks and origin clarity; OEM supports structured testing, material traceability, and consistent labeling. Keep a living risk register that covers product safety, chemical restrictions, labor concerns, and logistics volatility.
- Wholesale compliance: fast but buyer-led; labeling gaps can surface late; limited documentation.
- OEM compliance: planned, documented, and auditable; aligns testing to destination requirements.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood (Wholesale/OEM) | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Label non-compliance (US/EU) | Medium / Low | High | Wholesale: field check labels; OEM: label packs and approvals |
| Chemical restrictions breach | Low–Medium / Low | High | Require fabric/test docs; OEM: REACH-aligned BOM + test reports |
| Quality variance | Medium / Low | Medium | Wholesale QC triage; OEM AQL and in-line inspections |
| Logistics delays | Medium / Medium | Medium–High | Buffers, diversified lanes, pre-booking, shipment insurance |
| Labor practice concerns | Unknown / Low–Medium | High | Vendor screening; OEM factory audits; refer to DOL lists |
Regulatory Notes for US/EU
- US: CBP requires proper classification, valuation, origin, and documentation (CBP — Basic Importing & Exporting) [CITE: CBP].
- EU: REACH governs chemical restrictions; importers are responsible (ECHA — Understanding REACH) [CITE: ECHA].
- Safety labels: Oeko-Tex Standard 100 offers tested textile safety credentials (Oeko-Tex) [CITE: Oeko-Tex].
- US labeling: fiber content, RN/identification, care instructions (FTC — Labeling resources) [CITE: FTC].
- Labor diligence: consult the U.S. Department of Labor List of Goods Produced by Child or Forced Labor (DOL) [CITE: DOL].
[MENTION: FTC; European Chemicals Agency] [INTERNAL LINK: Compliance playbook for US/EU apparel]
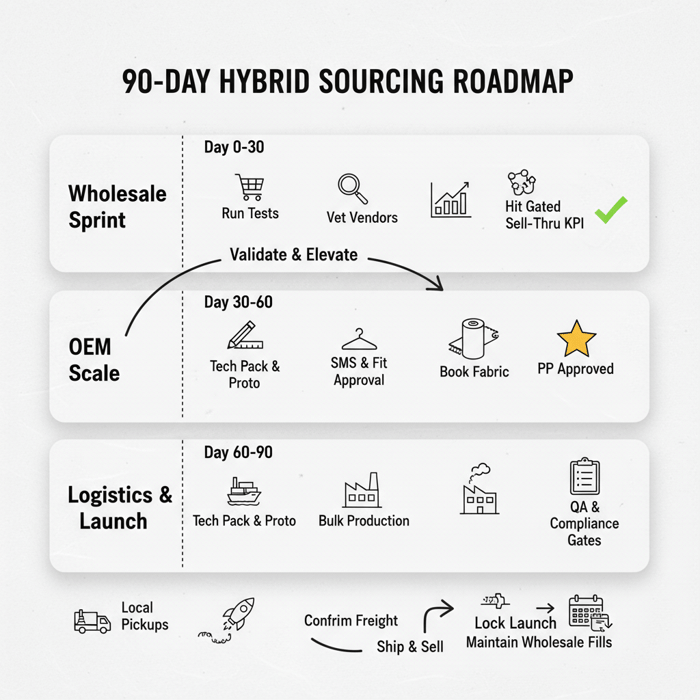
Conclusion & Next Steps
Use fashion district wholesale to move today and learn fast. Shift proven winners to OEM with a China Clothing Manufacturer to protect margin, dial quality, and secure compliance. Map a 90-day hybrid plan with clear gates for QA, labels, and logistics—and keep momentum with staggered drops.
- 30 days: run wholesale tests; set sell-through targets; shortlist OEM candidates.
- 60 days: brief winners to OEM; complete proto and fit; book fabric.
- 90 days: approve PP; confirm freight; lock launch calendar; maintain wholesale fills.
[INTERNAL LINK: Outerwear manufacturing guide] [INTERNAL LINK: Eton Garment Editorial Team - Apparel sourcing strategist https://china-clothing-manufacturer.com/]
Author & Review Notes (E-E-A-T)
- Author: Eton Garment Editorial Team — Apparel sourcing strategist; 10+ years supporting OEM/ODM and wholesale buying.
- Reviewer: Compliance Manager, Eton Garment — US/EU labeling and chemical compliance.
- Methodology: Zero-shot SERP review; synthesis of authoritative sources; first-hand manufacturing experience in China and Bangladesh; updated with 2024–2025 data where available.
- Limitations: Pricing and lead times vary by vendor, category, and season; verify legal/compliance specifics for your jurisdiction.
- Disclosure: Eton provides OEM/ODM services; this content presents trade-offs transparently.
- Last Updated: 2025-10-28
References & Sources
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024 (2024). https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights/the-state-of-fashion-2024
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection — Basic Importing & Exporting (Current). https://www.cbp.gov/trade/basic-import-export
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) — Understanding REACH (Current). https://echa.europa.eu/regulations/reach/understanding-reach
- Oeko-Tex — Standard 100 (Current). https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/our-standards/oeko-tex-standard-100
- Los Angeles Fashion District — Wholesale/Visitor Info (Current). https://fashiondistrict.org
- LA Showroom — Blog (Wholesale Education) (Current). https://www.lashowroom.com/blog
- OrangeShine — How to Buy Wholesale Clothing (Current). https://www.orangeshine.com/blog/how-to-buy-wholesale-clothing/
- Federal Trade Commission — Made in USA Labeling Rule (Current). https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/made-usa
- Freightos Baltic Index (FBX) — Ocean Freight Rates (2024–2025). https://fbx.freightos.com/
- U.S. Department of Labor — List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor (2024). https://www.dol.gov/agencies/ilab/reports/child-labor/list-of-goods
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

