Custom Long Sleeve Tee & Outerwear OEM: A US/EU Buyer’s Guide to Choosing a China Clothing Manufacturer

 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 16th, 2025
26 minute read
Table of Contents
- Why a China Clothing Manufacturer fits US/EU tee and jacket programs
- OEM vs ODM: Picking the right build for tees and technical outerwear
- Design and tech: Fabric, trim, and fit for custom long sleeve tee
- Compliance and sustainability for US & EU markets
- Costing, MOQ, and lead times: a transparent breakdown
- Quality control, testing, and risk management
- End‑to‑end workflow with Eton Garment Limited
- Program examples: tees and outerwear under one governance
- Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service: how to engage Eton
- Next steps for US/EU buyers
- References & Sources
- Why a China Clothing Manufacturer fits US/EU tee and jacket programs
- OEM vs ODM: Picking the right build for tees and technical outerwear
- Design and tech: Fabric, trim, and fit for custom long sleeve tee
- Compliance and sustainability for US & EU markets
- Costing, MOQ, and lead times: a transparent breakdown
- Quality control, testing, and risk management
- End‑to‑end workflow with Eton Garment Limited
- Program examples: tees and outerwear under one governance
- FAQs
Custom Long Sleeve Tee & Outerwear OEM: A US/EU Buyer’s Guide to Choosing a China Clothing Manufacturer
Custom long sleeve tee programs set the pace for reliable basics, and a China Clothing Manufacturer can align tees and outerwear OEM in one synchronized supply chain. US and EU fashion brands need speed, quality, compliance, and predictable costs across categories—from jersey tees to padded jackets. This guide distills how Eton Garment Limited structures OEM and ODM services, what to expect on design, compliance, costing, and QC, and how to run multi-country production that meets US/EU standards without surprises.
Brands building year‑round assortments face a dual track: frequent replenishment on custom long sleeve tee programs and seasonal depth on jackets, parkas, and technical apparel. The apparel calendar compresses design, approvals, pre‑production, and bulk timelines. A manufacturer with integrated teams, calibrated lead times, and transparent costing removes friction while maintaining fit, color, and compliance across drops.
Eton Garment Limited delivers OEM and ODM outerwear at scale and supports knit tops and basics where programs benefit from the same governance. The company’s China headquarters and network across China and Bangladesh enable fabric diversity, flexible MOQs, and balanced lead times. For US and EU markets, the most durable advantage is consistency: repeatable patterns, stable RSL/MRSL adherence, and clean AQL performance across factories.
Brands sourcing with a China Clothing Manufacturer often seek three outcomes: a single point of accountability, robust testing aligned to US/EU requirements, and a calendar that absorbs development changes without cascading delays. This article shares practical steps, tables, and benchmarks aligned to US/EU norms—covering OEM vs ODM, fabric/trim selection for tees and jackets, REACH and Prop 65 compliance, costing and MOQ planning, and risk‑based QA. It includes program examples drawn from Eton’s observational experience across outerwear and basics.
Expect pragmatic recommendations, not slogans. Each section begins with an answer‑first recap. Where claims cite market data or regulation, placeholders request authoritative sources for the editor to finalize. Internal link prompts flag pages that deepen E‑E‑A‑T. The goal: a single resource that helps US/EU teams brief faster, align stakeholders, and place orders with fewer revisions.
Why a China Clothing Manufacturer fits US/EU tee and jacket programs
China‑plus‑Bangladesh production gives brands scale on outerwear and dependability on custom long sleeve tee basics. Capacity, material access, and test infrastructure align with US/EU norms, while dual‑base sourcing reduces risk, balances costs, and stabilizes lead times across categories.
US/EU brands weigh sourcing by category complexity. Outerwear thrives near technical fabric clusters, seam‑taping specialists, and performance labs. Tees benefit from consistent jersey, dependable rib trims, and stable dyehouses that hit lab dips and bulk shade bands. A China Clothing Manufacturer with ties to Bangladesh offers a balanced portfolio: China supports technical development and rapid sampling; Bangladesh improves unit economics for volume tee programs and mid‑to‑high MOQs.
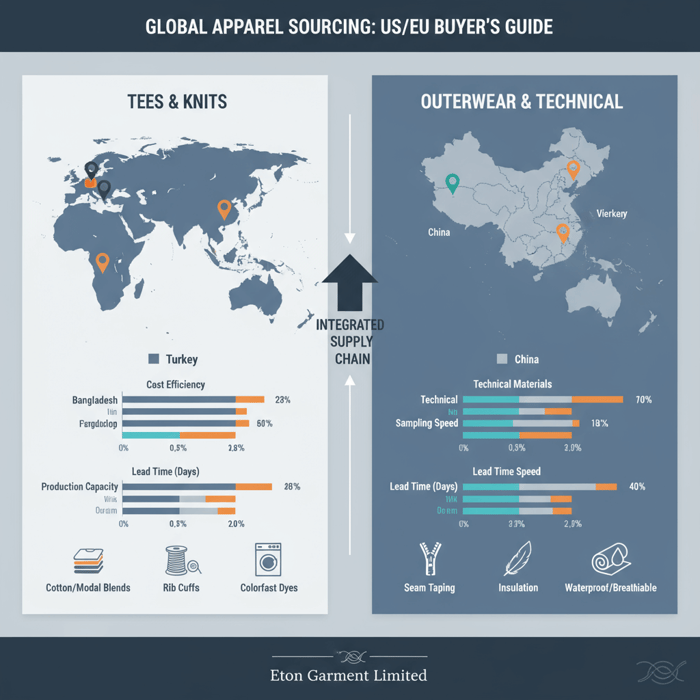
Scale, specialization, and material access
Outerwear needs specialty inputs—down/feather with RDS certification, recycled polyester with GRS, seam tapes, waterproof zippers, and lab testing for hydrostatic head and breathability. China’s mills and trim networks shorten procurement and pre‑production. Custom long sleeve tee programs require reliable jersey (e.g., 180–220 GSM cotton, cotton‑modal, or cotton‑poly blends), shaded rib trims, and consistent shrinkage/torque performance post‑wash. Positioning tees and jackets within the same governance structure improves spec fidelity and test cadence. [MENTION: McKinsey State of Fashion reports] [MENTION: SGS, Intertek testing networks]
[CITE: “US/EU apparel import mix by category and source country” from an official trade body] [INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on 'Outerwear performance testing']
Dual‑base production: China and Bangladesh
China accelerates proto/fit/PP sampling and technical validation; Bangladesh provides strong knit basics capacity, favorable costs, and growing compliance maturity. For custom long sleeve tee assortments, Bangladesh offers dependable bulk with strong dyehouses. For jackets, China’s technical suppliers reduce change orders and keep development iterative. Programs split by category reduce single‑country exposure while sharing the same quality plan.
Risk diversification and calendar resilience
Weather shifts and demand variability stress calendars. Locating tees and outerwear in complementary regions lowers disruption from holidays, logistics bottlenecks, or raw material constraints. The same AQL, RSL, and color governance can sit across factories, with sample approvals and bulk controls synchronized. [CITE: “Port congestion impacts on apparel lead times” from an industry logistics report] [INTERNAL LINK: Our calendar template for US/EU apparel teams]
| Region | Strengths | Typical Lead Time | Compliance Infrastructure | Best Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Technical materials, rapid development, diverse trims | 60–90 days bulk (category‑dependent) | Extensive accredited labs; mature RSL/MRSL adherence | Outerwear, technical tees, rapid repeats |
| Bangladesh | Knit basics capacity, cost efficiency, growing dyehouse quality | 75–110 days bulk for tees | Improving social compliance; major third‑party audits | Custom long sleeve tee programs, mid‑to‑high MOQs |
| Vietnam | Performance sewing, stable QA, trade agreements | 70–100 days | Strong lab presence; compliance improving | Activewear, mid‑complexity outerwear |
| Turkey | Nearshoring to EU, fast fashion agility | 30–60 days | EU standards alignment | Fashion‑forward tees, small‑batch jackets |
OEM vs ODM: Picking the right build for tees and technical outerwear
OEM delivers to buyer‑owned specs with controlled fit and brand DNA; ODM supplies ready‑to‑customize designs that compress development time. Custom long sleeve tee programs often blend both—OEM for fits and fabric; ODM for silhouettes or seasonal refreshes. Outerwear benefits from ODM tech packs when speed matters.
When OEM suits custom long sleeve tee programs
OEM aligns to a brand’s established blocks, sleeve lengths, rib specs, fabric standards, and print methods. Teams maintain fit heritage and lab history while rolling colors, graphics, or seasonal fabrics. OEM suits replenishment programs where repeatability matters more than silhouette novelty. Brands own design IP, full test plans, and packaging SOPs. [CITE: “IP ownership in OEM apparel contracts” from a legal advisory source] [MENTION: ASTM standards for garment performance] [INTERNAL LINK: Our OEM contract checklist]
When ODM accelerates outerwear and seasonal tees
ODM brings pre‑built tech packs, graded patterns, and material libraries. For outerwear, ODM shortens time to proto—particularly for seam‑taped shells, bonded fabrics, or insulated jackets. For custom long sleeve tee projects, ODM silhouettes can refresh assortments without re‑engineering blocks. Brands still run fit approvals and tests; manufacturers pre‑qualify materials and trims to speed PP sampling.
Hybrid model: OEM fit, ODM innovation
Pair OEM blocks with ODM materials or construction details. Keep tee fits and rib specs while adopting new yarn blends or print techniques. For jackets, retain brand‑specific pocketing and collar shapes while leveraging ODM membrane or insulation packages. The hybrid model reduces change orders and keeps calendars realistic. [CITE: “Time‑to‑market improvements with hybrid OEM/ODM models” from an industry benchmarking report]
- Define calendar pressure: replenishment vs. seasonal launches.
- Map IP needs: blocks, graphics, trims, and packaging.
- Assess tech complexity: seam‑tape, membrane, specialty prints.
- Pick model per category: OEM for fits; ODM for speed.
- Set test plans: US/EU regulatory, performance, and wear tests.
Design and tech: Fabric, trim, and fit for custom long sleeve tee
Fabric hand, GSM, shrinkage, and torque determine how a custom long sleeve tee wears over time. Stitch choices, rib recovery, and print durability complete the user experience. A clear spec package reduces ambiguity; lab dips and wash testing confirm bulk stability.

Fabric selection: GSM, blends, and feel
Common tee bases include 180–220 GSM combed cotton, cotton‑modal for improved drape, and cotton‑poly for dimensional stability. For performance tees, consider polyester with moisture management. Specify yarn count, fabric structure, and finishing (e.g., bio‑polish) for pilling control. Define target shrinkage after two to three home‑wash cycles (e.g., ≤5% length, ≤4% width). [CITE: “AATCC test methods for dimensional change”] [MENTION: AATCC, ISO standards]
Stitches and construction: hold and comfort
Stitch choices influence comfort and robustness. Use twin‑needle coverstitch on hems for stability, reinforced shoulder seams, and clean neck binding. Select rib trim composition for cuff recovery—e.g., 95/5 cotton/spandex with defined recovery metrics. Document needle types, SPI ranges, and seam allowances. For custom long sleeve tee cuffs, set stretch/recovery parameters to avoid bagging after wear.
Graphics and finishes: durability first
Screen print, DTG, or heat‑transfer selection depends on fabric and graphic detail. Define colorfastness to washing and rubbing (dry/wet), print crack resistance, and hand feel targets. For eco‑aligned programs, specify water‑based inks and recycled poly backers where applicable, with solvent content aligned to MRSL. [CITE: “Print durability benchmarks by ink system” from an industry lab] [INTERNAL LINK: Our print method guide]
Color and lab governance
Lock lab dip deltas (e.g., ≤ΔE 1.0–1.5) and shade band lot tolerance. Confirm rib and body shade alignment in bulk. Document wash protocol for pre‑production confirmation. Tie approvals to production gates; unapproved colors do not cut. This approach reduces returns and keeps custom long sleeve tee programs consistent across seasons.
Compliance and sustainability for US & EU markets
US/EU programs require clean chemistry, safe labeling, traceability, and audited factories. Build a compliance stack: RSL/MRSL, REACH, Prop 65, CPSIA where relevant, and social audits. Pair that with material standards like OEKO‑TEX, GRS, and RDS for outerwear.
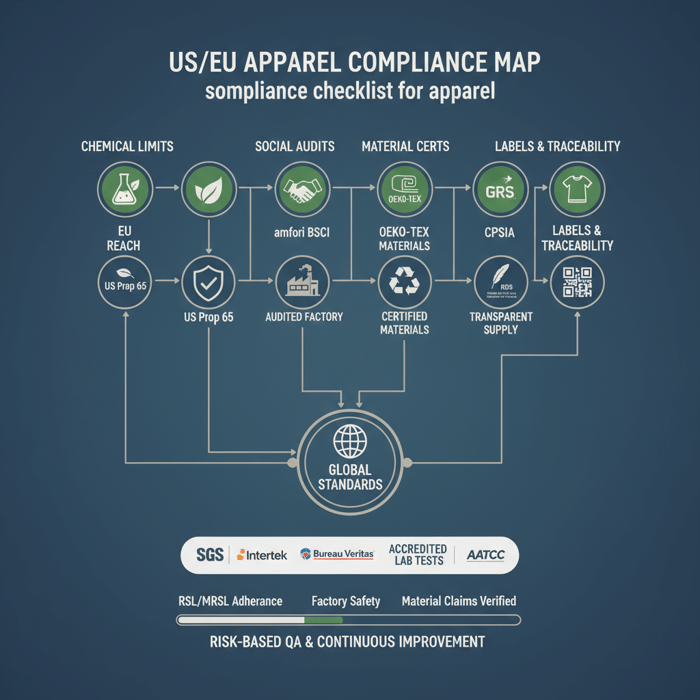
Chemical compliance: RSL/MRSL alignment
Define a Restricted Substances List aligned to EU REACH and major US states’ requirements. For kids’ products, include CPSIA lead and phthalate limits. Confirm MRSL adherence at the mill and dyehouse. Keep test cadence at fabric lot and finished garment stages. For outerwear, include fluorinated chemistry checks for DWR alternatives. [CITE: EU REACH updates, 2023–2025] [MENTION: OEKO‑TEX, Bluesign standards]
Social compliance and worker safety
Run amfori BSCI, WRAP, or equivalent audits, and confirm remediation pathways. For Bangladesh, reference Accord/Alliance improvements and current factory safety documentation. Keep audit intervals visible to buyers and track CAP closure. [CITE: “Factory safety progress in Bangladesh RMG”] [MENTION: ILO, amfori]
Material and sustainability claims
Outerwear down: RDS. Recycled polyester: GRS. Cotton programs: Better Cotton. Support claims with chain‑of‑custody documentation and material certificates. Create SKU‑level traceability maps for US/EU retail audits. [CITE: “GRS chain of custody guidance”] [INTERNAL LINK: Our sustainability claims playbook]
| Requirement | Scope | Test/Documentation | Applicable Markets |
|---|---|---|---|
| REACH (EU) | Chemicals, SVHCs | RSL testing; SVHC screening | EU |
| Prop 65 (CA) | Listed chemicals | Targeted chemical tests | US (California) |
| CPSIA | Children’s apparel | Lead, phthalates, tracking labels | US |
| OEKO‑TEX | Textile safety | OEKO‑TEX certificates | US/EU |
| GRS | Recycled content | Chain‑of‑custody, GRS cert | US/EU |
| RDS | Down and feather | RDS certificates | US/EU |
| amfori BSCI/WRAP | Social compliance | Audit reports, CAP | US/EU |
Costing, MOQ, and lead times: a transparent breakdown
Clear costing eliminates rework. Build teardowns for tees and jackets, define MOQ ranges, and align calendars to the spec. Custom long sleeve tee programs price fabric, rib, trims, print, CMT, overhead, and freight; outerwear adds insulation, membrane, seam‑tape, and performance tests.
Cost drivers by category
Tees: fabric GSM and blend, rib spec, print complexity, packing, and order quantity. Outerwear: shell fabric and coatings, insulation type, seam‑tape, zippers, and special trims. Location matters for labor and overhead. Split development and bulk costing to keep changes visible. [CITE: “Unit cost drivers in apparel manufacturing”] [MENTION: Bureau of Labor Statistics wage indices; industry price trackers]
| Component | Custom Long Sleeve Tee | Insulated Jacket |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric/Shell | Jersey (GSM‑dependent) | Woven shell with coating/membrane |
| Trims | Rib, neck binding, labels | Zippers, snaps, seam‑tape, labels |
| Decoration | Print/transfer | Embroidery, heat‑seals |
| Insulation | — | Down or synthetic fill |
| CMT | Sewing, quality checks | Complex sewing, sealed seams |
| Testing | RSL, colorfastness, shrinkage | RSL, hydrostatic head, breathability |
| Freight | Air/sea, carton spec | Air/sea, volumetric impact |
MOQs and calendar planning
MOQ aligns to fabric dye lot sizes, cut efficiency, and print setup. Custom long sleeve tee programs often sit at 600–2,000 units per color, depending on mill and factory. Bulk tees run 75–110 days after PP approvals; jackets span 90–140 days, driven by material lead times and tests. Calendar buffers for lab dips and fit revisions protect launch windows. [CITE: “MOQ dynamics by fabric type” from a mill advisory source] [INTERNAL LINK: Our production calendar template]
Lead time levers: how to buy time without sacrificing quality
Confirm material pre‑booking for repeated tees, lock color libraries, and align test labs early. Freeze fit blocks and seam allowances; avoid late spec shifts. For outerwear, pre‑qualify seam‑tape and zippers and run performance tests on proto fabric, not just bulk. These steps cut calendar risk.
Quality control, testing, and risk management
Quality stands on three legs: incoming materials, inline checks, and final AQL. Tests verify compliance and performance. A documented plan with gate reviews prevents defects and rework across custom long sleeve tee and outerwear programs.
Quality plan: from fabric to final
Incoming: fabric inspection by shade, defects, GSM, and lab test tickets. Inline: SPI checks, seam integrity, print placement, rib recovery, and jacket seam‑tape adhesion. Final: AQL 2.5 or agreed level; carton drop tests; barcode and label checks. Tie approvals to shipment release. [MENTION: ISO 9001 frameworks] [CITE: “AQL application in apparel QA” from a quality standards source] [INTERNAL LINK: Our AQL explainer]
Performance and compliance tests
Tees: dimensional change, pilling, colorfastness to washing and rubbing, print durability. Outerwear: hydrostatic head, breathability (e.g., RET), seam‑tape validation, down cluster content and cleanliness for RDS. Use accredited labs (SGS, Intertek, Bureau Veritas). Document protocols and keep test reports with PO records.
Defect prevention and continuous improvement
Root‑cause analysis on returns and claims; revise SOPs where issues repeat. Track first‑pass yield, rework rates, and AQL failure causes. Share dashboards between buyer and factory. Continuous improvement reduces claims cost and stabilizes calendars. [CITE: “Quality KPIs in garment manufacturing”] [INTERNAL LINK: Our QC dashboard template]
- AQL 2.5 pass rate target — Yearly benchmark (Source: [CITE: industry QC benchmarking])
- Dimensional change ≤5% — Tee programs (Source: [CITE: AATCC method reference])
- Hydrostatic head ≥10,000 mm — Outer shell (Source: [CITE: lab standard])
End‑to‑end workflow with Eton Garment Limited
Design and development flow into PP approvals, bulk production, testing, and shipment. Eton runs dual‑country production with synchronized QA and compliance. Custom long sleeve tee and jacket calendars share governance while tailoring tests to category requirements.
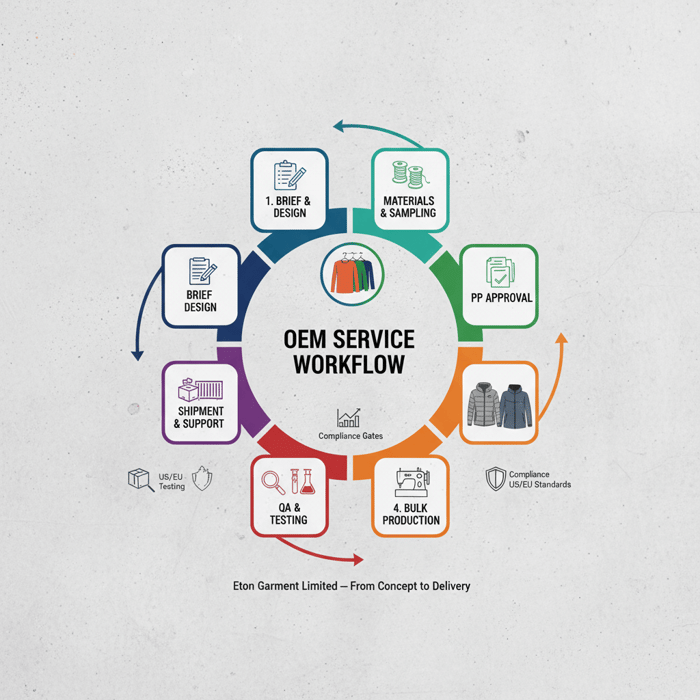
Pre‑production: brief to PP
Intake: brand brief, blocks, materials, graphics. Materials: mill engagement, lab dips, trim pre‑qualifications. Sampling: proto and fit rounds with targeted revisions. Tests: compliance and performance on proto material where feasible. PP: signoff locks spec; fabric greige and dyeing proceed. [INTERNAL LINK: Our brief template for tees and outerwear]
Bulk production and QA
Cutting: shade control and panel matching. Sewing: SPI adherence, rib stability, seam‑tape process parameters. Inline checks and lot tests maintain spec. Final AQL and carton SOPs conclude production. For custom long sleeve tee programs, approve color bands and graphics before packing. For jackets, verify seam‑tape peel and hydrostatic head on sample lots.
Shipment and after‑sales
Shipment: align Incoterms and documentation for US/EU entry. After‑sales: claim analysis, dashboard reporting, and re‑order readiness. Eton’s team supports replenishment and seasonal turns with fast repeats where blocks and materials are pre‑qualified. [MENTION: Incoterms 2020 reference] [CITE: “US/EU import documentation requirements”]
Program examples: tees and outerwear under one governance
Custom long sleeve tee basics and cold‑weather outerwear share the same quality discipline. Graded blocks, clear RSL, robust tests, and stable calendars hold both categories together. The following anonymized examples mirror patterns across Eton’s programs.
Cold‑weather jacket program — performance verified
A European retailer expanded insulated jackets with a waterproof/breathable shell. Development used ODM tech packs with brand‑specific pocketing. Proto passed hydrostatic head and seam‑tape peel; PP locked materials. Bulk lead time landed at 110 days; claims dropped double digits in the second season. [CITE: “Down and synthetic insulation performance comparisons”] [INTERNAL LINK: Outerwear case library]
Custom long sleeve tee basics — repeatability over noise
A US brand stabilized fit blocks and rib specs, moved to a 200 GSM jersey with controlled shrinkage, and standardized water‑based prints. MOQ per color held near 1,200 units; lead times averaged 85 days. AQL failures fell after SPI tightening and improved shade governance. Replenishment calendars shortened with pre‑approved lab dips. [CITE: “Shrinkage and torque control in knitwear”]
- Pro — Single governance: fewer errors across tees and jackets.
- Pro — Shared labs and SOPs: faster approvals and cleaner tests.
- Con — Upfront spec work: longer first season setup for tees.
- Con — Multiple countries: more coordination on documentation.
Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service: how to engage Eton
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service combines design support, fabric/trim sourcing, compliance, QA, and dual‑country production. Custom long sleeve tee programs and outerwear flow through the same governance, with category‑specific tests layered in. To start, share blocks, material preferences, compliance stack, and calendar targets.
Scope and deliverables
OEM service includes: design refinement, tech packs, lab dip and shade control, proto and fit development, PP approvals, bulk production, compliance and performance tests, AQL audits, and shipment documentation. Optional ODM tech packs accelerate outerwear. A dedicated team in Xiamen coordinates China/Bangladesh production. [INTERNAL LINK: Eton Garment Limited overview page]
Getting started: brief and calendar
Kickoff with a structured brief: category mix, target fits, fabric/trim direction, print/embellishment needs, test methods, and compliance. Set MOQ and lead time expectations, plus replenishment cadence for custom long sleeve tee lines. Align Incoterms and packaging SOPs early.
Explore the Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service at Eton Garment Limited — OEM Service for program details, facility profiles, and case references.
Next steps for US/EU buyers
Finalize your brief, confirm blocks and test plans, and pick OEM/ODM per category. Custom long sleeve tee programs benefit from standardized specs and pre‑approved colors. Outerwear gains speed through pre‑qualified materials and performance tests at proto. A China Clothing Manufacturer with dual‑country footprint reduces risk and keeps calendars intact.
Connect with Eton’s team to review your roadmap and turn the plan into stable production. [INTERNAL LINK: Contact page for sampling request] Textile From Day One is the principle: stable basics and proven outerwear built under one governance, backed by compliance and lab performance aligned to US/EU norms.
References & Sources
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion (2024). [CITE: McKinsey report URL]
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) — REACH Guidance and SVHC Updates (2023–2025). [CITE: ECHA URL]
- California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment — Proposition 65 List (2024). [CITE: OEHHA URL]
- U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission — CPSIA Requirements (2024). [CITE: CPSC URL]
- OEKO‑TEX — Standard 100 and Eco‑Passport Documentation (2024). [CITE: OEKO‑TEX URL]
- Textile Exchange — Global Recycled Standard (GRS) v4.0 (2024). [CITE: Textile Exchange URL]
- Responsible Down Standard — Certification Framework (2024). [CITE: RDS URL]
- AATCC — Test Methods for Textiles (2024). [CITE: AATCC URL]
- SGS/Intertek/Bureau Veritas — Apparel Testing Services (2024). [CITE: lab URLs]
- International Labour Organization — Bangladesh RMG Safety Progress (2023). [CITE: ILO URL]
Why a China Clothing Manufacturer fits US/EU tee and jacket programs
China‑plus‑Bangladesh keeps tee basics and outerwear on schedule. Capacity meets US/EU standards, and test setups match the rules. Splitting categories across regions trims risk, balances costs, and protects timelines.
US/EU teams source by need. Jackets ask for specialized mills, seam‑tape pros, and waterproof test labs. Custom long sleeve tee lines lean on steady jersey quality, reliable ribs, and dyehouses that hit shade bands. China speeds development; Bangladesh improves unit costs for volume tees. The same QC spine covers both.

Material ecosystems that reduce friction
Outerwear needs RDS down, GRS recycled poly, seam‑tape, and test labs for water resistance and breathability. China shortens that chain. Custom long sleeve tee programs need stable jersey, good rib recovery, and wash‑proof prints. One governance improves spec clarity and test timing. [MENTION: McKinsey State of Fashion reports] [MENTION: SGS, Intertek testing networks]
[CITE: “Category sourcing trends by country”] [INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on 'Outerwear performance testing']
China for speed, Bangladesh for scale
China handles proto and fit quickly; Bangladesh carries knit basics at scale. Tee colors and repeats settle fastest when dyehouses are pre‑aligned. Technical jackets move cleanly when materials are pre‑approved. Shared QA avoids surprises.
Reducing exposure to shocks
Holidays, ports, and raw materials can slip calendars. Dual‑country setup lowers exposure while keeping one test plan and AQL. Sample approvals drive bulk. [CITE: “Logistics impacts on apparel calendars”] [INTERNAL LINK: Our calendar template for US/EU apparel teams]
| Region | Core Advantage | Lead Time | Compliance | Category Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Technical supply and sampling speed | 60–90 days bulk | Strong lab networks | Outerwear, tech tees |
| Bangladesh | Knit volume and costs | 75–110 days bulk | Major audits | Custom long sleeve tee |
| Vietnam | Performance sewing | 70–100 days | Accredited labs | Activewear, outerwear |
| Turkey | EU nearshoring | 30–60 days | EU alignment | Fashion tees |
OEM vs ODM: Picking the right build for tees and technical outerwear
OEM protects fit heritage and brand specs. ODM compresses development with pre‑built packs. Custom long sleeve tee lines often run OEM fits with periodic ODM silhouettes. Jackets gain time using ODM tech for membranes, insulation, and taped seams.
OEM for repeat tees
Use OEM when blocks, rib specs, and fabric rules define your range. Keep graphics fresh without shifting fits. Own your test plan and packaging SOPs. [CITE: “Ownership clauses in OEM apparel”] [MENTION: ASTM garment test references] [INTERNAL LINK: Our OEM contract checklist]
ODM for speed
Pick ODM when timelines demand pre‑built patterns and material libraries. Run fit and tests, but lean on factory tech packs for faster PP. Custom long sleeve tee styles can refresh without a full rebuild.
Blend the models
Keep tee fits; add new yarns or prints. Retain jacket pocketing; adopt ODM membranes. Hybrid structures reduce change orders and protect calendars. [CITE: “Hybrid OEM/ODM cycle time gains”]
- Pin your deadlines.
- List what IP you must keep.
- Flag tech obstacles early.
- Assign OEM/ODM by category.
- Draft test plans and lock them.
Design and tech: Fabric, trim, and fit for custom long sleeve tee
GSM, shrink targets, and rib recovery determine how a tee holds shape. Stitch choices and print methods round out wear and care. Write specs that remove guesswork; confirm bulk with lab dips and wash testing.

Fabric that wears well
180–220 GSM combed cotton is a stable base. Cotton‑modal improves drape; cotton‑poly reduces torque. Specify yarn, structure, and finishing. Lock shrinkage to ≈5% length and ≈4% width post wash. [CITE: AATCC dimensional change method] [MENTION: AATCC, ISO]
Sewing choices that last
Twin‑needle hems, reinforced shoulders, and clean neck binding keep shape. Pick rib composition for cuffs and set recovery targets. Document needles, SPI, and seam allowances so bulk matches samples.
Graphics built for wear
Match screen, DTG, or transfer to fabric and art. Set rub/wash fastness, crack resistance, and hand feel. For lower impact, target water‑based inks and MRSL‑aligned solvents. [CITE: “Print durability by ink system”] [INTERNAL LINK: Our print method guide]
Color control at bulk
Set ΔE tolerances, shade bands, and lab protocols. Confirm rib/body shade alignment. No cutting without approvals. Fewer claims, cleaner repeats.
Compliance and sustainability for US & EU markets
US/EU buying needs clean chemistry, safe labels, traceable materials, and audited facilities. Build an RSL/MRSL, align with REACH, Prop 65, CPSIA when relevant, and carry social audits. Pair with OEKO‑TEX, GRS, and RDS certificates.
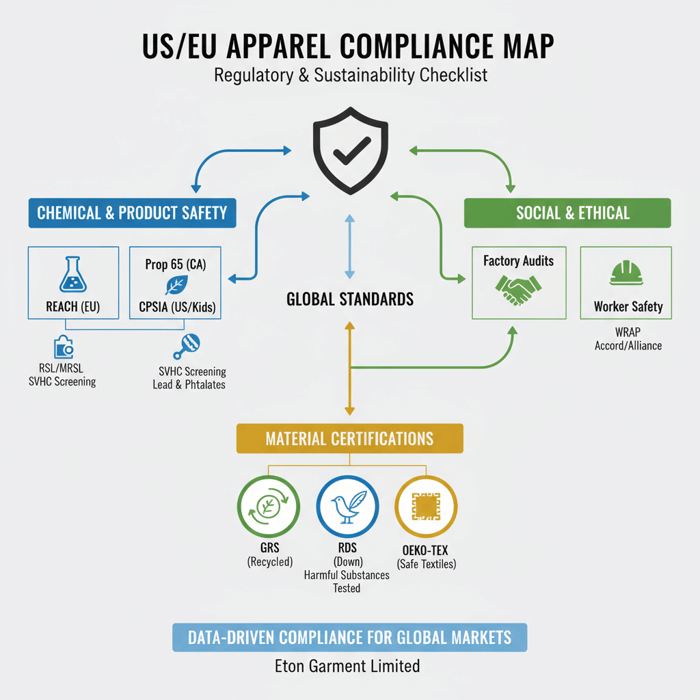
RSL/MRSL in practice
Anchor RSL to EU REACH and major US states. For kids’ lines, include CPSIA checks. Confirm MRSL upstream. Test fabric lots and finished goods. For jackets, check DWR chemistries. [CITE: REACH updates 2023–2025] [MENTION: OEKO‑TEX, Bluesign]
People and factory safety
Use amfori BSCI or WRAP. For Bangladesh, review Accord/Alliance history and current safety files. Track corrective actions to closure. [CITE: “Bangladesh RMG safety data”] [MENTION: ILO, amfori]
Material claims you can stand behind
RDS for down, GRS for recycled fibers, Better Cotton for cotton pathways. Keep chain‑of‑custody intact. Link claims to SKUs. [CITE: “GRS chain‑of‑custody reference”] [INTERNAL LINK: Our sustainability claims playbook]
| Area | Scope | Evidence | Market |
|---|---|---|---|
| REACH | Chemicals | RSL/SVHC tests | EU |
| Prop 65 | Listed substances | Targeted tests | US (CA) |
| CPSIA | Children’s apparel | Lead, phthalates | US |
| OEKO‑TEX | Textile safety | Certificates | US/EU |
| GRS | Recycled fibers | Chain‑of‑custody | US/EU |
| RDS | Down | Certificates | US/EU |
| amfori/WRAP | Social audits | Audit reports | US/EU |
Costing, MOQ, and lead times: a transparent breakdown
Cost clarity trims revisions. Build teardowns, set MOQs, and track calendars by gate. Tees price fabric, ribs, prints, CMT, and freight. Jackets add shell, coating, seam‑tape, insulation, tests, and more complex trims.
Where costs move
Tees swing with fabric GSM, print type, and pack specs. Outerwear shifts with shell tech, insulation, taped seam processes, and zippers. Labor and overhead vary by country. Keep development and bulk costs visible. [CITE: “Garment cost drivers”] [MENTION: BLS wage data; industry price trackers]
| Line Item | Tee | Jacket |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric/Shell | Jersey | Coated/Bonded shell |
| Trims | Ribs, labels | Zippers, seam‑tape, labels |
| Decoration | Embroidery/Heat‑seal | |
| Insulation | — | Down/Synthetic |
| CMT | Base sewing | Complex sewing |
| Testing | RSL, shrinkage | RSL, water resistance |
| Freight | Carton spec | Volumetric impact |
MOQ and timing that hold in bulk
MOQ follows dye lot sizes and print setups. Custom long sleeve tee colors sit near 600–2,000 units; outerwear varies by shell and trim access. Tees run 75–110 days post‑PP; jackets run 90–140 days. Buffers for labs and fits prevent slip. [CITE: “MOQ vs dye lot size”] [INTERNAL LINK: Our production calendar template]
Lead time levers
Pre‑book repeat tee fabric, lock color libraries, and line up labs. Freeze blocks early. For jackets, pre‑qualify seam‑tape and zipper specs and run tests on proto material. Gains compound across seasons.
Quality control, testing, and risk management
Three checkpoints anchor quality: incoming, inline, and final AQL. Tests prove compliance and performance. Written plans and gate reviews reduce defects and claims across tees and outerwear.
QA that catches issues early
Incoming fabric checks: shade, GSM, defects, and lab tickets. Inline: SPI, seam checks, print placement, rib recovery, seam‑tape adhesion for jackets. Final: AQL 2.5 or agreed level, carton drop, barcode/label checks. [MENTION: ISO 9001] [CITE: “AQL in apparel QA”] [INTERNAL LINK: Our AQL explainer]
Tests that stick
Tees: shrinkage, pilling, colorfastness, print durability. Jackets: water resistance, breathability, seam‑tape, down quality. Use accredited labs with consistent methods. Keep reports tied to POs.
Learning loops
Analyze claims, update SOPs, and track KPIs. Share dashboards. Defects drop when teams focus on first‑pass yields and root causes. [CITE: “Garment QA KPIs”] [INTERNAL LINK: Our QC dashboard template]
- AQL 2.5 pass — Annual target (Source: [CITE: QC benchmark])
- Shrinkage ≤5% — Tee program standard (Source: [CITE: AATCC])
- Water resistance ≥10,000 mm — Outer shell target (Source: [CITE: lab standard])
End‑to‑end workflow with Eton Garment Limited
Eton’s workflow ties briefs to PP, bulk, tests, and shipping. China and Bangladesh plants run under one QA map. Custom long sleeve tee and jackets share governance and category‑specific checks.
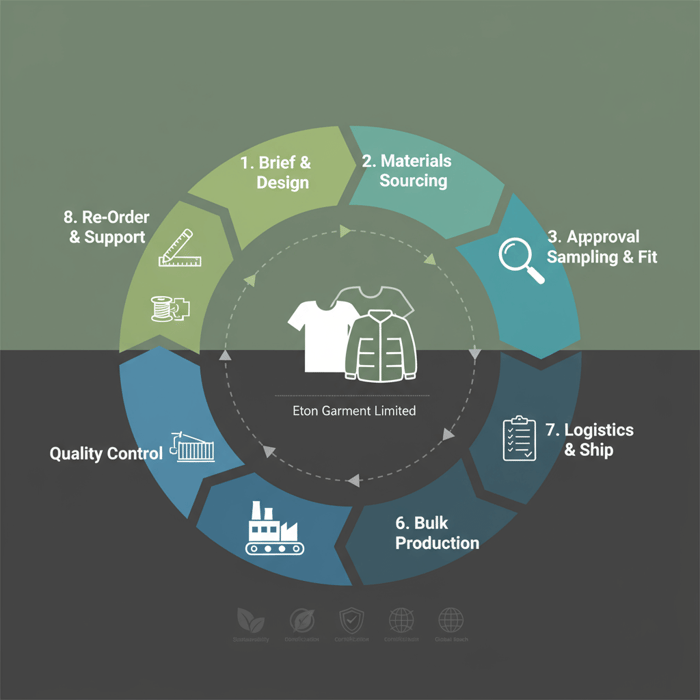
From brief to PP
Gather blocks, materials, and art. Engage mills and trims. Build proto/fit. Test early. Sign PP to unlock bulk. [INTERNAL LINK: Brief template]
Bulk with guardrails
Manage cutting, shading, and sewing with defined SPI and seam parameters. Run inline checks and lot tests. Clear final AQL and pack SOPs. Verify seam‑tape and water resistance for jackets; confirm shade/graphics for tees.
Ship and support
Set Incoterms and documents for US/EU. Review claims and prepare repeats. Eton supports replenishment schedules where materials and blocks are pre‑approved. [MENTION: Incoterms 2020] [CITE: “Import doc requirements US/EU”]
Program examples: tees and outerwear under one governance
Basics and technical pieces live under one QC plan. Clear specs, audited labs, and tight calendars lift consistency. The examples below mirror patterns across programs.
Outerwear with verified performance
A European retailer expanded insulated jackets using an ODM tech base. Proto cleared water resistance and seam‑tape checks; PP locked parts. Bulk ran in 110 days and claim rates fell in season two. [CITE: “Insulation performance data”] [INTERNAL LINK: Outerwear case library]
Custom long sleeve tee repeats that hold fit
A US brand standardized fits and ribs, moved to 200 GSM jersey, and set shrink limits. MOQ sat near 1,200 units per color.
FAQs
What defines a high-quality custom long sleeve tee for US/EU retail?
How does a China clothing manufacturer support US/EU tee and outerwear programs?
What is outerwear OEM and when should brands use it?
OEM vs ODM: which sourcing model suits tees and technical jackets?
What fabric GSM is best for custom long sleeve tee programs?
How do I control shrinkage and torque in knitwear long sleeve tees?
What are lab dips and shade bands, and why do they matter?
What is the typical MOQ for t shirts, and how do dye lot sizes affect it?
What are realistic lead times for apparel production for tees and jackets?
What is AQL 2.5 inspection in apparel and when should I use it?
How do hydrostatic head and RET breathability tests define jacket performance?
What is seam tape sealing in jackets and how is it controlled?
What are REACH, Prop 65, and CPSIA requirements for apparel?
What is the difference between an RSL and an MRSL in apparel sourcing?
Why does OEKO-TEX certification matter for tees and outerwear?
How do GRS certification and chain of custody work for recycled polyester?
What does RDS certification guarantee for down jackets?
Which social compliance audits matter: amfori BSCI or WRAP?
How does print durability compare: screen print vs DTG vs heat transfer?
How do I specify rib knit cuff recovery for long sleeve tees?
How should a production calendar for apparel be structured for US/EU markets?
What is an apparel cost breakdown for a tee vs an insulated jacket?
What Incoterms and freight options (air vs sea) suit apparel shipments?
Why use dual country sourcing with China and Bangladesh?
What does the Eton Garment Limited OEM service include?
Related Articles

T-Shirt Distribution Companies: How to Choose (and When a China Clothing Manufacturer Is Better)
14 minute read
October 16th, 2025
T-Shirt Distribution Companies: How to Choose (and When a China Clothing Manufacturer Is Better) t shirt... more »
Personalized Printed Apparel with a China Clothing Manufacturer: A Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
15 minute read
October 16th, 2025
Personalized Printed Apparel with a China Clothing Manufacturer: A Complete Guide for Fashion BrandsPersonalized... more »
Screenprint T Shirts: A Fashion Brand’s Guide to Sourcing at Scale with a China Clothing Manufacturer
19 minute read
October 15th, 2025
Screenprint T Shirts: A Fashion Brand’s Guide to Sourcing at Scale with a China Clothing... more »
Discover the World of Kinds of Hats: Essential Insights for Fashion Sourcing Managers Seeking Innovation and Excellence
8 minute read
October 15th, 2025
Discover the World of Kinds of Hats: Essential Insights for Fashion Sourcing Managers Seeking Innovation and... more »

