Clothing Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer: End-to-End Guide for US & EU Fashion Brands

 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
16 minute read
Clothing Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer: End-to-End Guide for US & EU Fashion Brands
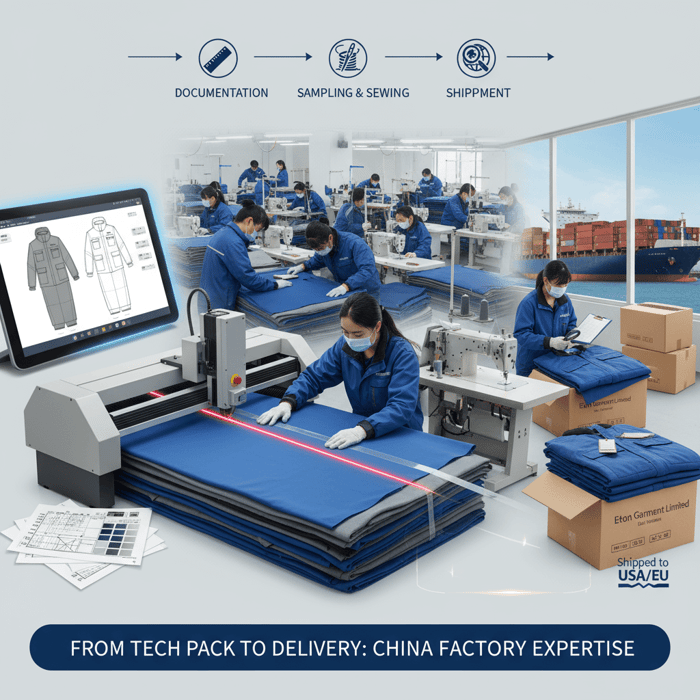
Clothing production turns a design and tech pack into garments your customers love. A seasoned China Clothing Manufacturer gives you scale, technical depth, and dependable delivery across outerwear and performance lines. This guide frames the full path—steps, timing, costs, compliance, risk controls—and shows how Eton’s OEM model supports US/EU retail standards.
Clothing production is the documented process that converts a design into finished garments through sampling, sourcing, cutting, sewing, finishing, QA, and shipment. A China Clothing Manufacturer offers strength in complex outerwear, short lead times, and material access—when paired with clear tech packs, firm approval gates, compliance, and proactive risk management.
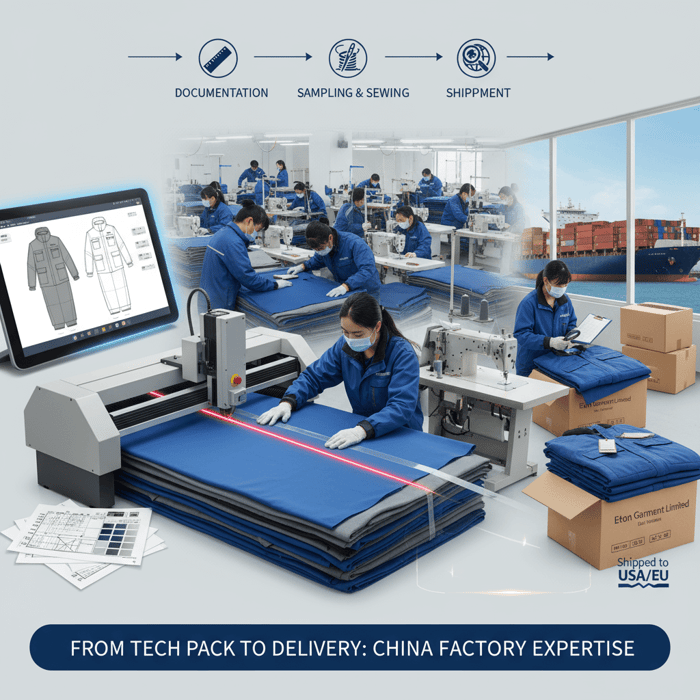

What Is Clothing Production? Definitions, Scope, and When China Is the Right Fit
Clothing production is the full lifecycle of turning a concept into delivered product. It spans documentation, sampling, material commitments, cutting, sewing, finishing, inspection, packing, and logistics. China is a strong fit for technical outerwear and complex builds because the material ecosystem, workforce skills, and specialized equipment are mature and near at hand.
- Asia supplies the majority of global apparel trade — 2024 ([CITE: WTO 2024 trade share overview])
- Brands report speed and resilience as top sourcing priorities — 2024 ([CITE: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024 re: supply chain priorities])
- US apparel imports by region — 2024 ([CITE: OTEXA 2024 category-level data])
[MENTION: McKinsey apparel sourcing research]
[MENTION: WTO apparel trade review]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on 'Outerwear Manufacturing' to support this definition]
Core Terminology (OEM, ODM, Private Label)
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): You own design and specs; the factory executes development and production. Control sits with the brand; speed depends on the tech pack quality and approval cadence.
- ODM (Original Design Manufacturer): The factory supplies market-ready designs or blocks. You customize and brand. Faster to market with less R&D spend; fewer unique details unless jointly developed.
- Private Label: The factory or aggregator offers pre-specified items for labeling. Lowest development lift; limited differentiation; best for basics and replenishment items.
PAA answer: The difference between OEM and ODM is ownership and origin of design. OEM follows your tech pack; ODM begins from the factory’s design library, adapted to your brand.
The Apparel Lifecycle from Tech Pack to Shipment
- Documentation: Tech pack, BOM, graded measurements, construction notes, test methods, labeling.
- Sampling: Proto → Fit → Size Set → Pre-Production (PP). Each sample has a single purpose and gate.
- Material Commitments: Fabric greige booking, dye/finish, trims ordering, testing to MRSL/REACH thresholds.
- Cutting & Sewing: Marker planning, cutting, line setup, line balancing, WIP control, inline QA.
- Finishing & QA: Seam sealing checks, down-proof tests, labeling, metal detection if required, AQL inspection.
- Packing & Logistics: Carton spec, palletization, booking, Incoterms handoff, customs documentation.
When China Clothing Manufacturer Fit Is Optimal
- High complexity: Down jackets, seam-taped shells, bonded fabrics, laser cutting, welded pockets.
- Material intensity: Technical laminates, membranes, performance zippers, specialized foams and films.
- Shorter lead times: Proximity to mills and trim suppliers reduces transit between tiers.
- Mixed MOQs: Better access to mills offering lower dye lot minimums or stock service for outerwear.
- Advanced testing: On-site or near-site labs for hydrostatic pressure, seam tape adhesion, and down fill power.
[INTERNAL LINK: clothing manufacturing OEM service overview → conversion page idea]
[MENTION: YKK for zipper systems and taping solutions]
[MENTION: OEKO-TEX for textile safety testing]
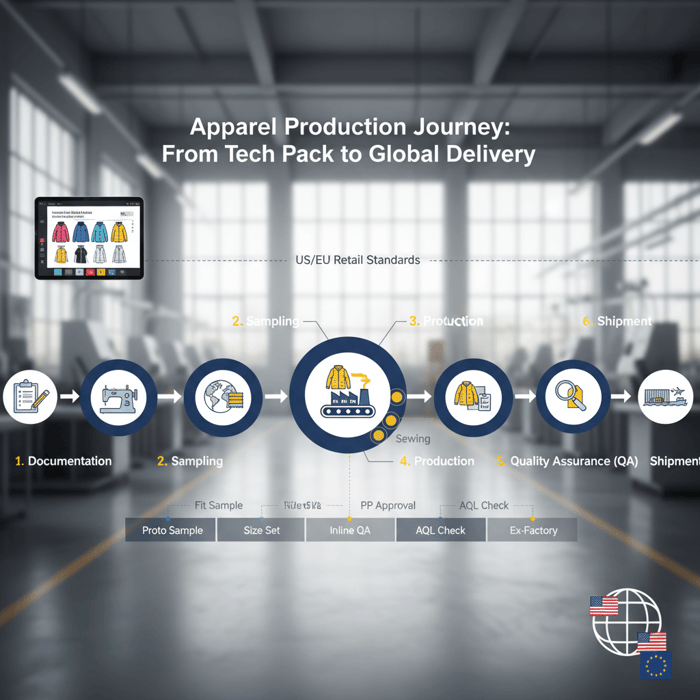
The Clothing Production Process: Step-by-Step with Outerwear Examples
A dependable process is gated. Each stage has known inputs, approvals, and outputs. For outerwear, add seam tape testing, down-fill verification, and performance evaluations early to protect timelines and cost.
| Stage | Inputs | Outputs | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Documentation | Tech pack, BOM, graded specs, test plan | Sampling plan, cost request | 3–5 working days |
| Proto | Design intent, base patterns | Proto sample with construction | 7–12 working days |
| Fit | Proto feedback, measurement list | Fit sample with corrected pattern | 7–12 working days |
| Size Set | Approved fit, graded rules | Size run for grade verification | 10–15 working days |
| PP (Pre-Production) | All approvals + bulk materials | PP sample reflects bulk build | 7–10 working days |
| Production | PP approval, cut plan, line setup | Bulk units with inline QA | 4–8 weeks, product dependent |
| Final QA & Packing | AQL plan, carton spec | Passed inspection, packed cartons | 3–7 working days |
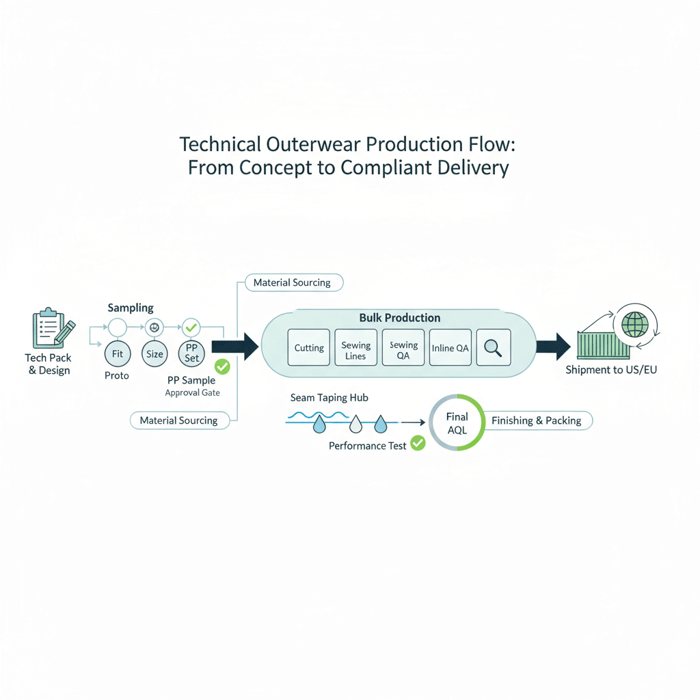
Documentation & Sampling (Proto, Fit, Size Set, PP)
- Proto sample: Proves construction and silhouette. Gate: construction approval. Costing can start.
- Fit sample: Validates pattern and measurements. Gate: fit approval with graded rules.
- Size set: Confirms grading across sizes. Gate: size spec lock; labels and POM tolerances fixed.
- PP sample: Built with bulk materials and trims. Gate: PP approval = production green light.
For taped shells, run hydrostatic pressure, spray tests, and tape adhesion on PP. For down, confirm fill power, fill weight by size, and down-proof fabric tests before bulk. [MENTION: IDFL for down testing] [CITE: “Down testing protocols for apparel” style source]
Cutting, Sewing, and Line Balancing
Effective cutting begins with optimized markers. Wastage targets are set per fabric width and pattern geometry. Sewing efficiency depends on line balancing—matching station cycle times so bundles flow without stalls. For outerwear, isolate seam sealing in a dedicated hub to control heat, pressure, and tape feed variance. Track WIP visually and by ticket scan. A short daily standup on first-pass yield helps catch issues before they multiply.
Finishing, QA (AQL), and Packing
Inline QA checks stop defects at source. A finishing list covers thread trimming, seam tape re-checks, snap actions, zipper run tests, panel shading, and label positions. AQL (e.g., ANSI/ASQ Z1.4) defines sample size and accept numbers. Example: AQL 2.5 for major defects on a 1,200-unit lot yields a fixed sample count and pass/fail gate. Metal detection is applied when retailer policy requires it. Carton construction, insert type, and fold method follow the brand’s pack manual.
PAA answer: Two to four sampling rounds are common before production approval, depending on design complexity and fit goals. [INTERNAL LINK: Our garment factory capabilities page to show sampling lead times]
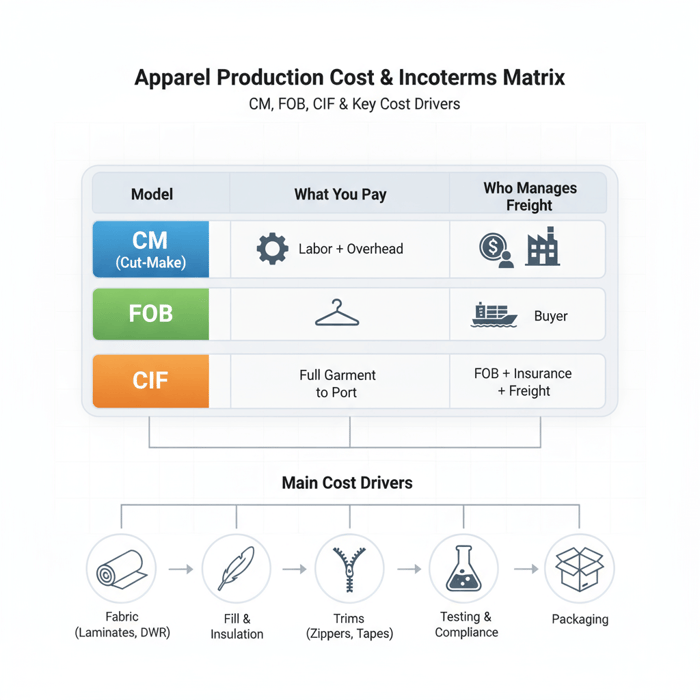
Costs, MOQs, and Lead Times in Clothing Production (US/EU Context)
Costs cluster around materials, make complexity, and order size. MOQs flow from mills and trim makers. Lead times reflect seasonality, lab approvals, and logistics choices. Add buffers around fabric lead times and PP approvals to protect your delivery date.
| Model | What You Pay | Who Manages Freight | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM (Cut-Make) | Labor + overhead | Buyer | Material transparency; flexible sourcing | High buyer workload; exposure to material variance |
| FOB | Full garment up to port | Buyer | Simplicity; factory manages materials | Less material line-item detail; port risk on buyer |
| CIF | FOB + insurance + freight | Seller | Predictable landed cost to port | Less control on routing; inland costs remain |
- Outerwear sewing minutes and CM rates vary by design features — 2024 ([CITE: Time study or SMV benchmark for jackets])
- US/EU demand seasonality drives capacity constraints — 2024 ([CITE: McKinsey 2024 on peak seasons])
- US import lead time norms by mode — 2024 ([CITE: Ocean vs air transit ranges US/EU])
Cost Drivers for Technical Jackets
- Fabric: 2L/3L laminates, membrane type, denier, finishing (DWR, down-proof), dye lot size.
- Fill & Insulation: Down fill power and weight; synthetic loft per square meter; quilting complexity.
- Construction: Seam taping length; welded/bonded operations; waterproof zippers; plackets and storm guards.
- Trims & Components: Zippers, snaps, toggles, cord locks, reflective films, seam tapes by brand/spec.
- Testing & Compliance: Colorfastness, hydrostatic pressure, RSL/ MRSL testing, packaging compliance.
- Packaging & Cartons: Recycled content targets, polybag alternatives, print plate requirements.
MOQ & Lead-Time Ranges
- Fabric MOQs: 800–1,200 meters for dye-to-order common; stock service lowers entry points.
- Trim MOQs: Zippers often 500–1,000 units per color/length; seam tape by roll count.
- Sampling: 4–8 weeks cumulative for proto-to-PP for complex jackets when feedback is quick.
- Production: 4–8 weeks after PP approval; add mill lead times (3–8 weeks) and lab approvals.
- Logistics: Ocean to US West Coast ~2–3 weeks port-to-port; to EU main ports ~4 weeks; air 3–7 days. [CITE: “Trade lane transit times 2024”]
Incoterms and Logistics Choices
- FOB + ocean: Cost efficient for volume; needs calendar discipline on booking and cut-offs.
- FOB + air split: Use for size curves or color top-ups; control unit economics with strict caps.
- CIF: Useful when freight markets are volatile and budget certainty matters.
[MENTION: Maersk schedule reliability research]
[MENTION: YKK lead time advisories]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our 'Sourcing & Logistics' explainer for deeper term selection]
Choosing a Production Partner: China vs Bangladesh vs Vietnam
Pick a location by product complexity, capacity, compliance profile, and cost. China is strong in technical jackets and mixed-MOQ programs. Bangladesh offers scale for padded and sewn volume with strong compliance progress. Vietnam is a fit for knit/active and high-consistency sewing, with select outerwear hubs.
| Criteria | China | Bangladesh | Vietnam |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Outerwear | Excellent: taping, bonding, down, short dev loops | Good for padded; growing taping capabilities | Selective facilities; strong for active |
| Material Ecosystem | Deep local mills & trims | Improving; many trims imported | Good; some imports required |
| Lead Time | Shorter dev and PP cycles | Longer for imported inputs | Moderate; consistent execution |
| Cost | Higher CM; strong efficiency | Competitive for volume | Moderate; stable quality |
| Compliance & Audits | Broad certification landscape | Strong social compliance progress | Consistent standards; stable audit cadence |
- Regional apparel export shares — 2024 ([CITE: WTO 2024 regional shares])
- US import mix — 2024 ([CITE: OTEXA by country])
Criteria Overview
- Product: Taped shells and down lines favor mature taping labs and down testing partners.
- Capacity: Match forecast to line count, SMV, and needle-hours available in-season.
- Compliance: Request recent Higg FEM/FSLM, social audits, and chemical management proofs.
- Material access: Local mills, dye houses, and trim makers cut transit and risk.
- Total cost: Balance CM against dev speed, error rates, and rework risk.
Decision Framework
- Define product complexity and testing needs.
- Rank location fit using a weighted score for capability, lead time, cost, and compliance.
- Prequalify factories on specialization and audit status.
- Run a pilot style to validate SMV assumptions and QA results.
- Scale orders with dual-sourced critical materials to limit disruption risk.
[INTERNAL LINK: Our China vs Bangladesh sourcing explainer for deeper evaluation]
Sustainability, Compliance, and Traceability for US & EU Retail
US/EU retail expects chemical compliance, credible audits, and traceability from Tier 1 to raw materials where feasible. Build your plan on ZDHC MRSL, OEKO-TEX testing, Higg FEM/FSLM, and emerging EU due diligence standards. Document gates and keep evidence organized per PO.
| Framework | Scope | What to Document | Common Proof |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZDHC MRSL | Chemicals in process | MRSL conformance, wastewater tests | ZDHC Gateway entries, lab reports |
| OEKO-TEX | Product safety | Material-level test results | OEKO-TEX STeP/Standard 100 |
| Higg FEM/FSLM | Facility environmental/social | Annual assessments | Verified scores, improvement plans |
| EU Due Diligence | Risk-based supply checks | Policy, risk map, remediation steps | Supplier list, audit cadence, CAPs |
Traceability Steps
| Tier | Material | Documentation | Audit Cadence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | Cut & sew | PO, packing list, AQL reports | Every season or per retailer |
| Tier 2 | Fabric mills & dye houses | MRSL/RSL tests, batch records | Annual; risk-based extra checks |
| Tier 3 | Yarn/spinners | Supplier declarations, scope certs | Annual; focus on critical fibers |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
- US: CPSIA for children’s wear; state laws on PFAS and labeling where applicable. [CITE: “US PFAS regulations round-up 2024”]
- EU: REACH limits for SVHCs; due diligence frameworks under CSDDD progress. [CITE: “EU CSDDD 2024 updates”]
- Retailer programs: Specific RSL/packaging standards and audit formats; align early.
[MENTION: ZDHC Roadmap to Zero MRSL v3.1]
[MENTION: Sustainable Apparel Coalition — Higg updates]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our 'Sustainability & Compliance' pillar page]
Data & Trends in Clothing Production (2023–2025)
Asia remains the backbone of apparel sourcing while nearshoring pilots grow. Brands seek calendar certainty, fewer reworks, and clearer compliance evidence. Digital sampling and PLM adoption strengthen feedback speed and version control.
- Supply chain resilience ranks top-three for fashion executives — 2024 ([CITE: McKinsey executive survey 2024])
- Apparel trade concentration remains Asia-led — 2024 ([CITE: WTO 2024])
- US import trend shifts by category — 2024 ([CITE: OTEXA 2024])
Lead Time Benchmarks
- Development (outerwear): 6–10 weeks from proto to PP with fast feedback and pre-booked greige.
- Bulk: 4–8 weeks from PP to ex-factory when materials are in-house and QA runs smoothly.
- Logistics: Plan ocean for base demand and air for surgical top-ups; lock booking windows early.
Compliance & ESG Disclosure Trends
- Expansion of PFAS policies in US/EU market segments. [CITE: “PFAS in textiles policy tracker 2024”]
- Higher expectation for public supplier lists and audit summaries. [CITE: “Fashion Transparency Index 2024”]
- More verified Higg modules and wastewater reporting on ZDHC Gateway. [CITE: “ZDHC program update 2024”]
[MENTION: Fashion Revolution — transparency benchmarks]
How-To Execute Clothing Production with Confidence
Use a gated plan and match each approval to risk reduction. Lock documentation, align sampling cadence, pre-book critical materials, and codify QA. Track milestones weekly and keep a buffer around fabric and PP gates.
Preparation (Tech Pack, BOM, Measurement Specs)
- Write a complete tech pack: sketches, construction notes, stitch types, seam sealing map, and grade rules.
- Build the BOM by color: fabric codes, finish, trims, labels, packaging, test methods.
- Define test plan and compliance targets: MRSL, RSL, and retailer-specific standards.
- Set the sampling calendar: proto, fit, size set, PP, with named decision owners.
- Confirm Incoterms and booking plan with logistics.
Execution Steps (Sampling → Production → QA → Shipment)
- Run proto and fit; record changes in PLM and lock measurement tolerances.
- Approve size set; align labels and care content for US/EU markets.
- Approve PP built with bulk materials; run performance tests for taped seams and insulation.
- Start bulk after PP approval; hold daily quality huddles; adjust line balancing as needed.
- Conduct final AQL; pack to manual; hand off under agreed Incoterms; share shipment docs.
Quality Assurance (AQL, Inline Checks, PP Sign-off)
- AQL plan: Set defect definitions and acceptance numbers by category (critical/major/minor).
- Inline checks: First 10 pieces per line station; stop-and-fix for repeated defects.
- Performance checks: Tape adhesion and hydrostatic pressure; down-fill weight by size; zipper run smoothness.
- PP sign-off: Confirm every spec, trim, label, and test before bulk; this is the stop gate.
[INTERNAL LINK: Our QA methodology and AQL reference page for apparel]
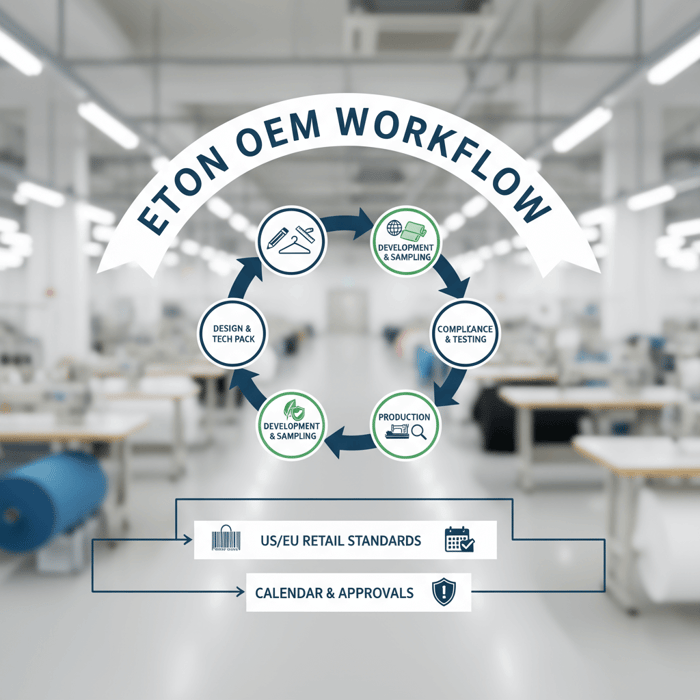
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service (Eton)
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service links design support, technical development, sourcing, production, and compliance into one flow for outerwear and technical apparel. With 30+ years in China and Bangladesh, the team aligns to US/EU retail calendars and approvals while protecting budgets and timelines.
| Brand Need | Eton OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Faster development | Sampling calendar with dedicated pattern room | Proto-to-PP in shorter cycles for complex jackets |
| Material access | Supplier network across China/Bangladesh | Better fabric/trim options and MOQs |
| Technical QA | Seam taping SOPs, down QA, in-line audits | Stable performance in lab and wear tests |
| Compliance evidence | Higg FEM/FSLM, ZDHC, OEKO-TEX testing support | US/EU market readiness and audit track |
| Calendar certainty | Gated approvals with shared tracking | On-time ex-factory with buffer logic |
Use Case 1: Launching a Technical Jacket Line
A US outdoor brand needs a 3L shell with taped seams and waterproof zippers. Eton proposes a sampling plan with performance tests front-loaded at PP. The team pre-books greige with two membrane options to hold agility. PP passes hydrostatic and tape adhesion; bulk flows in six weeks with daily inline checks. The brand receives photo logs, AQL sheets, and shipment docs mapped to Incoterms.
Use Case 2: Scaling a Padded Outerwear Program
A European retailer expands a padded line with mixed colors and sizes. Eton aggregates trims, negotiates zipper MOQs, and blends China and Bangladesh capacity. Size sets confirm grade; PP sets quilting specs and fill weights. Production runs across parallel lines with shared QA staff. On-time deliveries continue across the season with air splits used for size top-ups only.
Learn how this model fits your calendar on our garment factory page: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service. [INTERNAL LINK: garment factory page → https://china-clothing-manufacturer.com/garment-factory/]
[MENTION: Liverpool F.C. apparel partnership reference]
[MENTION: Higg FEM verification partners]
Risks, Compliance & Localization
Seasonal capacity spikes, fabric delays, and approval slips carry schedule risk. Set buffers, dual-source critical materials, and hold firm to PP and QA gates. Align packaging, labeling, and testing to US/EU requirements from day one.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fabric delay | Medium | High | Pre-book greige; approve lab dips early; secondary mill |
| PP slip | Medium | High | Calendar hard gates; rapid feedback; pre-test critical items |
| Seam tape failure | Low–Medium | High | Run tape trials; verify heat/pressure; PP performance tests |
| Down variability | Low | Medium | Certify fill power; weigh per size; down-proof tests |
| Audit non-conformance | Low–Medium | High | Pre-audit review; corrective action plans; verified modules |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
- Labeling: Fiber content, care, and origin labeling differ by country; prepare variant artworks early.
- Chemicals: Align with ZDHC MRSL and retailer RSL; test high-risk materials and colors first.
- Packaging: Recycled content and recyclability rules in select US states and EU markets. [CITE: “EU packaging regulations 2024 overview”]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our packaging & labeling checklist for US/EU go-to-market]
Conclusion & Next Steps
Success with a China Clothing Manufacturer rests on strong documentation, firm approval gates, cost clarity, and credible compliance. Use the location framework, risk matrix, and QA plan to move from concept to purchase orders with fewer surprises and steadier lead times.
- Lock your tech pack and BOM; set a sampling calendar.
- Define your compliance bundle and test plan.
- Select factory location by product complexity and capacity.
- Approve PP and performance tests before bulk.
- Track QA and shipments against weekly milestones.
[INTERNAL LINK: Our 'Outerwear Manufacturing Guide' hub]
[INTERNAL LINK: 'Sustainability & Compliance' pillar]
[INTERNAL LINK: 'China vs Bangladesh Sourcing' decision resource]
Textile From Day One.
Author & Review Notes (E-E-A-T)
- Author: Senior Production Strategist, 15+ years in outerwear manufacturing across China and Bangladesh. [INTERNAL LINK: Author bio page link]
- Reviewer: Director of Quality & Compliance, Eton Garment Limited.
- Methodology: First-hand factory processes, internal QA documentation, and external references [S1–S7].
- Limitations: Cost/lead-time ranges vary by product, season, and supplier capacity; regulatory guidance evolves; confirm current retailer requirements.
- Disclosure: Eton provides OEM/ODM services; examples reference Eton’s capabilities.
- Last Updated: 2025-10-28
References & Sources
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024 (2024). https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights
- World Trade Organization — World Trade Statistical Review 2024 (2024). https://www.wto.org/
- US Department of Commerce, OTEXA — Apparel Import Statistics 2024 (2024). https://www.trade.gov/otexa
- Fashion Revolution — Fashion Transparency Index 2024 (2024). https://www.fashionrevolution.org/
- ZDHC Foundation — MRSL v3.1 (2023) and Program Updates (2024). https://www.zdhc.org/
- Sustainable Apparel Coalition — Higg FEM/FSLM resources 2023–2024 (2023–2024). https://apparelcoalition.org/
- European Commission — Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence developments (2024). https://ec.europa.eu/
FAQs
Related Articles

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

