Choosing a Sportswear Company: A US/EU Buyer’s Playbook with a Trusted China Clothing Manufacturer

 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
10 minute read
Choosing a Sportswear Company: A US/EU Buyer’s Playbook with a Trusted China Clothing Manufacturer
Sportswear company choice sets your season’s ceiling. For US/EU brands, the right China Clothing Manufacturer brings performance engineering, transparent costing, and scale without compromising compliance or ethics. This playbook maps definitions, vetting criteria, testing, timelines, cost drivers, and integration models—grounded in real factory workflows and the demands of performance apparel.
What qualifies as a modern sportswear company?
A modern sportswear company delivers technical performance, repeatable fit, and production reliability. It integrates OEM/ODM design support, lab-validated fabrics, and compliance for US/EU. It differentiates sportswear (training, teamwear) from athleisure (comfort-first) and technical outerwear (weather protection), and shows evidence of process control, certifications, and scale.
Definition and scope: sportswear vs athleisure vs technical outerwear
Sportswear targets performance in motion—stretch, breathability, sweat management, abrasion resistance, and durability under training loads. Athleisure prioritizes comfort, handfeel, and daily wear aesthetics while borrowing some sporty features. Technical outerwear focuses on weather protection—waterproofness, windproofness, seam-sealing, thermal regulation—and survives harsher environments.
The best sportswear company builds category-specific blocks: training tops and tights (poly/spandex), teamwear (mesh, tricot), outdoor performance (nylon/spandex, ripstop), and hybrid crossover pieces. It standardizes fabric testing and fit grading so sizes remain consistent across seasons.
OEM vs ODM in sportswear
OEM manufactures to your tech pack; ODM provides design concepts, patterns, and ready-to-adapt specs. For new lines, ODM lowers development time; for established brands, OEM preserves identity and fit continuity. Elite partners blend both—rapid ODM proposals backed by OEM discipline.
[MENTION: Nike and adidas R&D models and their supplier ecosystems]
[CITE: A detailed taxonomy study distinguishing sportswear and athleisure from a reputable industry source]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on performance apparel specs]

Vetting a sportswear company for US/EU compliance and scale
Vetting starts with proof: certificates, lab reports, audit summaries, and production run data. A capable sportswear company should show REACH/CPSIA conformance, ethical audits, process maps, and a clean testing history—plus references from brands with similar volumes and profiles.
Core vetting checklist
- Certifications: OEKO-TEX Standard 100, bluesign approval or adoption, Higg FEM, ZDHC MRSL compliance.
- Regulatory coverage: EU REACH (ECHA), US CPSIA (CPSC), California Prop 65 (OEHHA).
- Audit frameworks: BSCI, WRAP, SMETA/SEDEX, ISO 9001/14001.
- Testing partners: SGS, Intertek, Bureau Veritas; recent reports aligned to AATCC/ASTM/ISO/JIS.
- Evidence of scale: line capacity, historical on-time delivery metrics, and MOQ flexibility by product type.
[MENTION: European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC)]
[CITE: ECHA guidance on REACH compliance (latest version)]
[CITE: CPSIA rule summary and component testing updates]
Certification and compliance matrix
| Requirement | Region | Standard/Body | What to request |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical compliance | EU | REACH (ECHA) | RSL alignment, third-party test reports [CITE: ECHA official list] |
| Children’s products | US | CPSIA (CPSC) | Lead/phthalates tests, tracking labels [CITE: CPSC guidance] |
| Substances list | US | Prop 65 (OEHHA) | Risk assessment, supplier attestations [CITE: OEHHA updates] |
| Textile safety | US/EU | OEKO-TEX Standard 100 | Certificates by material category |
| Chemical program | Global | ZDHC MRSL | MRSL v3 conformance, wastewater testing [CITE: ZDHC Roadmap] |
| Sustainability | Global | bluesign | Approved fabrics, system partner status |
| Ethical audits | Global | BSCI/WRAP/SMETA | Current audit reports and CAPA logs |
[INTERNAL LINK: Eton compliance and sustainability overview on our site]

Materials and performance engineering
Performance starts with fibers, yarns, and finishes. A sportswear company builds fabric libraries spanning polyester/nylon blends, spandex content tuned to movement, and finishes for moisture management. For weather pieces, membranes and seam technology handle waterproofness and windproofness.
Fabric families and why they matter
- Polyester knits: durability, quick-dry; pair with spandex for stretch.
- Nylon wovens: abrasion resistance; ideal for outer shells and training shorts.
- Recycled inputs: rPET yarns, recycled nylon; supported by GRS where available [CITE: GRS certification program].
- Yarn tech: filament counts, microfibers, hollow fibers for thermal/lightweight targets.
[MENTION: AATCC and ASTM committees for textile performance standards]
[CITE: Comparative study on polyester vs nylon abrasion performance]
Moisture management and breathability
Moisture-wicking relies on capillary action and surface chemistry. Specs reference wicking tests (AATCC 197), drying time, and air permeability (ASTM D737/ISO 9237). Breathability metrics include MVTR (ASTM E96), and RET (ISO 11092) where heat loss and moisture vapor transport are critical.
Weather protection and seam technology
For technical outerwear: hydrostatic head (AATCC 127/ISO 811) validates waterproof performance; DWR spray ratings (AATCC 22/ISO 4920) indicate repellency. Seams use taping or bonding; stitch types like flatlock reduce chafe for training tops and tights.
Lab testing protocol—build the spec and verify
| Property | Test | Standard | Sample Spec Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wicking | Vertical wicking | AATCC 197 | ≥ 20 cm in 30 min |
| Air permeability | Air flow rate | ASTM D737 / ISO 9237 | Varies by knit/woven; 50–400 L/m²/s |
| Dry time | Evaporation rate | Brand method / ASTM references | Quicker is better; benchmark control |
| Waterproofness | Hydrostatic head | AATCC 127 / ISO 811 | ≥ 10,000 mm for rain shells |
| Repellency | Spray test | AATCC 22 / ISO 4920 | Grade 90/100 target |
| Stretch/recovery | Elongation & growth | ASTM D5034 / brand method | 20–40% stretch, minimal growth |
| Abrasion | Martindale | ISO 12947 | ≥ 20,000 cycles (training) |
[CITE: AATCC resources on test method updates]
[CITE: ISO/ASTM standards catalogs for textile testing]
Sampling, fit, and lab validation workflow
A proven sportswear company runs a disciplined sampling path: concept, proto, fit set, salesperson sample, PP sample, then bulk. Each gate logs fabric and trim approvals, lab validations, and measurement sign-offs across US/EU size scales.
Step-by-step development flow
- Brief & tech pack: materials, fit block, finish targets, tests required.
- Proto sample: silhouette and construction methods.
- Fit sample set: sizes tested on mannequins and live wearers.
- Lab testing: AATCC/ASTM/ISO per property; issue corrective actions as needed.
- Salesman sample: colorways, trims ready for range viewing.
- PP sample: pre-production verification with final lab checks.
- Bulk: sealed spec; inline inspections tied to AQL.
[MENTION: Tech pack standard frameworks and digital PLM tools]
[CITE: Case study on fit consistency reducing returns in EU markets]
Fit standards and grading for US/EU
Differences in US vs EU measurement blocks require defined grade rules. A tight grade keeps sleeve length, waist rise, and thigh ease consistent across sizes, improving return rates and customer satisfaction. Brands should record garment ease by category and monitor tolerance at each checkpoint.

Costs, MOQs, lead times, and freight—China vs Vietnam vs Bangladesh
Cost drivers sit in fabrics, trims, seam technology, and testing. MOQs and lead times vary by hub and product complexity. The right sportswear company will show realistic ranges and mitigation plans for price, time, and capacity.
Hub comparison (indicative ranges)
| Hub | Strengths | Typical MOQ | Lead Time (days) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Technical depth, fast sampling, specialty trims | 300–800/style | 75–120 | Higher fabric variety; cost premium vs neighbors |
| Vietnam | Strong knits, stable labor market | 500–1000/style | 90–140 | Growing tech; sometimes longer fabric lead times |
| Bangladesh | Value at scale, strong wovens | 600–1500/style | 90–150 | Best for volume basics; tech pieces pair with China dev |
[CITE: Trade reports on apparel lead times and capacity by country, 2023–2024]
[MENTION: World Trade Organization apparel trade summaries]
Landed cost anatomy
- Fabric and materials: 40–60%.
- Labor and overhead: 15–25%.
- Trims/hardware: 5–10%.
- Testing/compliance: 1–3%.
- Freight/duties: 5–15% (incoterms and destination dependent).
[CITE: Industry costing benchmarks for sportswear categories]
Compliance, chemical management, and ethical sourcing
A sportswear company shipping to US/EU maintains live chemical programs aligned to RSL/MRSL, audited labor practices, and certification coverage. Brands should request supplier declarations, test reports, and audit CAPA summaries.
Regulatory guardrails
- REACH: substances of very high concern (SVHC) screening and documentation [CITE: ECHA SVHC list updates].
- CPSIA: lead, phthalates, small parts; tracking labels for kids’ items [CITE: CPSC updates].
- Prop 65: exposure assessment and labeling decisions [CITE: OEHHA guidance].
Chemical management systems
- ZDHC MRSL: banned chemistries upstream; wastewater testing confirms practice.
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100: material-specific safety assurances.
- bluesign: input stream control and verified process safety.
[MENTION: ZDHC Roadmap to Zero program and bluesign system partners]
[CITE: ZDHC MRSL v3.1 documentation and adoption rates]
Quality assurance and scaling from pilot to mass
Quality hinges on planned checkpoints and data. A mature sportswear company uses PP approvals, inline AQL inspections, tolerance charts, and CAPA loops to hold fit and performance steady while scaling.
Quality gates
| Gate | Focus | Tools | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP approval | Spec lock, trims, prints | Golden sample, lab retests | Authorized for bulk |
| Inline inspection | Measurement, seam integrity | AQL plans, test swatches | Early detection |
| Final audit | Packing, labeling, carton tests | Carton crush, barcode checks | Ship-ready |
| CAPA loop | Root cause & fix | 5-Whys, Pareto analysis | Continuous improvement |
[CITE: Industry AQL tables and defect taxonomy references]
[MENTION: ISO 9001 framework in apparel quality management]
Orchestrating China–Bangladesh production: speed and value
A dual-hub model pairs China’s sampling and technical depth with Bangladesh’s cost-effective scale. A capable sportswear company runs tiered production: complex shells and critical test fabrics in China; volume basics, shorts, and mesh in Bangladesh—sharing patterns and QC.
Tiered production and risk control
- Development in China; bulk basics in Bangladesh.
- Shared measurement libraries and PP golden samples.
- Consolidated trims to reduce variability.
- Contingency capacity for peak seasons.
[MENTION: Logistics firms reporting transit times across Asia–US/EU lanes]
[CITE: Freight benchmark reports (ocean vs air) for apparel lanes, 2024]
Packaging, labeling, and customs
- Care labels aligned to US FTC and EU standards [CITE: FTC textile labeling rules].
- HS codes and tariff planning; Incoterms FOB/CIF/DDP.
- Carton crush tests, barcode validation, DC-compliant pack plans.
[INTERNAL LINK: Our carton and labeling standard operating procedure]
Partnering with Eton Garment—OEM service with technical outerwear depth
Eton Garment Limited blends China/Bangladesh capacity with 30+ years of technical apparel expertise. For brands seeking a sportswear company that can scale, Eton’s OEM and ODM support accelerates development and de-risks bulk.
What Eton runs well
- Outerwear: down jackets, parkas, taped shells.
- Training gear: tights, tops, shorts with wicking knits.
- Teamwear: durable fabrics, consistent grading, seasonal colorways.
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service integrates design, fabric sourcing, lab validation, and compliance documentation. Explore the service at Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service for detailed workflows and category coverage.
[INTERNAL LINK: Case studies with Liverpool F.C., Forever 21, and more on our site]
[MENTION: SGS/Intertek reports commonly used by Eton clients]
[CITE: Customer outcomes study—on-time delivery and return rate improvements]

Timelines, communication cadence, and speed-to-market
Timeline success is a function of clear briefs, disciplined sampling, rapid lab feedback, and honest capacity planning. A dependable sportswear company sets weekly checkpoints and tracks risks in shared dashboards.
Indicative timeline (per style)
- Week 0–2: Brief/tech pack and proto.
- Week 3–6: Fit set and lab testing.
- Week 7–9: Salesman samples and PP approvals.
- Week 10–18: Bulk production with inline AQL.
- Transit: Ocean 25–40 days to EU; 14–22 days to US West Coast; air 3–7 days [CITE: Carrier schedules and port-to-port benchmarks].
Cadence and outcomes
- Weekly cross-functional reviews: materials, tests, capacity.
- Biweekly risk logs: fabric lead times, lab queue, color standardizations.
- Post-season review: defect Pareto, returns, on-time delivery rate, sample cycle length.
[CITE: Apparel process efficiency studies linking cadence to cycle-time reduction]
[INTERNAL LINK: Our development calendar template]
Final takeaways for US/EU brands
Choose a sportswear company that proves performance, compliance, and scale on paper and on the line. Build a test-led spec, audit the factory’s QA
FAQs
Related Articles
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
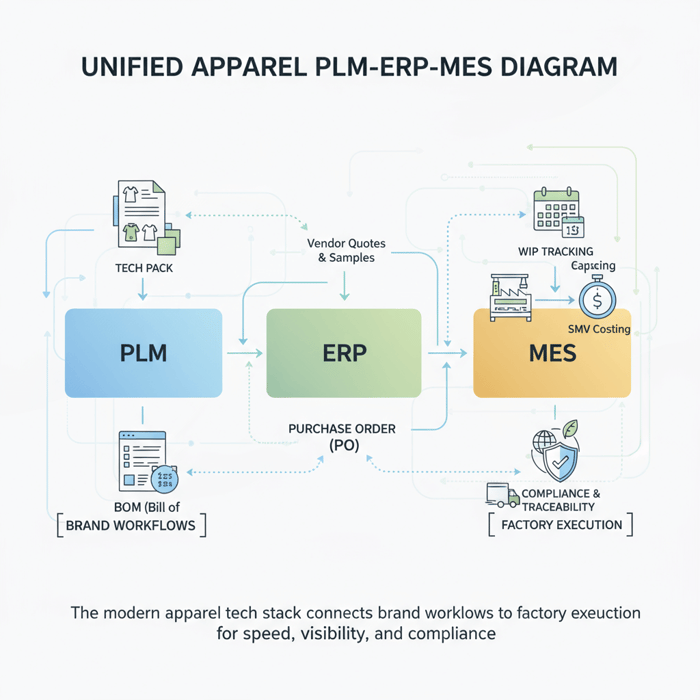
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »

