Best Clothing Printing Companies: How Fashion Brands Choose and Scale with a China Clothing Manufacturer
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
22 minute read
Best Clothing Printing Companies: How Fashion Brands Choose and Scale with a China Clothing Manufacturer
Best clothing printing companies give fashion teams a reliable path from concept to saleable product without color or wash surprises. For US/EU brands working with a China Clothing Manufacturer, the winning strategy is to choose method and vendor type by fabric, volume, and durability, lock compliance early, and integrate printing inside OEM production so samples and bulk behave the same.
The best clothing printing companies match fabric and graphics to screen, DTG, DTF, or sublimation, meet US/EU compliance, and scale from samples to bulk. Verify certificates, demand lab-tested strike-offs, and favor factory-integrated printing with an OEM partner to reduce handoffs, compress timelines, and keep color consistent from pilot to thousands of units.
Apparel teams in the US and EU face the same hurdles every season: prints that fade after washing, colors that shift away from Pantone targets, unclear minimum order quantities (MOQs), and opaque costs. The top-performing approach pairs method fit with governance—compliance documentation, disciplined sampling, and lab testing—and then orchestrates production through an integrated China Clothing Manufacturer that runs the same inks, pretreatments, and QC from prototypes to volume.
This blueprint provides a practical selection framework for best clothing printing companies and shows how to move from small drops to bulk output. It compares vendor types, maps print methods to fabrics, outlines typical costs and lead times, and includes a briefing and testing playbook. It also documents US/EU compliance and sustainability requirements and introduces how Eton Garment Limited integrates printing inside OEM/ODM manufacturing for technical outerwear, kidswear, and graphic apparel.
[MENTION: FESPA technical guides on textile printing methods] and [MENTION: Grand View Research market data on digital textile printing growth] indicate strong adoption of DTF and DTG for short runs and sublimation for polyester, while screen printing remains dominant for bulk spot-color orders. The guidance below grounds those trends in factory realities—ink chemistry, pretreatment, seam-aware placements—and in compliance frameworks required for US and EU retail.
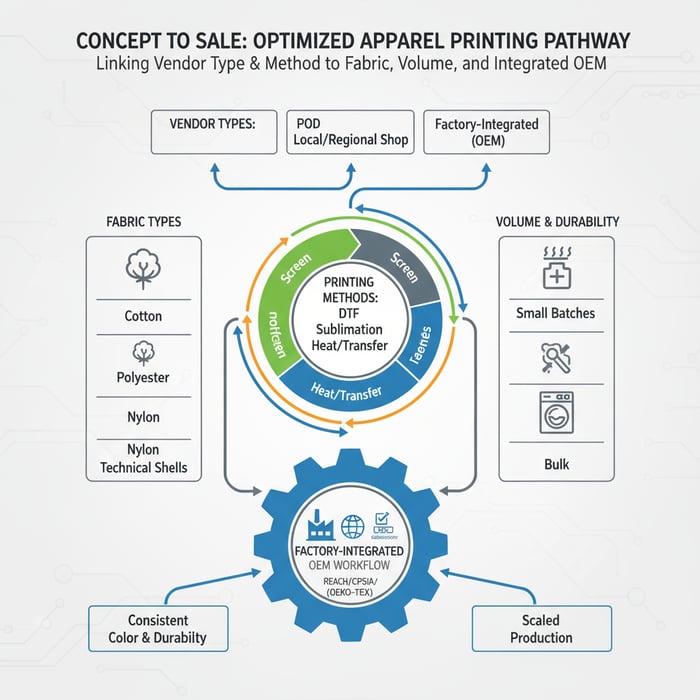
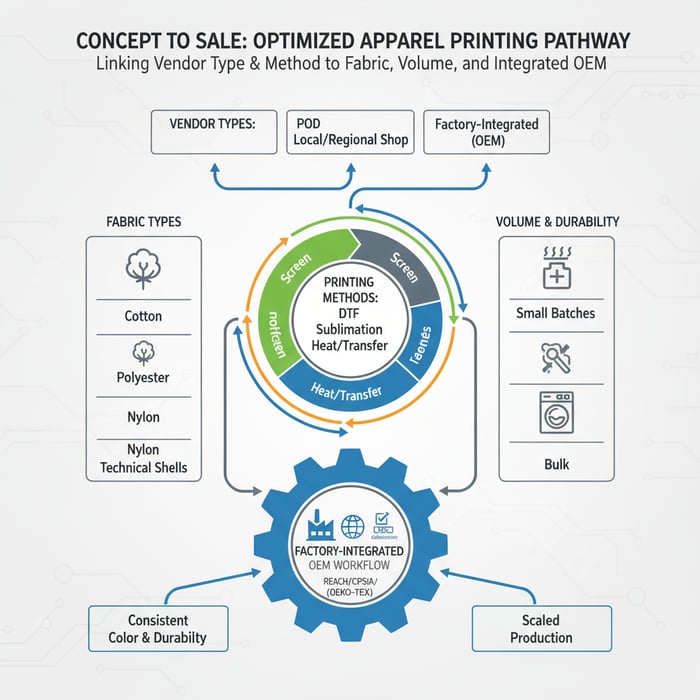
What “best clothing printing companies” means for fashion brands
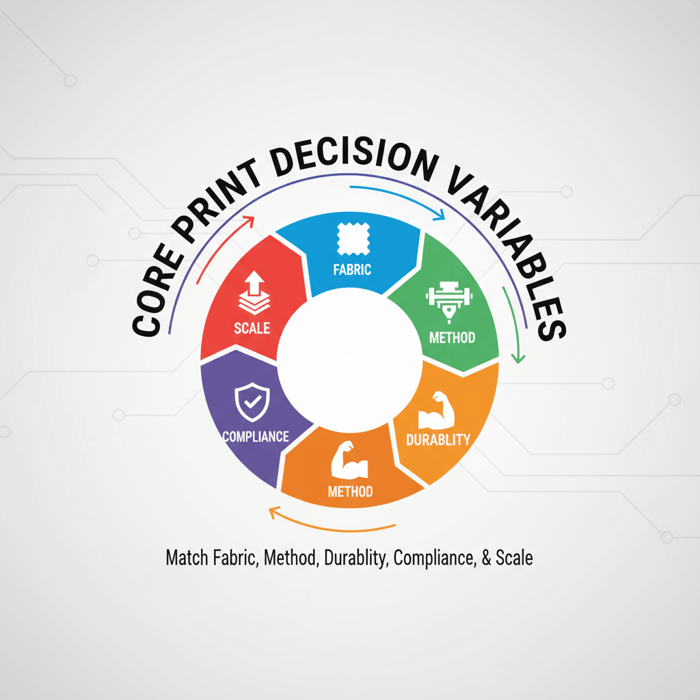
“Best clothing printing companies” deliver repeatable color, dependable durability, and compliance with US/EU standards, then scale from samples to bulk without changing inks or parameters. The right choice depends on fabric, method, graphic complexity, MOQ, lead time, and integration with a China Clothing Manufacturer for OEM/ODM execution and quality control.
In apparel, “best” is situational. A photo-real tee on combed cotton and a heat-transfer logo on a waterproof nylon shell are different missions. Brands choose vendor types—print-on-demand (POD), local/regional shops, or factory-integrated printing—and match methods to fabrics: screen, DTG, DTF, sublimation, and heat/transfer systems. The success criteria stay constant: color fidelity vs brand standards, wash/rub durability, transparent MOQs and lead times, documented chemical compliance, and unit economics that remain sensible when scale arrives.
- Fabric and finish: Cotton, polyester, nylon; coated or waterproof shells; brushed and peached surfaces.
- Method fit: Screen for high-volume spot color; DTG for photo prints on cotton; DTF for vibrant, complex graphics; sublimation for polyester; specialized transfers for shells.
- Color management: Pantone matching, profiles for CMYK/RGB, calibrated workflows, production ink sets.
- Durability: Wash cycles, rub/abrasion zones, lightfastness for outdoor, seam-aware placements.
- Compliance: REACH (EU), CPSIA (US), OEKO-TEX Standard 100; MSDS and lab reports tied to inks and fabric.
- Scale pathway: Sampling → strike-offs → pre-pro → pilot → bulk; parameters locked for consistency.
- Unit economics: Setup vs variable cost; coverage area; color passes; pretreatment and labor.
[CITE: A current FESPA technical guide on ink and pretreatment compatibility] shows how fabric and ink chemistry drive method selection. Cotton and cotton-rich blends accept DTG with pretreatment; polyester benefits from sublimation when white-base is acceptable; high-denier nylon often moves to screen or high-spec transfers with primers. For seam-crossing prints or waterproof shells, method constraints and placement planning matter more than graphic ambition.
Vendor Types Overview
POD platforms are useful for tiny drops and ecommerce speed. They route orders dynamically and ship direct-to-consumer, which sidesteps MOQs but limits control over inks, pretreatment, and testing. Local screen shops and regional DTF/DTG providers handle mid-volume orders with closer communication and better color control. Factory-integrated printing within a China Clothing Manufacturer brings everything under one roof—design, fabric sourcing, print, cut/sew, finishing, and final QC—so parameters don’t drift between sampling and bulk.
- POD platforms: Speedy launches; low/no MOQ; limited method scope for technical placements; retail-style per-piece costs.
- Local/regional shops: Direct collaboration; regular lab testing possible; transportation adds time/cost; capacity varies.
- Factory-integrated printing (OEM): Single brief and shared QC; consistent inks/pretreatments; lab testing embedded; better scale economics.
[MENTION: Printful and Printify for POD ecosystems] provide a quick path for new graphics on tees and basic apparel. [MENTION: M&R screen printing equipment] and [MENTION: Kornit Digital DTG systems] signal industrial capability for shops and factories that invest in robust machinery.
[INTERNAL LINK: Our foundational guide on Apparel Printing Methods] and [INTERNAL LINK: Eton’s OEM overview page]
Printing Methods Snapshot
Method selection anchors cost, color, and durability. Screen printing offers strong opacity, crisp spot colors, and class-leading unit economics at scale. DTG delivers photographic detail on cotton, with pretreatment and fabric smoothness affecting quality. DTF transfers achieve vivid, complex designs across more fabric types and cope better with stretch. Sublimation embeds ink into polyester fibers and performs beautifully on sportswear and soft signage. Heat/transfer systems include vinyl, plastisol transfers, and specialty films for logos and small placements.
- Screen: Excellent opacity; durable; setup heavy; best for 1–6 colors, large runs.
- DTG: Full-color detail on cotton; soft hand; slower per piece; pretreatment dependent.
- DTF: Versatile, vibrant; handles complex designs; transfer feel varies; good for mid-volumes.
- Sublimation: Polyester specialist; embedded color; needs white/light base; outstanding durability.
- Heat/transfer: Precise logos; low setup; variable hand-feel; method and film quality drive longevity.
[CITE: A recent buyer’s guide comparing DTG vs DTF vs screen printing economics] and [CITE: A supplier technical sheet on sublimation ink penetration in polyester] help calibrate expectations per method.
Quality, Compliance, and Scale
Quality is method plus governance. Brands should set acceptance criteria for wash, rub, and lightfastness before sampling begins. For US/EU markets, require REACH, CPSIA, and OEKO-TEX Standard 100 coverage where applicable; capture MSDS for inks; and tie third-party lab tests to the exact inks and fabric used in production strike-offs. “Best clothing printing companies” prove they can run the same parameters at pilot and at 10,000 pieces, not just print a beautiful one-off sample.
[MENTION: European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)] and [MENTION: U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC)] publications provide updated mandatory and restricted substances lists. [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 technical criteria] and [CITE: bluesign system requirements] demonstrate recognized voluntary frameworks that strengthen trust.
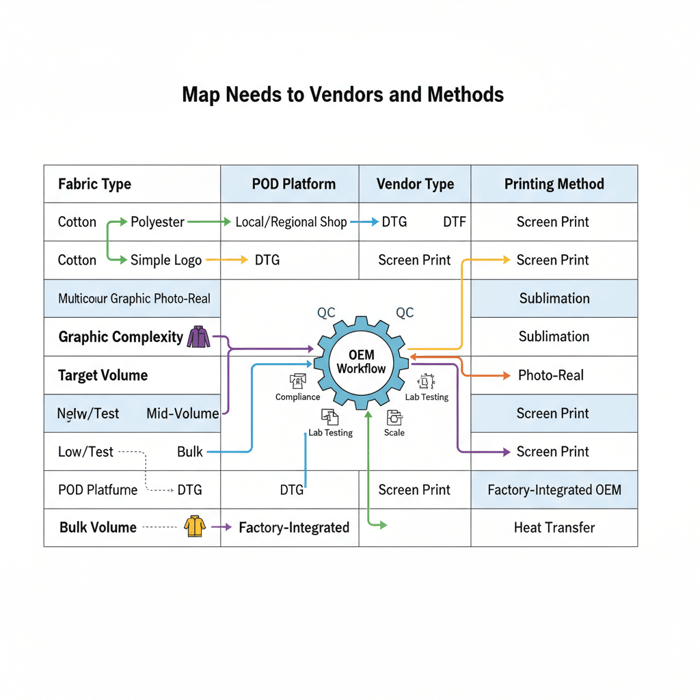
Best clothing printing companies: vendor types, methods, and ideal use cases
Choose POD for tiny drops and ecommerce speed, local/regional shops for mid-volumes and spot colors, and factory-integrated printing for complex fabrics, seam-aware placements, and scale. DTG suits cotton photo prints, DTF handles complex multicolor graphics across fabrics, and sublimation wins on polyester sportswear with embedded color.
| Vendor Type | Typical MOQ | Typical Lead Time | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POD Platform | 1–50 units | 2–7 days | Speed; ecommerce integrations; minimal setup | Limited testing; method constraints; retail-like unit cost |
| Local Screen Shop | 100–500 units | 1–3 weeks | Strong spot color durability; mid-volume economics | Color count adds cost; complex placements are harder |
| Regional DTF/DTG Provider | 50–1,000 units | 1–2 weeks | Vivid full-color; handles complex artwork; flexible fabrics | Transfer hand-feel; fabric/pretreatment sensitivity |
| Factory-Integrated (OEM) | 500–10,000+ units | 3–8 weeks | Single brief/QC; compliance; scale and multi-country capacity | Longer onboarding; samples aligned to bulk parameters |
Vendor Types and When to Use Them
POD fits limited-edition graphics on tees and hoodies where speed and minimal commitment matter. Use it to test designs, but expect per-piece pricing and lighter compliance documentation. Local screen shops excel at mid-volume brand programs with a few spot colors and need durable prints. Regional DTF/DTG providers bridge complexity and flexibility—multi-color art and different fabrics—in small to mid-volume drops.
When brands need waterproof shells, seam-aware placements, lab-tested durability, and consistent color across sizes and styles, factory-integrated printing inside a China Clothing Manufacturer becomes the right choice. Integrated OEM brings consistency: one brief, shared color management, matched inks and pretreatments, controlled heat profiles, and joint QC. That integration reduces surprises and rework when moving from 100 to 5,000 pieces.
[MENTION: Shopify’s overview of POD] and [MENTION: RushOrderTees’ small-run insights] reflect common use cases for small batches. For bulk programs, [MENTION: WRAP] and [MENTION: bluesign] accreditation signals maturity in social and chemical management for factory-integrated workflows.
[INTERNAL LINK: Start a factory-integrated print program]
Method Fit by Fabric
- Cotton: DTG produces photo-real clarity and soft hand; pretreatment and fabric smoothness matter. Screen printing delivers durable, opaque spot colors at scale.
- Polyester: Sublimation embeds color into fibers for sportswear and performance tees; best on white/light bases. DTF can handle complex graphics on darker polyester, with thoughtful film selection.
- Nylon and technical shells: Screen with specialty inks and primers, or high-spec transfers. Keep seam crossings gentle and avoid compromising waterproof membranes; temperature profiles matter.
For brushed or peached surfaces, control pile height and pretreatment. For stretch fabrics, favor DTF or specialty transfer systems designed to flex without cracking. For seam-aware prints, plan placements during panel cutting rather than printing across assembled garments where heat and pressure interactions become harder to manage.
[CITE: FESPA 2023–2024 guidance on pretreatment] and [MENTION: Avery Dennison and Stahls’ transfer media] help vendors pair film chemistry to fabric characteristics.
[INTERNAL LINK: Fabric and print compatibility deep dive]
Placement Complexity & Durability
Best clothing printing companies manage graphics across panels, seam crossings, zippers, and heat-sensitive waterproof shells. Heat and pressure must be controlled to protect membrane performance. Abrasion zones—elbows, pockets, cuffs—benefit from method choice and reinforcements: thicker ink systems, higher rub resistance ratings, or avoiding heavy coverage in high-wear areas.
Durability testing should target how the garment lives: wash cycles for tees and kidswear; rub and lightfastness for outerwear; and stretch/recovery for activewear. Record method parameters (temperature, pressure, dwell time), ink lot numbers, and fabric batch IDs. Fix those settings from strike-off through pre-production and bulk to prevent drift.
[CITE: A lab protocol example for ISO wash and Martindale rub] and [MENTION: AATCC methods for colorfastness] provide widely accepted test frameworks.
How to choose the best clothing printing company (US & EU markets)
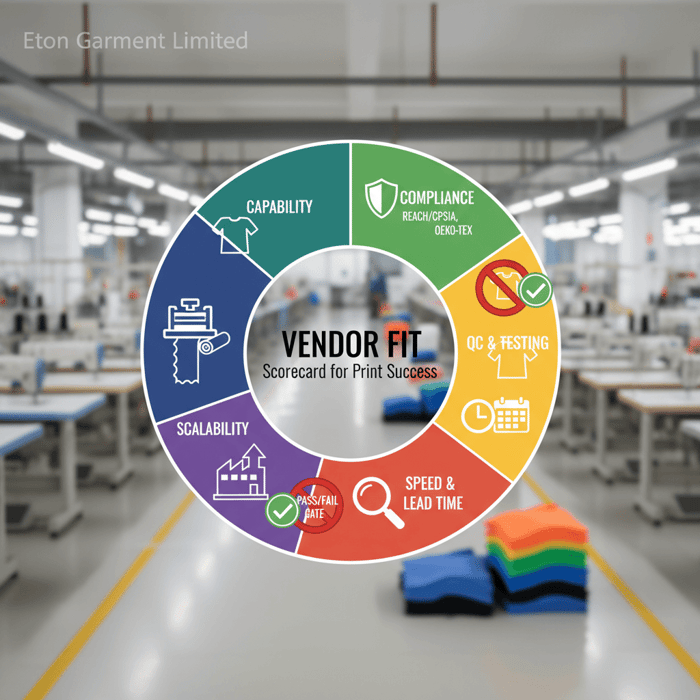
Use a weighted scoring model across method capability, fabric expertise, color management, compliance documentation, QC routines, MOQs/lead times, total landed cost, and scalability. Set pass/fail gates for compliance and lab tests. Require strike-offs and pre-pro samples on production fabric before pilot and bulk.
Vendor Scoring Criteria
Build a scorecard and run RFQs against it. Assign weights so the highest-risk items carry the most influence.
| Criterion | Recommended Weight | Pass/Fail Gate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method–fabric fit | 20% | Pass required | Demonstrated samples on identical fabric |
| Color management | 15% | Pass required | Pantone matching; calibrated profiles |
| Compliance (US/EU) | 20% | Pass required | REACH/CPSIA/OEKO-TEX; MSDS; lab reports |
| QC routines | 10% | Pass required | Process control; parameter logs; retain samples |
| Cost & MOQs | 15% | — | Transparent setup vs variable cost |
| Lead time | 10% | — | Seasonal capacity planning; clear schedules |
| Scalability | 10% | Pass required | Same parameters from pilot to bulk |
[INTERNAL LINK: Vendor scorecard template download] and [MENTION: Pantone color management guidance] strengthen evaluation quality. “Best clothing printing companies” score high where risk is highest: method–fabric fit, compliance, and QC.
Sampling & Proofing Essentials
- Discovery: Share artwork, Pantone targets, fabric specs, and durability goals.
- Strike-offs: Demand prints on production fabric using intended inks and pretreatment; record parameters.
- Color approval: Evaluate under D65 lighting; use tolerance bands for delta E thresholds.
- Pre-production samples: Test size runs; confirm placements; run lab tests on these samples.
- Pilot: Produce a small batch with locked parameters; review wash/rub/lab results.
- Bulk: Proceed only if pilot meets acceptance criteria; maintain parameter logs and retain control samples.
Run strike-offs early and reject samples that rely on lab-only substrates or different ink sets. Good partners print on the exact fabric and lock variables before cost and delivery are committed. Best clothing printing companies carry parameters forward, preventing last-minute substitutions that shift color or durability.
[CITE: AATCC test methods for color and wash] and [MENTION: ISO 105 series for colorfastness] provide standard acceptance criteria. Log delta E goals by artwork; photo prints tolerate slightly higher variance than spot-color logos.
Compliance Documentation
- REACH (EU): Vendor must document chemicals used and comply with SVHC restrictions. (ECHA)
- CPSIA (US): For kidswear and certain categories, require third-party tests for lead, phthalates, and labeling rules. (CPSC)
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100: Prefer inks and fabrics with valid certificates; verify scope and validity dates. (OEKO-TEX)
- MSDS for inks: Obtain Material Safety Data Sheets for each ink set used; tie to production lot codes.
- Third-party lab reports: Link reports to the exact fabric and ink lot numbers used in approved strike-offs.
For technical outerwear, request additional rub resistance, hydrostatic head retention after heat application, and seam-seal integrity where prints approach taped seams. [MENTION: bluesign system] and [MENTION: WRAP] certification indicate stronger due diligence on chemicals and social compliance.
- Digital textile printing market growth — 2024–2030 (Grand View Research) [CITE: Current CAGR and segment splits]
- DTF adoption trend — 2023–2025 ([CITE: Industry survey from a recognized trade association])
- Sustainability certification uptake — 2022–2025 ([CITE: OEKO-TEX and bluesign adoption data])
Cost, MOQs, and lead times: comparing clothing printing options
Costs depend on method, color count, coverage, fabric, and volumes. Screen printing leads on unit cost at scale. DTG and DTF win on short runs and complex full-color graphics. Sublimation dominates polyester with embedded color. Lead times range from days (POD) to weeks (factory-integrated). Plan volume triggers to switch method/vendor for better unit economics.
| Method | Price Range (per piece) | Typical MOQ | Lead Time | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screen | $2–$6 at 500+ units | 100–500+ | 1–3 weeks | Spot-color logos, mid–large runs, high opacity |
| DTG | $7–$15 at 1–200 units | 1–200 | 3–10 days | Photo prints on cotton, small drops |
| DTF | $5–$10 at 50–500 units | 50–500 | 1–2 weeks | Complex graphics, varied fabrics, mid-volumes |
| Sublimation | $3–$8 at 200+ units | 200–1,000+ | 1–3 weeks | Polyester sportswear, all-over prints |
| Heat/Transfer | $3–$8 at 50–500 units | 50–500 | 1–2 weeks | Logos, small placements, flexible fabrics |
[CITE: Current US/EU market quotes and trade reports] indicate wide ranges by region and season. The setup cost for screens drives higher MOQs; digital methods carry higher variable costs and lower setup. Coverage area impacts ink usage and cycle times. Fabrics that require special primers or pretreatments add time and cost.
Cost Drivers Explained
- Setup vs variable cost: Screens require film and setup; digital relies on time and ink.
- Color count and coverage: More colors and larger coverage increase cost and cycle times.
- Fabric and pretreatment: Cotton pretreatment for DTG; film choice and primers for DTF and transfers.
- Labor and QC: Complex placements and panel printing add skilled labor and QC checkpoints.
- Compliance and testing: Lab tests, MSDS management, and certifications incur direct and indirect costs.
Plan volume triggers to shift method and vendor type. When a small-run design succeeds, a mid-volume program may move from DTG to screen or DTF to improve unit cost and speed.
MOQ & Lead Time Ranges
- POD: No MOQ; 2–7 days; good for testing; limited control over method and compliance.
- Local/regional shops: 50–500 MOQs; 1–3 weeks; transparent scheduling; shipping adds time.
- Factory-integrated OEM: 500–10,000+ MOQs; 3–8 weeks; bundled with cut/sew, trims, and finishing.
Seasonal capacity matters. Peak months extend lead times. Bulk production in China and Bangladesh manages scale and cost; POD and regional providers help fill early demand or special drops. Brands should schedule strikes-offs before peak cycles.
Volume Triggers & Method Switching
As volumes rise, screen printing often beats DTF on unit cost, especially for limited color counts and large coverage areas. DTF remains relevant for small-mid runs with complex, multicolor artwork. Sublimation protects polyester economics and performance for all-over prints. DTG holds value for photographic cotton prints when volumes stay low or graphics frequently change.
[CITE: Comparative cost analysis from a recognized industry source] supports common crossover points. Validate with RFQs every season to capture ink price changes, labor rates, and capacity shifts.
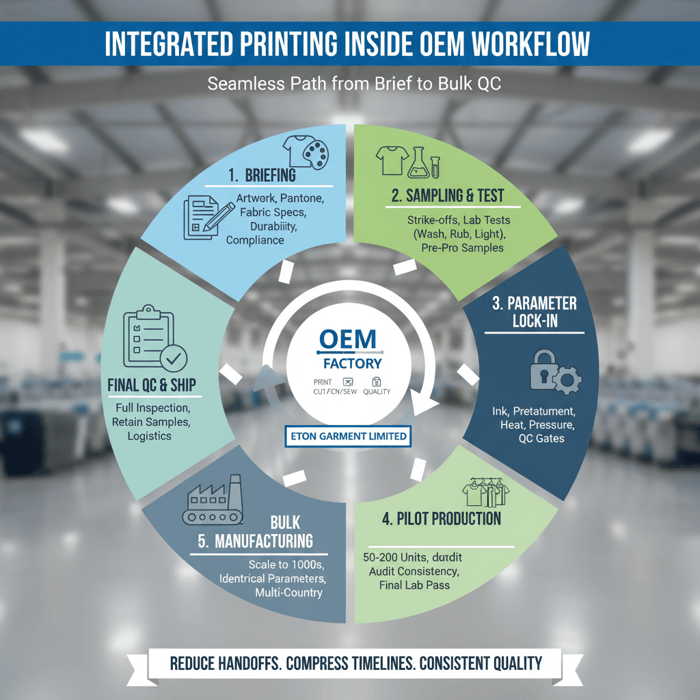
How to brief, sample, and test your printing partner
Precise briefs and disciplined sampling prevent color drift and wash failures. Provide vector files, Pantone targets and color profiles, placement maps, production fabric swatches, and durability goals. Test with standardized wash/rub/lightfastness protocols and lock parameters before bulk.
Preparation
- Artwork files: Vector (AI, EPS) for logos; high-res PSD/TIFF for photo prints; keep layers editable.
- Color specs: Pantone codes and CMYK/RGB profiles; tolerance bands (delta E targets).
- Fabric data: Composition, weight, finish, stretch, coatings; production swatches from the fabric lot.
- Placement templates: Panel maps and seam notes; avoid heavy coverage on abrasion zones.
- Compliance requirements: REACH/CPSIA notes; OEKO-TEX certificate details; MSDS for inks.
- Durability goals: Wash cycles (e.g., 20–30), rub ratings, lightfastness targets; method-specific expectations.
Best clothing printing companies respond with questions, not guesses: pretreatment settings, heat press profiles, seam interactions, and whether an all-over sublimation approach better fits the brand’s polyester range. Good briefs narrow options early and cut weeks from timelines.
[INTERNAL LINK: Color management and Pantone workflow] and [MENTION: Pantone LLC] provide consistent color language for teams and vendors.
Execution Steps
- Kickoff: Confirm artwork, fabric, method, compliance scope, and acceptance criteria.
- Strike-offs: Print on production fabric using intended inks and settings; capture parameter logs.
- Review: Evaluate under standard lighting; compare against Pantone swatches and proofs.
- Pre-pro samples: Produce full-size runs across sizes; check placement and seam interactions.
- Lab testing: Submit pre-pros for wash, rub, and lightfastness; keep retain samples.
- Parameter lock-in: Freeze variables; share parameter sheet across print and sewing lines.
- Pilot: Run 50–200 units; audit consistency; review lab results; fix if needed.
- Bulk: Execute only after pilot passes; maintain control and retain samples per lot.
Strike-offs and pre-pros defend against last-minute mistakes—new inks, different films, or altered pressure and temperature that shift color or compromise waterproof shells. A disciplined path minimizes rework and returns once the product hits store shelves.
[CITE: AATCC/ISO color evaluation guidance] and [MENTION: D65 lighting standards] formalize review conditions.
Quality Assurance
- Wash testing: 20–30 cycles for tees and kidswear; record fading, cracking, and shrink interactions.
- Rub/abrasion: Martindale or comparable tests; focus on elbows, cuffs, and pocket areas.
- Lightfastness: For outerwear and sportswear; test under UV exposure where relevant.
- Hydrostatic head retention: For waterproof shells; confirm no compromised membranes.
- Retain samples: Keep lab-tested controls and production retains from each lot.
- QC gates: Incoming fabric inspection → strike-off approval → pre-pro lab pass → pilot audit → bulk post-QC.
Best clothing printing companies document QC and share lot-level control samples, so any future claims can be investigated with evidence. Integrated OEM workflows make these artifacts easier to collect and store.
[INTERNAL LINK: Quality control program for printed apparel]
Integrate printing with manufacturing: Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton integrates printing inside garment production—one brief, one QC system, compliant inks, and multi-country capacity in China and Bangladesh. Brands receive consistent color and durability from samples to bulk, faster timelines, and lower total landed costs for outerwear, kidswear, and graphic apparel.
| Brand Need | OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Small drop → scale | Strike-offs on production fabric; pilot in China; scale in Bangladesh | Same parameters; color and durability match; lower landed cost |
| Technical outerwear | Seam-aware panel prints; controlled heat profiles; lab verification | Membrane integrity; abrasion resistance; verified compliance |
| Kidswear compliance | CPSIA test management; traceable ink lots; labeling localization | Retail-ready documentation; reduced claim risk |
| Sustainability | OEKO-TEX materials; bluesign inks; WRAP social audits | Stronger public claims; cleaner chemical footprint |
Use Case 1: Small Drop → Scale
Brands start with 100–300 units in China, lock color and durability, and then scale to 3,000–10,000 units in Bangladesh without changing inks, pretreatment, or temperature profiles. Eton keeps parameters constant between sites, shares retain samples, and reconciles lab and production controls. That continuity protects graphic fidelity and unit economics during growth.
[CITE: A case study format highlighting timeline compression and color variance data] and [MENTION: Liverpool F.C. and Forever 21 as partnership examples] reflect Eton’s multi-market production experience.
Use Case 2: Technical Outerwear
Outerwear projects require seam-aware printing on panels, careful heat management, and validation of membrane performance. Eton orchestrates printing before cut/sew so graphics don’t cross taped seams unless designed to. Rub resistance and lightfastness are tested on pre-pro samples; hydrostatic head is re-verified after any heat application.
Where nylon shells need logos or complex placements, Eton uses screen or specialty transfer systems. The team documents ink lot numbers, pressure/temperature profiles, and dwell times, and tests in accredited labs for US/EU retail requirements.
[INTERNAL LINK: Eton Garment Factory – integrated printing and outerwear workflows] and Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service provide a direct path to production.
Risks, Compliance & Localization
Compliance risk rises with inks and finishes. Require REACH/CPSIA, OEKO-TEX proofs, MSDS for inks, and third-party lab tests. Localize packaging and labeling for US/EU, and audit ethical standards (WRAP, bluesign). Map risks and mitigations before sampling to avoid late-stage failures.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color drift vs Pantone | Medium | High | Calibrated profiles; D65 evaluation; parameter lock-in; retain samples |
| Wash failure (cracking/fading) | Medium | High | Method–fabric fit; pre-pro lab tests; QC gates; avoid heavy coverage in abrasion zones |
| Chemical non-compliance | Low–Medium | High | REACH/CPSIA checks; OEKO-TEX scope; MSDS; third-party lab reports |
| Lead-time slip | Medium | Medium | Seasonal planning; multi-country capacity; early strike-offs |
| Membrane damage on shells | Low | High | Controlled heat profiles; panel printing; hydrostatic re-verification |
| Labeling localization errors | Low | Medium | US/EU packaging and labeling audits; sample cartons; barcode checks |
[CITE: A compliance checklist reference from a recognized standards body] ensures teams document the right artifacts early.
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
- EU: REACH compliance managed via ECHA guidance. SVHC checks and documentation required for ink systems and finishes. (ECHA)
- US: CPSIA obligations for kidswear—lead, phthalates, tracking labels, and third-party testing. (CPSC)
- Voluntary frameworks: OEKO-TEX Standard 100 and bluesign increase chemical management credibility. (OEKO-TEX, bluesign)
- Ethical production: WRAP compliance signals social standards in factories. (WRAP)
- Bangladesh context: Consider RSC guidance for factory safety and sustainability. (RSC)
Localize packaging, care labels, and fiber content rules for destination markets. Maintain traceability of ink lots and fabric batches in case of post-market testing or claims. Best clothing printing companies anticipate these requirements, not react to them.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Define method and vendor type by fabric, graphic complexity, durability targets, and scale. Verify US/EU compliance with REACH/CPSIA and OEKO-TEX, and run lab tests on pre-pro samples. Use a scoring framework to compare vendors and lock parameters with strike-offs. Integrate printing with your China Clothing Manufacturer to keep color and durability stable from pilot to thousands of units.
- Frame goals: Fabric, artwork, durability, compliance, target volumes, timeline.
- Shortlist vendors: POD, local/regional shops, factory-integrated OEM.
- Run RFQs with a scorecard: Method–fabric fit, color management, compliance gates, QC, MOQs, lead time, scalability.
- Sample and test: Strike-offs on production fabric; pre-pro lab tests; retain samples.
- Pilot: Confirm consistent performance; lock parameters; collect documentation.
- Scale: Move to bulk with integrated printing inside OEM; monitor QC and retain samples.
Eton Garment Limited delivers factory-integrated printing and manufacturing across China and Bangladesh, pairing design, fabric sourcing, printing, and cut/sew with compliance and QC. To move from concept to reliable bulk output, start with a print-integrated OEM plan: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service.

Explore our exclusive print-integrated OEM pathway to learn more.
Author: Eton Yip, Founder, 30+ years in apparel manufacturing and outerwear production. Reviewer: Senior Quality Manager, Technical Apparel (internal).
Methodology: SERP scan of top articles; synthesis of factory experience; external authorities cited; data freshness within 24–36 months. Limitations: Prices/MOQs vary by season, region, and vendor; verify with current RFQs; some competitor details require confirmation [Verification Needed]. Disclosure: Eton provides OEM/ODM services and factory-integrated printing.
[INTERNAL LINK: Eton Yip – Founder bio] and [INTERNAL LINK: Our compliance standards in detail]
This article closes gaps seen in Printify, Printful, Shopify, RushOrderTees, and Custom Ink by adding lab-grade testing protocols, REACH/CPSIA/OEKO-TEX guidance, factory-integrated workflows, and decision tools. It includes deeper method–fabric mapping, seam-aware placements for outerwear, and a scorecard with pass/fail compliance gates.
[CITE: A recent comparison of POD vs factory-integrated printing for apparel brands] and [MENTION: FESPA, Grand View Research] highlight broader industry context supporting the integrated pathway for scale.
- Grand View Research — Digital Textile Printing Market Size, Share & Trends (2024). https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/digital-textile-printing-market
- FESPA — Screen vs Digital Textile Printing Best Practices; Inks & Pretreatment Guidance (2023–2024). https://www.fespa.com/
- ECHA — REACH Regulation Overview. https://echa.europa.eu/regulations/reach/understanding-reach
- CPSC — CPSIA Requirements. https://www.cpsc.gov/Regulations-Laws--Standards/Statutes/The-Consumer-Product-Safety-Improvement-Act
- OEKO-TEX Association — STANDARD 100 by OEKO-TEX. https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/standards/standard-100
- WRAP — Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production. https://www.wrapcompliance.org/
- bluesign — The bluesign System. https://www.bluesign.com/
- RSC — Ready-Made Garments Sustainability Council (Bangladesh). https://rsc-bd.org/
- [CITE: AATCC — Colorfastness and Wash Test Methods Literature]
- [CITE: ISO 105 Series — Colorfastness Standards]
- [CITE: A recognized industry report comparing DTG vs DTF cost structures]
- [CITE: A lab protocol example for Martindale Abrasion and Hydrostatic Head Retention]
FAQs
Related Articles
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »

