Airlism Fabric Explained for Fashion Brands: Manufacturing It with a China Clothing Manufacturer
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
October 28th, 2025
14 minute read
Airlism Fabric Explained for Fashion Brands: Manufacturing It with a China Clothing Manufacturer
Airlism sparks interest among US/EU fashion brands who want cooling base layers built with a China Clothing Manufacturer. This guide clarifies what AIRism is, how to create brand-safe alternatives, which fibers and knits deliver cooling comfort, the tests that prove performance, and the OEM pathway from brief to bulk across China and Bangladesh.
Airlism is widely searched as an umbrella for ultra-light cooling knits, while AIRism is Uniqlo’s trademark. Brands can develop an AIRism-like program by specifying micro-denier synthetics (or cupro blends), fine-gauge knits, wicking and anti-odor finishes, and lab targets (AATCC/ISO/ASTM). Partner with a China Clothing Manufacturer to move from concept to validated production.
What “airlism” Really Means (and What It Doesn’t)
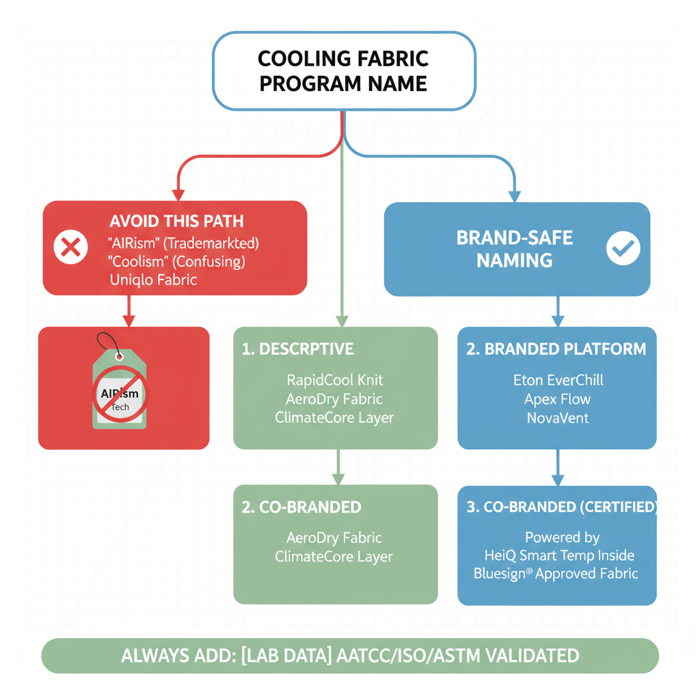
AIRism is Uniqlo’s trademarked platform for cooling, moisture-wicking base layers; “airlism” is a common search misspelling and should not be used as a product name. Brands can produce comparable performance under their own marks by defining fiber systems, knit structures, finishes, and measurable tests that validate comfort and quick-dry claims.
AIRism vs “airlism”: Trademark & Naming
AIRism is proprietary to Fast Retailing Co., Ltd. Using “AIRism” on hangtags, care labels, PDPs, or ads risks trademark infringement. Adopt a distinct program name and describe performance neutrally (e.g., “cooling knit,” “quick-dry base layer”) backed by lab data. Claims must be supported by recognized standards such as AATCC TM195 (Moisture Management), AATCC TM201 (Dry Time), ISO 11092 (Ret), and ASTM D737 (Air Permeability). [CITE: Official trademark database record confirming AIRism ownership] [MENTION: Fast Retailing corporate filings] [INTERNAL LINK: Our naming and labeling checklist for performance fabrics]
Core Properties of AIRism-like Fabrics
Well-built cooling knits deliver five pillars of comfort:
- Moisture-wicking: Moves sweat off skin. Target capillary action via yarn cross-sections and finishes. Validate with AATCC TM195. [CITE: AATCC TM195 method page]
- Quick-dry: Shorter dry time reduces cling. Validate with AATCC TM201. [CITE: AATCC TM201 method page]
- Breathability: Airflow through fabric. Validate with ASTM D737 (air permeability, L/m²/s) and ISO 9237. [CITE: ASTM D737 standard summary]
- Water-vapor transport: Comfort under heat and humidity. Validate with ISO 11092 (Ret, m²·Pa/W). [CITE: ISO 11092 documentation]
- Odor control: Chemistry or yarn structure that reduces odor build-up. Choose US/EU-compliant technologies and substantiate via bacteriostatic tests. [CITE: EU Biocidal Products Regulation guidance]
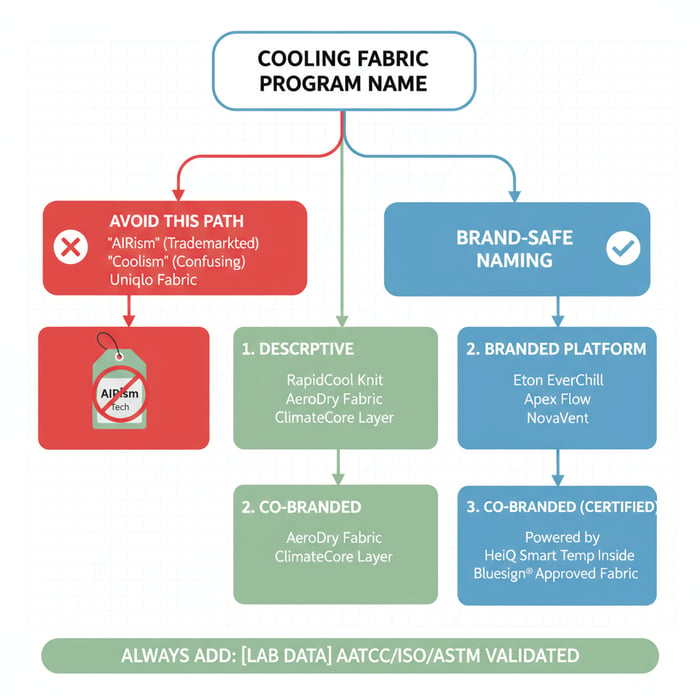
Cool-touch hand can be achieved via nylon-rich blends, cupro, yarn cross-sections, or topical finishes. Anti-cling and anti-static can be added for comfort. [MENTION: HeiQ and Polygiene odor-control technologies] [INTERNAL LINK: Performance definitions hub – moisture, breathability, Ret]
Inside the Fabric: Materials, Knits, Finishes for AIRism-like Performance
Replicate AIRism-like comfort through micro-denier synthetics (polyester or nylon) with elastane, fine-gauge circular knits, and a wicking finish. Add anti-odor and cool-feel treatments that pass US/EU chemical rules. Design for testing from day one so performance claims stand up in the lab and at scale.
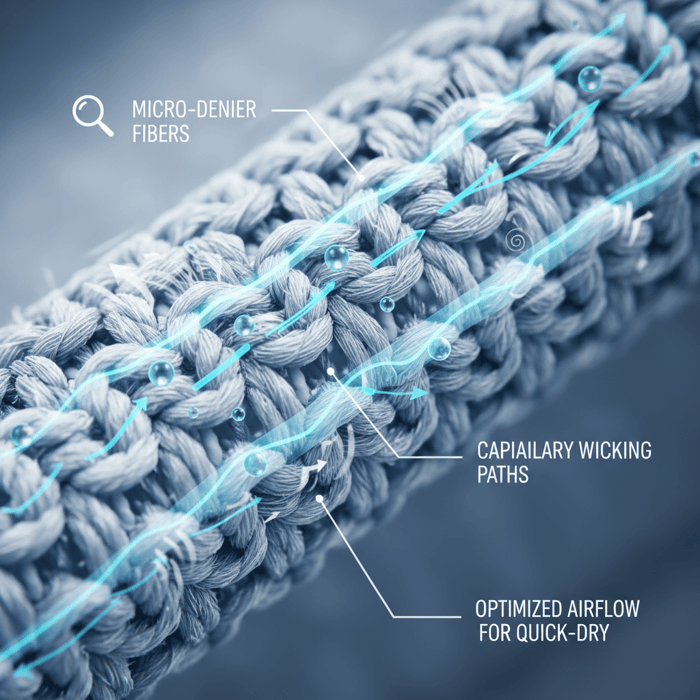
Material Stacks: Polyester, Nylon, Cupro, Elastane + Recycled Options
Common blends:
- Polyester (micro-denier) + Elastane: Durable, quick-dry, cost-friendly, strong colorfastness. Recycled options (rPET) available; slight cost uplift and potential lead-time impact. [CITE: rPET supply chain report]
- Nylon (micro-denier) + Elastane: Silkier hand and cool-touch, strong abrasion resistance, often higher FOB. Watch for snagging on open structures. [CITE: Nylon filament technical datasheet]
- Cupro (regenerated cellulose) blends: Luxurious cool hand, strong breathability, higher cost, sensitive supply chain. Often paired with polyester or nylon for stability. [CITE: Cupro fiber producer overview]
- Dope-dyed yarns: Color integrated at extrusion reduces water use and improves color consistency; limited shade availability; MOQ uplift. [CITE: Dope-dye environmental impact study]
Trade-offs: Nylon-rich blends often win on cool-feel and drape; polyester wins on price and wrinkle resistance; cupro raises perceived value but increases cost and risk. Recycled content boosts sustainability narratives in US/EU, with Bluesign and GRS pathways available. [MENTION: Invista Coolmax family; Asahi Kasei cupro] [INTERNAL LINK: Mill-approved recycled yarn catalog]
Knit Structures & Gauges: Jersey, Mesh, Tricot
Structure influences moisture spread and airflow:
- Fine-gauge single jersey (28–40 gg): Smooth hand, balanced opacity, versatile for tees and underwear. Target air permeability via stitch density and yarn count. [CITE: Circular knit gauge reference]
- Engineered mesh: Zoned breathability for high-heat areas; watch snag risk and transparency; blend with opaque panels. Validate with ASTM D737 and garment-level sweat mapping. [CITE: Garment microclimate study]
- Tricot and warp knits: Stable, snag-resistant, smooth interior; suitable for lingerie and close-to-skin layers; may increase FOB. [CITE: Warp knit technical guide]
Dial in stitch length, yarn count (dtex/denier), and finishing route to hit target Ret and dry-time metrics. Confirm shrinkage, torque, and spirality at proto stage. [MENTION: Santoni circular knitting machines] [INTERNAL LINK: Knit structure playbook for quick-dry programs]
Finishes & Additives: Wicking, Anti-odor, Cool-feel
Wicking finishes modify surface energy to move sweat rapidly. Anti-odor chemistries range from silver-based to non-biocidal solutions; pick options that meet US/EU rules and retailer RSLs. Cool-feel finishes and yarn cross-sections can create instant cool-touch. Confirm REACH, CPSIA, and Prop 65 compatibility and secure OEKO-TEX Standard 100 Class II for next-to-skin products. [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100] [CITE: REACH Regulation] [CITE: CPSIA summary] [CITE: California Prop 65 list] [MENTION: Microban odor-management technologies] [INTERNAL LINK: Approved chemical finishes list]
AIRism vs Alternatives: Which Cooling Fabric Strategy Fits Your Line?
Pick the right system for your use-case: AIRism-like synthetics, Dri-FIT-style performance knits, Coolmax, bamboo viscose, or merino. Weigh climate, hand-feel, odor control, care, sustainability, and price. Tie selection to testable targets instead of marketing language.
| Fabric System | Comfort Traits | Testing Focus | Best Use-Cases | Sustainability Notes | Typical FOB Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIRism-like synthetics | Quick-dry, breathable, cool-touch | TM195, TM201, ISO 11092, ASTM D737 | Hot-humid dailywear, travel basics | rPET options, Bluesign mills | Low–mid; scalable in China/Bangladesh |
| Dri-FIT-style knits | Athletic wicking, durable | TM195, abrasion/pilling | Light sport, training tees | rPET feasible; watch finish chemistries | Low–mid; wide supply base |
| Coolmax (poly) | Engineered capillary channels | Moisture management, dry time | Running socks, base layers | Certified yarn; cost uplift | Mid; licensed yarn programs |
| Bamboo viscose | Soft hand, breathable | Pilling, shrinkage, dry time | Lifestyle tees and underwear | Chemistry scrutiny; cellulosic processing | Mid; finish-dependent |
| Merino wool | Odor-resistant, thermoregulating | Micron, pilling, wash retention | Travel underwear, premium tees | Natural fiber; mulesing-free sourcing | High; premium positioning |
Criteria Overview: Comfort, Wicking, Breathability, Odor, Sustainability, Cost
Frame decisions with measurable metrics: dry time (min), air permeability (L/m²/s), Ret (m²·Pa/W), odor control method, RSL compliance, and FOB brackets by fiber and finish. Lifestyle programs favor smooth hand and low care; performance lines chase lower Ret, faster dry time, and targeted odor management. [CITE: Thermal comfort benchmarks for apparel] [MENTION: Nike Dri-FIT family; Invista Coolmax] [INTERNAL LINK: Spec target library for cooling knits]
Decision Framework: Lifestyle vs Performance vs Value
- Lifestyle tees: Nylon-rich or cupro blends for cool hand, moderate dry time, low transparency.
- Performance base layers: Micro-denier poly/nylon with controlled stitch density, strict TM195/TM201 targets, engineered meshes.
- Value basics: rPET polyester jersey with wicking finish, consolidated colors, and stable trims to hit volume pricing.
Run wear-test feedback loops for cling, odor build-up, and wash-down over 10–20 cycles. Match SKU mix to climate and channel. [CITE: Wear-trial protocol guidance] [MENTION: REI product testing articles] [INTERNAL LINK: Wear-test checklist for US/EU launch]
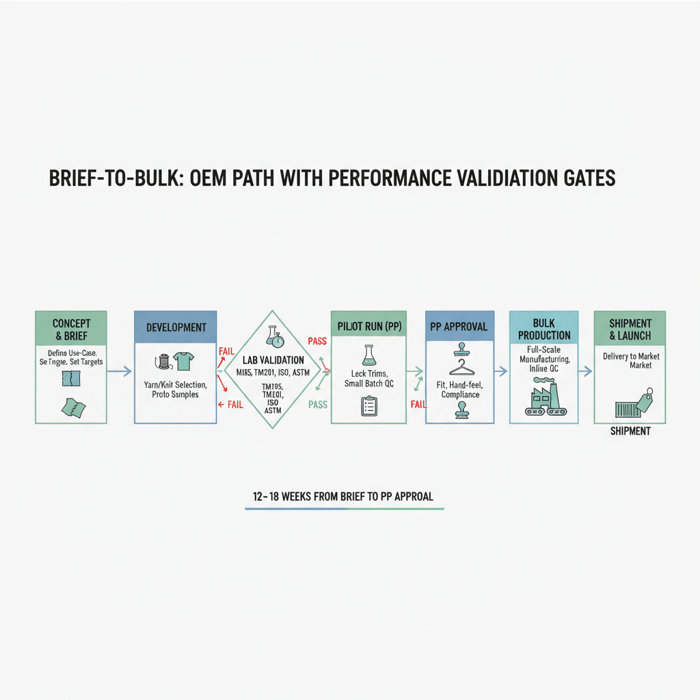
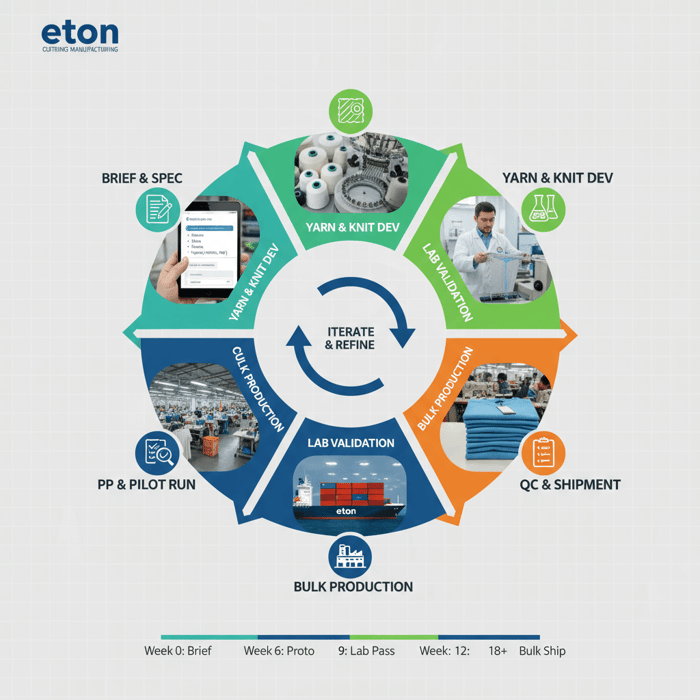
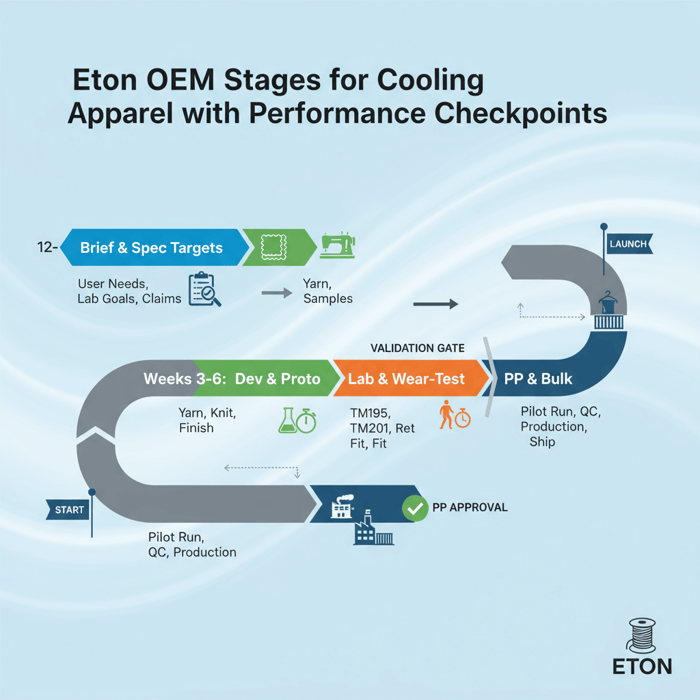
How to Develop an AIRism-Style Program with a China Clothing Manufacturer
Turn concept into production with a disciplined OEM path: clarify use-case, lock yarn/knit/finish, set lab targets, sample, validate, pilot, and scale. Gate risks early—IP, compliance, and fit—to lower rework and returns.
Preparation: Brief, Target Specs, Claim Strategy
- Define the user: climate, activity, garment type, wash frequency.
- Set targets: TM195 wicking grade, TM201 dry-time mins, ASTM D737 airflow, ISO 11092 Ret band, pilling/abrasion, shrinkage.
- Claims: Build claims around validated metrics; avoid trademarked phrasing.
- Compliance scope: REACH, CPSIA, Prop 65, OEKO-TEX Standard 100 Class II.
- Budget and calendar: FOB target, style count, color harmonies, drop dates.
Translate these into a tech pack: fiber content, yarn count, gauge, stitch length, finishes, test methods, size specs, care instructions, trims, and labeling. [CITE: Retailer RSL/RMS references] [MENTION: AATCC standards body; ISO technical committees] [INTERNAL LINK: Tech pack template for cooling knits]
Execution Steps: Dev → Proto → Lab → PP → Bulk
- Fiber & yarn alignment: Reserve yarn with mills; confirm MOQ and lead-time windows.
- Knitting and greige: Run fine-gauge trials; check spirality and torque.
- Dyeing/finishing: Apply wicking and odor finishes; record chemical lot traceability.
- Prototype build: Cut/sew samples; confirm fit, transparency, and hand.
- Lab validation: Test TM195, TM201, ASTM D737, ISO 11092; iterate if off-target.
- Pilot run (PP): Lock trims, care labels, artwork; run 200–500 units for process tuning.
- Bulk production: Trigger after PP approval and lab pass; maintain inline QC.
Collect wear-test data alongside lab results; refine stitch length or finish pick-up to meet the target comfort band. [CITE: Inline quality control case studies] [MENTION: SGS and Intertek textile labs] [INTERNAL LINK: PP approval checklist]
Quality Assurance: AQL, RFT Goals, Test Cadence
- AQL: Define inspection levels for critical defects (shade, fit, seam strength).
- Right-first-time (RFT): Track sampling cycles; aim for RFT over 80% by PP.
- Test cadence: Pre-lab at proto; full lab at PPS; spot checks in bulk; wash-down validation at EOL.
- Documentation: BOM chemical lists, trim certifications, lab reports tied to style IDs.
Build acceptance criteria by test method, not by generic claims, to reduce disputes. [CITE: Retail QA standards summary] [MENTION: Bureau Veritas apparel testing] [INTERNAL LINK: Acceptance criteria template]
Costing, MOQs, and Lead-Times for Cooling Apparel in China and Bangladesh
Expect yarn/fabric MOQs of 500–1,000 meters per color and finished garment MOQs of 500–1,000 units per color/style. Development typically spans 45–90 days; bulk runs take 60–120 days. FOB varies by fiber system, finishes, and order size.
| Item | Typical MOQ | Lead-time | Primary Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micro-denier polyester jersey | 500–1,000 m/color | 20–35 days (fabric) | Yarn count, gauge, dye route, wicking finish |
| Nylon + elastane jersey | 500–1,200 m/color | 25–40 days (fabric) | Nylon grade, elastane %, cool-feel treatment |
| Cupro blends | 1,000–2,000 m/color | 30–60 days (fabric) | Fiber cost, dye reproducibility, mill capacity |
| Finished tee, China | 500–1,000 units/color/style | 60–90 days (bulk) | Fiber/finish, trims, embellishment, volume |
| Finished tee, Bangladesh | 800–1,500 units/color/style | 75–120 days (bulk) | Volume, lead-time windows, logistics |
FOB bands (indicative): polyester cooling tees sit in low–mid ranges; nylon-rich and cupro blends lift FOB; odor-control chemistries add per-unit cost. Consolidate colors, align dye windows, and standardize trims to lower waste and MOQ pressure. [CITE: Apparel costing benchmark report] [MENTION: Maersk lead-time advisories] [INTERNAL LINK: Low-MOQ pilot program details]
Pilot volumes of 200–300 units are feasible through a controlled PP run; costs run higher per unit, but feedback de-risks bulk commitments. [CITE: Small-batch manufacturing case study]
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service by Eton
Eton’s OEM service translates your cooling concept into validated production across China and Bangladesh: design support, material sourcing, lab testing, fit confirmation, and compliant manufacturing for US/EU launch dates. Programs are built around target metrics, ethical practices, and predictable lead-times.
| Brand Need | OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling tee/underwear concept | Fiber/knit selection and finish routing | Comfort tuned to TM195/TM201 targets |
| Claims and compliance | Standards-based specs and RSL alignment | US/EU-safe labeling and defensible claims |
| Cost/MOQ realism | Mill network with China/Bangladesh options | FOB aligned to margin; timeline fit |
| Sustainability | rPET programs and Bluesign/OEKO-TEX pathways | Credible sustainability story for retail |
| Quality and returns risk | Lab/QA cadence and PP gates | Lower defect rates; smoother bulk |
Explore the Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service at https://china-clothing-manufacturer.com/garment-factory/. [MENTION: Liverpool F.C. licensed apparel; Forever 21 programs] [INTERNAL LINK: Case studies on outerwear and technical knits]
Use Case 1: Hot-Humid Dailywear Tee → AIRism-like Alternative
Brief: US Southeast summer dailywear tee; cool-touch and quick-dry. Stack: nylon micro-denier + 6–8% elastane, 32–36 gg single jersey, wicking finish, optional cool-feel additive. Targets: TM201 ≤ 20–30 minutes, Ret 5–8 m²·Pa/W, ASTM D737 airflow tuned for opacity and drape. Risk notes: snagging on meshes; pick tighter jersey and stabilize stitch length. [CITE: Climate comfort ranges for apparel] [MENTION: NOAA heat/humidity data] [INTERNAL LINK: Knit tuning checklist for hot-humid markets]
Use Case 2: Travel Underwear Capsule → Fast-Dry, Anti-Odor
Brief: Weeklong travel underwear; low odor, fast wash-and-wear. Stack: polyester micro-denier + elastane, tricot or fine jersey for stability, wicking finish plus US/EU-compliant odor control. Targets: TM201 ≤ 15–25 minutes, odor test per retailer protocol, low-pilling and high burst strength. Labeling: neutral claims grounded in tests; avoid antimicrobial claims without approvals. [CITE: EU Biocidal Products Regulation guidance] [MENTION: Polygiene odor-control approaches] [INTERNAL LINK: Label copy best practices for odor-managed products]
Risks, Compliance & Localization (US/EU)
Manage four risk categories: IP (trademarks), chemicals (RSL/RMS and regulations), labeling (fiber content, care, origin), and claim substantiation (AATCC/ISO/ASTM tests). Build compliance into artwork, BOMs, trims, and care labels early.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trademark misuse (AIRism) | Medium | High | Use brand-safe naming; legal review |
| Restricted substances | Medium | High | REACH/CPSIA/Prop 65 and OEKO-TEX roadmaps |
| Labeling errors | Medium | Medium | EU 1007/2011 and FTC guidance; artwork checks |
| Unsubstantiated claims | Medium | Medium | Standards-backed testing and neutral language |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
- EU REACH: Restricted chemicals; create a BOM chemical registry and vendor declarations. [CITE: ECHA REACH portal]
- US CPSIA: Children’s products testing; phthalates and lead content limits. [CITE: CPSC CPSIA page]
- California Prop 65: Warning requirements for listed substances. [CITE: OEHHA Prop 65 page]
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100: Product-level safety certification; Class II for next-to-skin garments. [CITE: OEKO-TEX Standard 100]
- EU 1007/2011 textile labeling: Fiber content declarations and language requirements. [CITE: EU Textile Regulation 1007/2011]
- US FTC labeling: Fiber content, country of origin, care labels. [CITE: FTC Textile and Wool Acts]
Retailer RSLs add brand-specific constraints; secure lab reports and supplier declarations before PP approvals. [MENTION: H&M and Inditex RSL frameworks] [INTERNAL LINK: Compliance portal with label templates]
Market Demand & Data Trends for Cooling Base Layers
Cooling basics continue to grow alongside athleisure and hotter summers. Track sell-through, return reasons (fit and hand-feel), and sustainability preferences in US/EU channels. Align color drops and inventory timing to heat waves and travel calendars.
Trend 1: Performance Basics in Lifestyle Channels
Lifestyle retailers are expanding performance basics—tees and underwear with wicking and quick-dry claims—without overt “athletic” positioning. Success drivers: soft hand, neutral colors, clean trims, and wash-down stability across 10–20 cycles. [CITE: US/EU retail sell-through report] [MENTION: Zara and Uniqlo seasonal feature pages] [INTERNAL LINK: Merchandising playbook for cooling essentials]
Trend 2: Sustainability-Driven Substitutions (Recycled, Dope-Dyed)
Brands are swapping virgin polyester for rPET and trialing dope-dyed yarns to cut water and dyestuff use. Trade-offs include color range limits, MOQ uplift, and lead-time shifts. Position recycled content with clear percentages and certifications (GRS, Bluesign). [CITE: GRS certification overview] [MENTION: Bluesign system partners] [INTERNAL LINK: Recycled yarn supplier index]
Conclusion & Next Steps
Build an AIRism-like program by defining use-case, specifying micro-denier fibers, fine-gauge knits, and compliant finishes, and validating performance via AATCC/ISO/ASTM tests. Protect trademarks, meet US/EU chemical and labeling rules, and plan MOQs and lead-times with mills in China and Bangladesh.
- Week 1–2: Brief and spec targets; naming and claims alignment.
- Week 3–6: Yarn booking, knit trials, finishing routes; proto samples.
- Week 7–9: Lab validation; fit and wear-testing; revise if needed.
- Week 10–12: PP approvals and pilot run; artwork and labels final.
- Week 13+: Bulk production; inline QC and shipment scheduling.
Start your cooling program with Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service: https://china-clothing-manufacturer.com/garment-factory/. [INTERNAL LINK: Contact Eton’s OEM team] [INTERNAL LINK: Author bio – Senior Technical Apparel Strategist]
- Uniqlo — AIRism Feature Hub (2025). https://www.uniqlo.com/us/en/contents/feature/airism/
- AATCC — TM195 Moisture Management (2023). https://www.aatcc.org/test/m195/
- AATCC — TM201 Dry Time (2023). https://www.aatcc.org/test/m201/
- ISO — 11092: Physiological effects — Measurement of thermal and water-vapor resistance (2022). https://www.iso.org/standard/73283.html
- ASTM — D737 Air Permeability of Textile Fabrics (2022). https://www.astm.org/d0737-18.html
- OEKO-TEX — Standard 100 (2025). https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/our-standards/oeko-tex-standard-100
- ECHA — REACH Regulation (2024). https://echa.europa.eu/regulations/reach
- CPSC — CPSIA Summary (2024). https://www.cpsc.gov/Regulations-Laws--Standards/Statutes/The-Consumer-Product-Safety-Improvement-Act
- OEHHA — Proposition 65 (2024). https://oehha.ca.gov/proposition-65
- EU — Textile Regulation 1007/2011 (2024). https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32011R1007
- FTC — Textile and Wool Acts (2024). https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/rules-regulations
- Fast Retailing — Sustainability (2025). https://www.fastretailing.com/sustainability/
- Bluesign — System Partners (2025). https://www.bluesign.com/en/brands/partners
- Global Recycled Standard — Certified (2025). https://textileexchange.org/standards/global-recycled-standard/
- SGS — Textile Testing Services (2024). https://www.sgs.com/en/services/textile-testing
- Intertek — Apparel Testing (2024). https://www.intertek.com/consumer/apparel/
FAQs
Related Articles

Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands
20 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Custom Clothing Embroidery: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Complete Guide for Fashion Brands Custom... more »

T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer
16 minute read
October 28th, 2025
T Shirt Decal Maker: From DIY Designs to Scalable Production with a China Clothing Manufacturer A t... more »
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Clothing production software: A fashion brand’s guide with a China Clothing Manufacturer’s perspective... more »
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer
17 minute read
October 28th, 2025
Sustainable clothing manufacturers USA: A practical guide to partnering with a China Clothing Manufacturer... more »

