Shirts Manufacturers: A Complete Guide to Choosing the Right China Clothing Manufacturer
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Garment Industry
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Garment Industry
October 13th, 2025
17 minute read
Table of Contents
- What a Shirts Manufacturer Actually Does (OEM, ODM, CMT, Full-Package)
- Shirt Cost Breakdown and Typical MOQs (By Category and Region)
- Where to Manufacture Shirts: China vs Bangladesh vs Vietnam vs Turkey vs Portugal
- How to Source and Qualify Shirts Manufacturers (Step-by-Step)
- Tech Packs, Materials, and Quality for Shirts
- Timelines, Logistics, and Delivery to the US & EU
- Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
- Risks, Compliance & Localization for US & EU
- Conclusion & Next Steps
- References & Sources
- FAQs
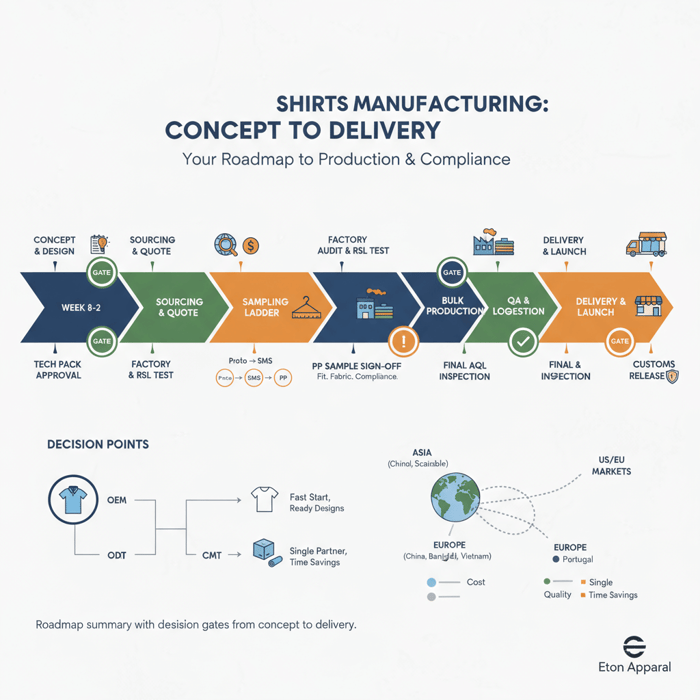
Fashion brands searching for shirts manufacturers need clear choices, fast sampling, and reliable bulk production. This guide maps how to evaluate a China Clothing Manufacturer and regional alternatives, compare OEM/ODM/CMT models, plan costs and MOQs, and pass US/EU compliance while keeping timelines on track.
The fastest way to pick reliable shirts manufacturers is to lock your tech pack, shortlist region-fit factories (China/Bangladesh/Vietnam/Turkey/Portugal) by MOQs, lead times, and compliance, then run proto/SMS/PP sampling with lab tests. Use a risk matrix for US/EU rules like REACH and UFLPA, validate capacity and pricing, and place bulk orders with a firm calendar.
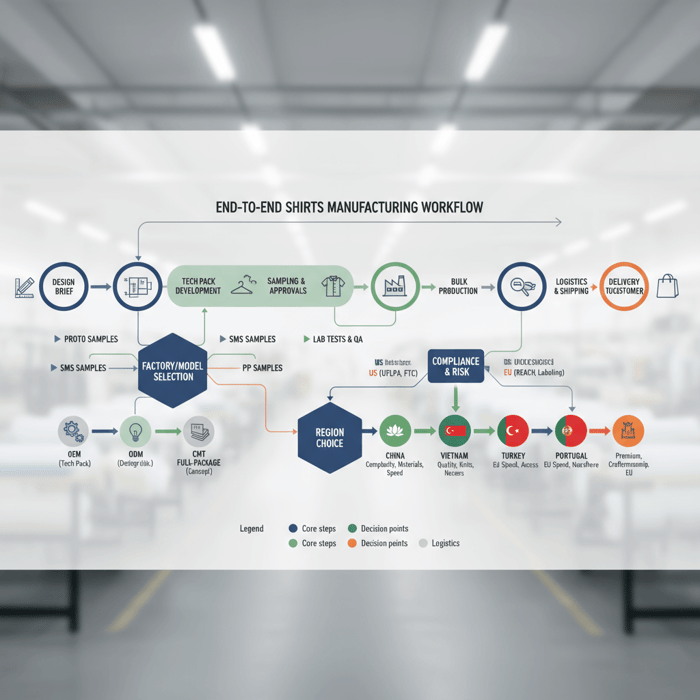
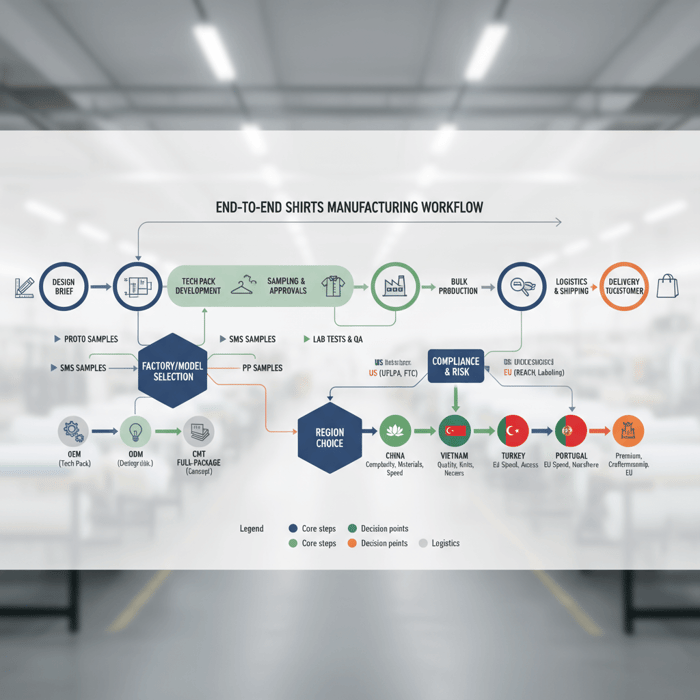
What a Shirts Manufacturer Actually Does (OEM, ODM, CMT, Full-Package)
Shirts manufacturers operate under OEM, ODM, or CMT models, and some offer full-package service that spans design through delivery. Woven dress shirts and knit tees/polos share core steps, yet each needs different machines, patterns, and finishing. Selecting the right model and capability fit reduces rework, unit costs, and missed launch dates.
| Model | Inputs from brand | Factory deliverables | Pros | Trade-offs | Typical MOQ band | Best fit shirt categories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Tech pack, fabrics/trims spec, branding, size run | Pattern/grade, sample ladder, sourcing support, bulk production | High control, fit precision, scalable | Needs clear specs; more brand ownership upfront | Medium to high | Dress shirts, polos, technical knit shirts, uniform shirts |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Design direction, target price, quality level | Factory designs, fabric suggestions, ready-to-brand samples | Fewer development steps, faster starts | Less uniqueness; shared bodies across clients in some cases | Medium | Tees/polos programs, seasonal capsules, private label shirts |
| CMT (Cut, Make, Trim) | All materials provided, finalized patterns, markers | Cutting, stitching, finishing | Low factory overhead in cost build; flexible for niche runs | Brand manages sourcing and liabilities; higher coordination | Low to medium | Simple tees, fashion shirts with unique fabrics supplied by brand |
| Full-package | Design brief, budget, brand standards | Design to delivery: sourcing, pattern, grading, sampling, production, logistics | Single accountable partner, time savings | Higher margin for services; less granular control unless defined | Medium to high | Multi-style programs, retailer basics, performance shirts |
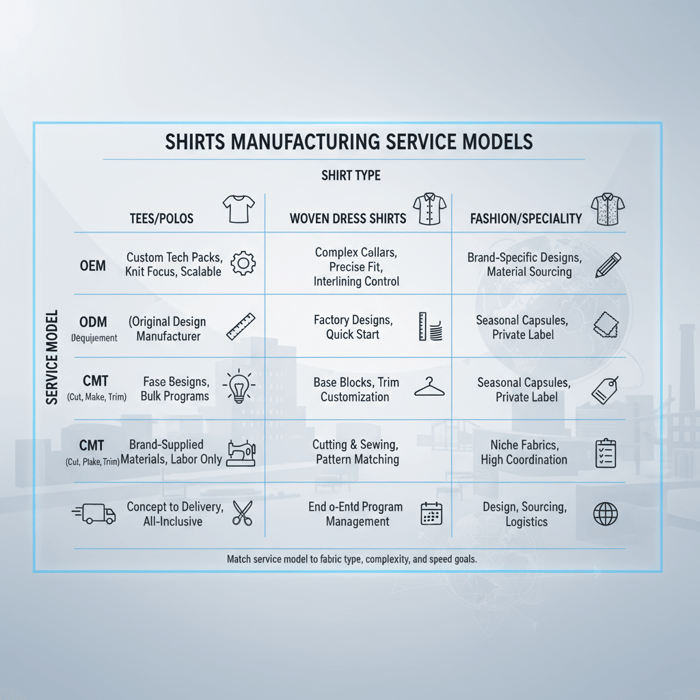
OEM vs ODM vs CMT Defined for Shirts
OEM for shirts: the brand owns the tech pack and aesthetic, while the factory builds patterns, samples, and production. This model fits brands with distinct collar builds, yoke treatments, or performance knit specs. ODM offers factory-originated designs and fit blocks, which trims development time and still allows branding. CMT focuses on manufacturing labor and finishing only, with all materials and patterns supplied by the brand, which suits teams that hold fabric supply chains or special shrinkage recipes.
Knit vs Woven: Process Differences for Tees/Polos vs Dress Shirts
Knit shirts (tees/polos) rely on circular or flat knit fabrics, coverstitch and overlock machines, and collar/cuff knitting for polos. Fit tolerance can be wider with stretch. Woven dress shirts need single-needle stitching, higher stitch density, precise collar/cuff construction with interlinings, and details like plackets, sleeve vents, and pattern matching. Yarn-dyed checks and stripes bring extra requirements on shading, shrinkage control, and seam slippage resistance.
What Full-Package Really Includes
A complete service spans concept to delivery. Checklist:
- Fabric and trim sourcing with mill/vendor mapping
- Pattern, grading, markers, and consumption optimization
- Sample ladder: proto, size set, SMS, pre-production
- Collar/cuff builds, fusing recipes, and laundry/garment wash steps where needed
- Packaging, carton specs, pallet patterns
- Compliance documentation, lab tests, and inspection plans
- Freight booking and Incoterms alignment
When to Switch Models as You Scale
Startups often begin with ODM to get market feedback without heavy sampling cycles. As volumes grow, OEM helps lock signature fits, interlining feel, and collar rolls. Mature brands run hybrid programs: OEM for core dress shirts, ODM or CMT for fashion capsules or licensed programs, and full-package for seasonal drops that need tight calendars with minimal brand-side coordination.
Shirt Cost Breakdown and Typical MOQs (By Category and Region)
Fabric forms the largest share of shirt cost, followed by trims, cut-make labor, finishing, overheads, and logistics. MOQs shift by fabric type, dyeing method, and factory model. Tees and polos often allow lower MOQs than woven dress shirts. Unit cost comes down by improving markers, consolidating colors, and planning material commitments without downgrading quality.
| Cost component | Indicative share of FOB | Ways to reduce without hurting quality | Watch-outs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fabric | 40–60% | Higher yardage commitments, unified color standards, shared fabric across styles | Dye lot variation; shade bands; shrinkage variance |
| Trims & accessories | 5–10% | Trim consolidation; standard buttons/zippers; carton spec harmonization | Branding impact; lead-time exposure with custom trims |
| Cut-Make (CM) | 15–25% | Marker efficiency; balanced line planning; reduce complex operations | Over-simplification can affect appearance and durability |
| Finishing & laundry | 3–8% | Batch process planning; fewer unique finishes; shared wash recipes | Hand-feel or color shift risk if recipes change |
| Overheads & testing | 6–12% | Combine test runs; use standard packaging SKUs | Do not skip RSL or fit-related tests |
| Duty & customs | 0–20%+ (market-dependent) | HTS code accuracy; trade programs; origin planning | Misclassification penalties; origin tracing gaps |
| Freight | 3–10% | Consolidations; sea over air when calendar allows | Launch misses if buffers are thin |
- Global apparel trade remained concentrated among China, Bangladesh, and Vietnam — 2023 (Source: WTO World Trade Statistical Review)
- Brands report ongoing cost pressure from cotton price swings — 2023–2024 (Source: McKinsey State of Fashion)
- US/EU due diligence expectations rising for traceability and chemical safety — 2024 (Source: OECD Guidance; EU REACH)
Cost Components Explained
Fabric: Yarn count, GSM, weave/knit structure, and dyeing method drive the biggest share. Yarn-dyed shirtings carry higher costs and MOQs than piece-dyed cotton or PFD knits.
Trims: Buttons, interlinings, labels, hangtags, and packaging add up. Standardizing across multiple styles lifts buying power and improves delivery reliability.
Cut-Make: Sewing minutes rise with collar stands, plackets, sleeve vents, and pattern matching. Efficient markers, balanced sewing lines, and stable fabric yield reduce labor minutes per unit.
Finishing: Garment wash, enzyme treatments, or wrinkle-resistant finishes add cost. Plan by batch and reuse recipes to keep hand-feel consistent and reduce retesting.
Overheads & testing: Pre-production fit work, lab tests for shrinkage and colorfastness, and inspections sit here. These guard against costly returns and chargebacks.
Duty & freight: Tariff rates depend on HS codes and origin. Freight shifts with mode and fuel. Early booking and accurate carton specs protect cost and timeline.
MOQs for Tees, Polos, Dress Shirts by Region
- Tees: lower MOQs possible, especially with core cotton jersey; factories in China, Vietnam, and Turkey often accept more flexible batches when fabric is common.
- Polos: MOQs rise with knitted collars/cuffs or special yarn blends; planning shared colorways across bodies helps.
- Woven dress shirts: yarn-dyed checks/stripes push fabric MOQs; solid poplins and oxfords allow more flexibility; Bangladesh and China handle scale well.
Why MOQs vary: dyehouse minimums, mill loom planning, lab dip and bulk shade lot control, and line balancing needs. Fabrics that are shared across multiple bodies lower risk for mills and often unlock better terms.
Negotiation Levers That Don’t Hurt Quality
- Consolidate colorways and trims across styles and seasons
- Move to shared core fabrics for multiple shirts to build yardage
- Trim down non-functional design complexity while protecting brand identity
- Commit to rolling forecasts to support mills and factories with capacity planning
These steps cut cost variance and speed up raw material booking while protecting performance and appearance.
Duty, Freight, and Landed Cost Considerations
Align on Incoterms early. FOB puts freight on the buyer’s side, EXW shifts more responsibility, and CIF/CFR packages freight into the agreement. Build landed cost with duty, customs fees, inland drayage, and last-mile costs for the US or EU, and set buffers for peak season surcharges.
Where to Manufacture Shirts: China vs Bangladesh vs Vietnam vs Turkey vs Portugal
China offers depth in materials and complex builds with fast development. Bangladesh delivers cost efficiency and large-scale basics and yarn-dyed shirting. Vietnam balances quality and trade access. Turkey and Portugal offer nearshoring speed for EU drops. Choose based on complexity, budget, and delivery windows.
| Region | Strengths | Relative price band | Typical MOQ band | Indicative production lead time (weeks) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Fabric variety, trims ecosystem, complex collars and finishing, rapid sampling | Mid | Medium | 6–10 for knits; 8–12 for woven after PP | Strong for technical polos and premium dress shirts |
| Bangladesh | Cost efficiency, high capacity, yarn-dyed shirting | Low | Medium to high | 8–14 after PP | Solid basics, large programs; plan fabric lead times |
| Vietnam | Quality consistency, stable labor environment, trade access | Mid to high | Medium | 8–12 | Clean finishing; strong compliance culture |
| Turkey | Speed to EU, shorter transport, strong knits | Mid to high | Low to medium | 6–10 | Ideal for EU in-season drops and fast repeats |
| Portugal | Premium finishing, craftsmanship, EU proximity | High | Low to medium | 6–10 | Best for premium polos and small-batch capsules |
- China, Bangladesh, and Vietnam remain top apparel exporters by value — 2023 (Source: WTO)
- Nearshoring interest keeps rising among EU retailers for speed — 2024 (Source: McKinsey State of Fashion)
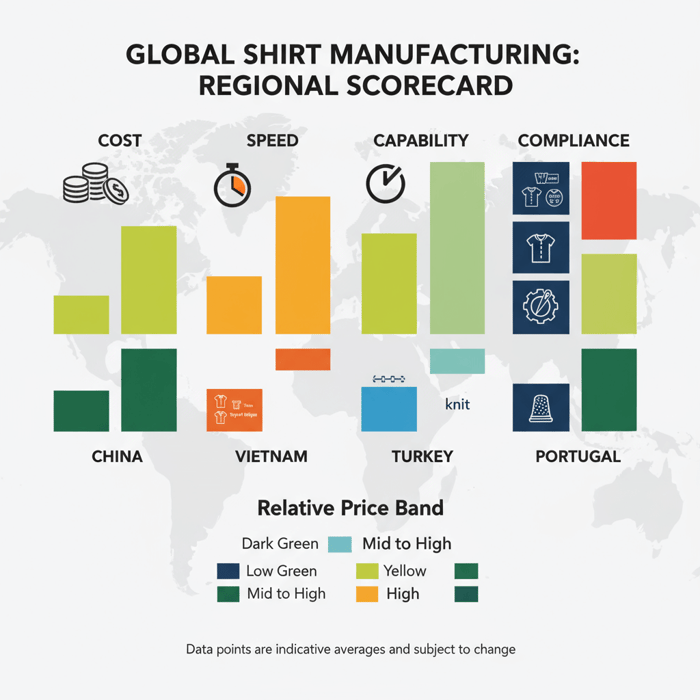
Capability & Complexity by Region
China supports complex woven collars, precise fusing, and technical knit polos with engineered collars. Bangladesh excels in scale for solids and yarn-dyed shirting. Vietnam brings stable quality and controlled stitch lines across programs. Turkey and Portugal offer short runs, premium hand-feel, and rapid repeats for EU markets.
Lead Times and Logistics to US & EU
Standard production windows vary by style and factory loading. Sea freight from Asia to the US/EU ranges from roughly 3–6 weeks door-to-door based on port pairs and season. Turkey and Portugal shorten both production and transit, which suits EU in-season deliveries and reorders. Air is a last resort for launch-critical units.
Risk & Compliance Environment
US importers follow UFLPA screening and CBP documentation. EU buyers apply REACH chemical controls and EU textile labeling rules. All regions require traceability progress, especially for cotton. Factory social audits, chemical management, and security certifications support smoother customs and retail onboarding.
How to Source and Qualify Shirts Manufacturers (Step-by-Step)
Run a staged process: market scan, RFI/RFQ, capability and compliance checks, sample ladder, factory audit, and a pilot run. Score suppliers against cost, capacity, quality, and compliance with set acceptance criteria before awarding bulk.
- Market scan: build a longlist by category fit, region, and model (OEM/ODM/CMT).
- RFI/RFQ: request capability decks, machines, sample images, and cost bands.
- Compliance screening: request social, quality, and chemical certifications.
- Sampling ladder: run proto → SMS → PP with defined approval criteria.
- Factory audit: quality systems, needle control, fusing, laundry controls, and inline QC.
- Pilot run: small production lot with full QA and delivery rehearsal.
- Scale-up gate: move to bulk only after meeting pass/fail metrics.
Market Scan → RFI/RFQ → Shortlist
Inputs: style counts, fabric types, target FOB, launch dates, and compliance needs. Outputs: factory capability matrices, initial cost and lead time ranges, and a trimmed shortlist. Timing: 1–2 weeks for market scan and RFI; 1–2 weeks for RFQ returns if tech packs are solid.
Sampling Ladder: Proto, SMS, PP
Proto confirms design intent and base fit. SMS locks fit, construction, and branding touchpoints across sizes. PP verifies bulk-ready specs, trims, and workmanship with final fabrics. Approval criteria define measurement tolerances, stitch density, fusing feel, colorfastness, and shrinkage targets.
Factory Audits & Compliance Proof
Request social audit reports, chemical program documentation, metal detection or needle control SOPs, lab test histories, inline and final inspection procedures, and security certifications if shipping direct to retail DCs. A walk-through of collar fusing, pressing, and final folding gives a direct read on shirt quality and packing consistency.
Pilot Run & Scale-Up Gate
Execute a controlled production lot. Track defect rates, PP adherence, measurement tolerance pass rates, and on-time shipment. Only award full bulk after meeting target AQL and delivery milestones. If metrics slip, hold a corrective action review or revert to an alternate supplier on the shortlist.
Tech Packs, Materials, and Quality for Shirts
A strong tech pack reduces sampling loops. Include graded measurements, a complete BOM, stitch types and densities, collar and cuff interlining details, button specs, shrinkage allowances, washing or pressing instructions, labeling, and packaging. Validate with a targeted lab test plan and AQL-based inspections.
| QA test | Reference standard | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrinkage (knit/woven) | AATCC 135 | Dimensional stability after laundering | State shrinkage allowance and finish method |
| Colorfastness to laundering | AATCC 61 | Color change and staining control | Covers solid and yarn-dyed fabrics |
| Seam strength/ slippage | ASTM D1683 | Seam integrity under stress | Critical for side seams, armholes, yokes |
| Button attachment strength | Common retailer protocols | Button pull resistance and durability | Define minimum pull and cycle counts |
| Pilling resistance (knits) | AATCC 125/ASTM methods | Surface durability and appearance | Monitor for cotton/poly blends |
| Chemical compliance (RSL) | Brand RSL aligned to REACH | Restricted substances screening | Test at material and finished goods levels |
Building a Shirts Tech Pack
Include: cover sheet with style codes, revision control, graded size charts, tolerance tables, detailed BOM, stitch diagrams, seam allowances, interlining specs, collar and cuff construction, placket types, button size and position, care label copy, packaging, and carton markings. Add callouts for any pressing or wrinkle-resistant finishes.
Lab Tests & On-Body Quality
Set lab tests by fabric and finish. Pair AATCC 135 shrinkage with fit reviews after home wash cycles. Run AATCC 61 colorfastness, and ASTM D1683 for seam strength. Add abrasion or pilling where knits are involved. Write acceptance criteria by garment category and market standards to protect US/EU launches.
Tolerances, Fit, and Size Sets
Define garment measurements per size with tolerances that match fabric stretch and shrinkage. Validate on-model or dress form for collar stand height, shoulder slope, sleeve mobility, and sweep. Use size sets across core sizes, and lock the fit during SMS to reduce PP rejections.
AQL Plans and Inline/Final Inspections
Pick an AQL level aligned to brand risk. Plan inline checks for stitch density, fusing peel, button security, and pressing. Final inspection covers measurements, appearance, folding, ticketing, and carton specs. Track defect types by severity and feed corrective actions into line training.
Timelines, Logistics, and Delivery to the US & EU
A clear calendar links sampling, raw material bookings, production, inspections, and shipping. Pick sea or air by launch date and margin. Set Incoterms and customs data early to prevent port delays and relabeling.
- Asia–US/EU ocean schedules vary seasonally; reliability improved from 2022 lows — 2023–2024 (Source: Industry shipping trackers)
- Air freight used as buffer raises landed cost materially — 2023–2024 (Source: McKinsey State of Fashion)

Typical Lead Times by Category & Region
Knits (tees/polos): 6–10 weeks after PP for many regions when fabrics are common. Woven dress shirts: 8–12 weeks after PP, longer for yarn-dyed or specialty finishes. Nearshore EU suppliers run shorter windows. Add transit and customs buffers at peak season.
Shipping Modes, Incoterms, and Landed Cost Impacts
Sea freight suits core boxes and stable calendars. Air or rail fill urgent gaps. Confirm Incoterms with suppliers, then roll duty, inland haul, and DC intake fees into landed cost. Book early and share production visibility to limit premium freight.
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
A mature OEM program streamlines shirts development with disciplined tech packs, strong material networks, and compliance-first production. Eton’s teams in China and Bangladesh run repeatable workflows that trim sampling loops, stabilize fit, and keep calendars on track for US/EU deliveries.
| Brand need | OEM process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Fast proto on new dress shirt block | Pattern and grading with collar/cuff build library | First fit aligned to brand hand-feel |
| Yarn-dyed shirting with stable shrinkage | Mill sourcing, test yardage, shrinkage mapping | Predictable bulk allowances and sizing |
| Private label polos across regions | Shared fabric programs and collar knit specs | Consistent look and performance across suppliers |
| US/EU compliance coverage | RSL testing aligned to REACH and documentation prep | Smoother customs and retailer onboarding |
| On-time delivery for capsule drops | Calendar gating with PP readiness and booking buffers | Lower air freight exposure |

Eton builds on three decades of outerwear and shirts production with teams that know how to protect collar roll, fusing feel, and stitch consistency. For brands ready to formalize programs, the Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service brings a single accountable partner across China and Bangladesh with design support, material selection, and compliance-ready documentation. Learn more at Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service.
Use Case 1: New Capsule Drop with Tight Timelines
Brief: 12-week clock, mixed polos and woven shirts for EU retail. Approach: standardize core fabrics, compress sampling with clear tolerances, and gate PP approvals to lock bulk booking. Result: calendar buffers preserved for sea freight into the EU DC.
Use Case 2: Scaling Core Shirts Program Across Regions
Brief: replicate a hero dress shirt in multiple regions. Approach: share graded patterns and interlining specs, use lab-tested mills, and harmonize trims. Result: consistent fit and hand-feel with region-appropriate lead times and duty planning.
Risks, Compliance & Localization for US & EU
Common risks include fiber content errors, unplanned shrinkage, colorfastness failures, restricted substances, and supply chain traceability gaps. A documented due diligence program, targeted lab tests, and region-specific labeling keep goods moving into the US and EU.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrinkage out of tolerance | Medium | High | AATCC 135 testing; fabric relax; clear allowances in grading |
| Color bleeding or shade mismatch | Medium | Medium | AATCC 61 testing; shade band management; bulk lab dips |
| Seam slippage or button failure | Low to medium | High | ASTM seam tests; button pull tests; SOP audits |
| Restricted substance exceedance | Low to medium | High | RSL aligned to REACH; upstream chemical controls and testing |
| Traceability gaps under UFLPA | Medium | High | Supplier mapping; transaction and origin records; cotton tracing |
| Labeling non-compliance | Low | Medium | US FTC and EU 1007/2011 label checks; bilingual care where needed |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
US: fiber content labels, country of origin, and care instructions must meet FTC rules. Children’s products require CPSIA conformance. UFLPA enforcement expects traceability documentation for at-risk materials.
EU: follow REACH for chemicals and maintain documentation. Label textile fiber names to Regulation 1007/2011. Keep product safety and labeling in local languages where required by market.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Define your shirt categories and target costs, pick region-fit factories with the right model, and run a structured sampling and QA plan. Align compliance from day one. Award bulk only after a pilot run hits AQL and delivery targets, then protect time-to-market with a clear calendar and buffers.
- Week 0–2: finalize tech packs and materials
- Week 2–4: RFI/RFQ and shortlist
- Week 4–8: proto and SMS, lab tests
- Week 8–10: PP approvals and bulk booking
- Week 10–22: production with inline checks
- Week 22–24: final inspection, pack, book freight
- Week 24–30: transit, customs, DC intake
References & Sources
- Wikipedia: T-shirt
- Wikipedia: Dress shirt
- McKinsey & Company: The State of Fashion 2024
- OECD: Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains in the Garment and Footwear Sector
- WTO: World Trade Statistical Review 2023/2024
- US CBP: Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) resources
- EU REACH (European Chemicals Agency)
- EU Regulation 1007/2011 on textile fiber names and related labeling
- AATCC Testing Standards
- ASTM D1683 Seam Strength
FAQs
What does OEM vs ODM vs CMT mean for shirts, and when should a brand choose each model?
What is a full-package manufacturing service for shirts and what’s included?
What should a shirts tech pack include to reduce sampling loops?
What are typical MOQs for shirts by category and region, and why do MOQs vary?
How does the FOB cost breakdown for shirts typically allocate fabric, labor, trims, and freight?
What do Incoterms FOB, EXW, and CIF mean for apparel shipments of shirts?
What US/EU compliance requirements apply to shirts, including REACH and UFLPA?
How do AQL inspections for shirts work, and what defect checks should be included?
What is a sampling ladder for shirts, and how do proto, SMS, and PP differ?
Related Articles

Custom Merch for Businesses: OEM Manufacturing Guide for US & EU Brands
6 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Custom Merch for Businesses: OEM Manufacturing Guide for US & EU Brands Custom merch for businesses... more »

Top American Made Companies in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Fashion Brands Seeking Domestic Excellence
14 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Top American Made Companies in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Fashion Brands Seeking Domestic... more »

United States Apparel Sourcing Guide: Top Manufacturers and Strategies for Fashion Brands in 2024
18 minute read
October 13th, 2025
United States Apparel Sourcing Guide: Top Manufacturers and Strategies for Fashion Brands in 2024 In the... more »
Types of Tank Tops: The Complete Style, Fabric, and Manufacturing Guide from a China Clothing Manufacturer
12 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Types of Tank Tops: The Complete Style, Fabric, and Manufacturing Guide from a China Clothing... more »

