How to Choose a Hoodies Company: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Guide for Fashion Brands
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Garment Industry
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Garment Industry
October 13th, 2025
15 minute read
Table of Contents
- What “Hoodies Company” Means: OEM, ODM, and Private Label Explained
- Fabric, Fit, and Construction Standards for Premium Hoodies
- Supplier Selection: A Vetting Checklist for Hoodies Manufacturers
- Hoodie Costs, MOQs, and Pricing Tiers
- Lead Times & Production Workflow in China and Bangladesh
- Sustainability, Compliance & Risk for US/EU Markets
- Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
- Hoodie Market Trends & What’s Next
- Conclusion & Next Steps
- References & Sources
- FAQs
How to Choose a Hoodies Company: A China Clothing Manufacturer’s Guide for Fashion Brands
hoodies company selection sets the tone for fit, fabric integrity, and delivery reliability. A seasoned China Clothing Manufacturer with OEM and ODM capacity, proven QA, and US/EU compliance reduces risk and keeps programs on calendar. This guide maps decision models, spec standards, MOQs, lead times, and audits—then ties them to multi-country production in China and Bangladesh.
The best hoodies company for fashion brands offers OEM/ODM development, consistent fabric and construction standards, proven US/EU compliance, and scalable capacity. Evaluate suppliers with a clear vetting checklist, cost/lead-time models, and QA checkpoints — then align orders to multi-country production (China + Bangladesh) for resilience and speed.
What “Hoodies Company” Means: OEM, ODM, and Private Label Explained
For a hoodies company, three models dominate: OEM (build to your tech pack), ODM (adopt the supplier’s designs under your brand), and private label (brand a preset range). Pick OEM for fit control and custom fabric; ODM for speed; private label for simplicity and margin balance. Match model choice to brand maturity, design bandwidth, and inventory strategy.
| Model | Control | Speed | Cost | MOQ | Risk Profile | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Build-to-Spec) | High — fabric, fit, trims, embellishment | Medium — requires development | Medium–High (setup + testing) | Medium–High | Development risks; mitigated by QA gates | Brands needing custom fits, premium fabrics, unique graphics |
| ODM (Supplier Designs) | Medium — tweak existing blocks and fabrics | Fast — design foundation is ready | Medium — fewer setup costs | Medium | Style alignment; fit tolerances must be validated | Smaller teams, tight calendars, capsule drops |
| Private Label | Low–Medium — fixed range with branding | Fastest — ready-to-order core range | Low–Medium — limited customization | Low–Medium | Differentiation limits; volume needed for margin | Value retail, core basics, entry programs |

When to Choose OEM (Build-to-Spec)
Pick OEM when the collection requires custom blocks, performance fabric blends, and precise embellishment quality. Example: US/EU brands targeting premium fleece (330–380 GSM) with low shrinkage, tight pilling tolerance, and specialty graphics across chest, sleeve, and back. Benefits: deeper fit control and fabric handfeel precision. Trade-offs: longer sampling and higher MOQs; offset with clear tech packs and staged QA.
When ODM Speeds Market Entry
ODM helps teams on compressed timelines launch a hoodies company program without building blocks from scratch. Use ODM for seasonal trend capsules or fast-track basics where supplier patterns already meet fit targets. Validate lab dips, handfeel, and grading consistency before SMS approvals. Keep branding and graphics distinct to avoid overlap across retailers.
Private Label Scenarios
Private label suits core basics and value programs requiring quick turns and price points under tight margin. Use fixed fabrics and trims, apply brand labeling and simple graphics, and scale through volume. Fit differentiation remains limited, so lock measurement charts and TOP sample tolerances to avoid returns.
Fabric, Fit, and Construction Standards for Premium Hoodies
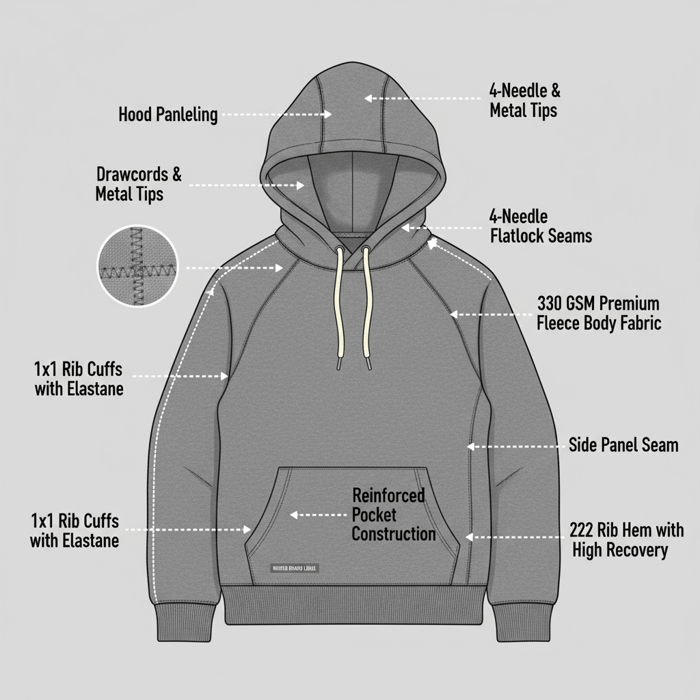
Lock GSM ranges by fabric, shrinkage and pilling tolerances, seam construction, rib recovery, and drawcord/zipper quality to create consistent retail-grade hoodies. Pair accurate pattern grading with US/EU test protocols for colorfastness and chemical safety. Technical discipline lowers defects and supports repeat replenishment.
| Component | Spec Range | Test Method | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fleece GSM | 280–380 GSM [Verification Needed] | Mass per unit area | Within ±5% of target GSM |
| Cotton/Poly Blend | 60/40 to 80/20 | Fiber content testing | Label accuracy per FTC Textile Rules US FTC Textile Labeling |
| Shrinkage | <5% length/width | Home laundering method | Meets brand tolerance; stable after 2–3 washes |
| Pilling Resistance | Target Martindale level | Martindale abrasion/pilling | Grade matched to premium fleece standard [Verification Needed] |
| Colorfastness | Wash/rub/light | ISO/ASTM methods | Pass per US/EU program specs; align with REACH ECHA REACH |
| Seam Construction | 4-needle flatlock/overlock | Seam strength testing | No seam slippage; balanced tension |
| Rib Cuffs/Hem | 1x1 or 2x2 rib, elastane content 2–5% | Elastic recovery tests | Recovery ≥ 90% after extension [Verification Needed] |
| Drawcords | Core-spun, tipped ends | Tensile, tip pull-off | No fraying; tip secure under pull |
| Zippers (if applicable) | Reversed coil or molded, brand-grade | Cycling test | Pass cycles without tooth damage |
| Labeling | Fiber, care, origin | Label inspection | Conforms to US/EU labeling rules (US FTC; EU Textile Labelling) |
Fabric & Finishing (Cotton, Blends, Fleece, Terry)
Premium fleece lands between midweight and heavyweight for warmth and drape. Cotton/poly blends (60/40 to 80/20) balance handfeel, durability, and colorfastness. Brushed back fleece increases softness; French terry offers breathable loopback for trans-seasonal wear. Stabilize shrinkage with preshrink steps, mercerization, or tumble-relaxing, then validate with laundering tests aligned to program specs and retail claims (ISO Textiles).
Construction & Durability (Seams, Ribs, Trims)
Flatlock seams reduce bulk and chafe; overlock with precise tension keeps edges clean. Reinforce stress points at pocket corners and hood junctions. Rib cuffs and hems need elastane content and recovery testing; specify rib architecture and target recovery percentage. Drawcord tips, eyelets, and zipper brands (e.g., trusted coil/molded lines) require cycle tests and pull checks for retail reliability.
Fit Consistency & Grading
Create a base block per gender and region, then grade across sizes with controlled increments. Lock measurement charts—chest, body length, sleeve, across shoulder—and set tolerances (e.g., ±1 cm) for PP, SMS, and TOP. Use measurement audits and sealed samples to keep factories aligned for evergreen programs and replenishments.
Testing & Compliance (Colorfastness, REACH/CA Prop 65)
US/EU-bound hoodies must satisfy chemical safety and labeling rules. Align restricted substances with EU REACH and manage hazardous substances in prints and trims (ECHA REACH). For California, screen graphic inks, coatings, and metals under Proposition 65 warning thresholds (CA Prop 65). Use third-party labs and program-level protocols; confirm OEKO-TEX Standard 100 where applicable (OEKO-TEX Standard 100).
Supplier Selection: A Vetting Checklist for Hoodies Manufacturers
Pick a hoodies company with documented compliance, audited capacity, knitwear lines, and strong sample quality. Review certifications, test reports, and references. Run a pilot production to validate line output, QA behavior, and calendar discipline before scaling programs.
- Define your model and range: OEM vs ODM vs private label; fabric and embellishment scope; size spread.
- Shortlist suppliers with hoodies history: factory photos/videos, machine lists, knit sewing lines, sample rooms.
- Request documents: business license, certifications (OEKO-TEX, WRAP, BSCI), lab reports, buyer references.
- Run sampling: PP and SMS rounds with sealed measurements and pass/fail criteria.
- Audit capacity and calendars: demonstrate production plans, peak season handling, and workforce stability.
- Launch a pilot order: limited styles/units to validate QA checkpoints and throughput.
- Scale with dual sites: split PO lines across China/Bangladesh for resilience and speed.
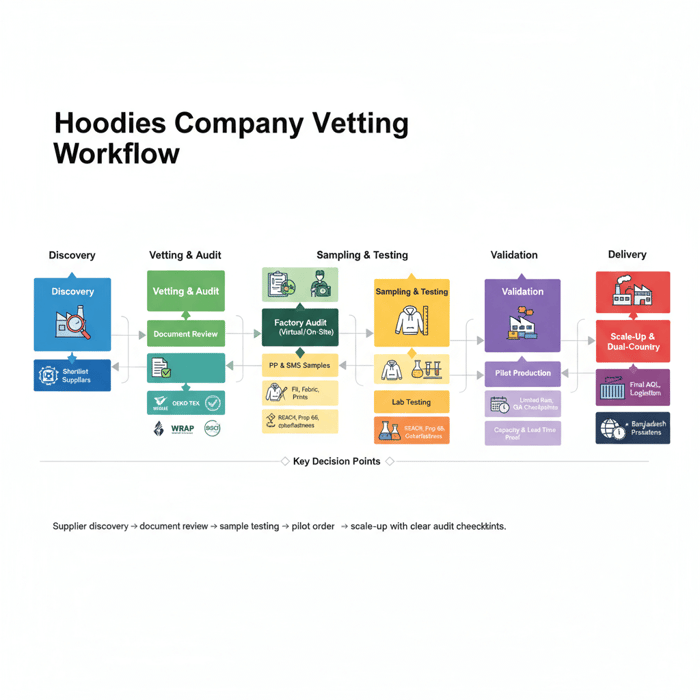
Verification Documents & Certifications
Check OEKO-TEX Standard 100 for material safety, WRAP or amfori BSCI for social compliance, and recycled claims supported by GRS for polyester content (WRAP; amfori BSCI; Textile Exchange GRS). Request recent audit reports, CAPs, and lab test summaries to confirm ongoing adherence.
Sample Quality & Pilot Production
Define PP and SMS acceptance criteria: handfeel, GSM, shrinkage, pilling grade, colorfastness, stitching, and measurement tolerances. Seal TOP samples before bulk production. Run a pilot with measurement audits and AQL sampling to capture defect trends and line behavior (ISO 2859 AQL).
Capacity & Lead Time Proof
Ask for monthly output, machine lists, and staffing plans. Review material booking calendars, trim lead times, and QA resource allocation. Confirm how the factory navigates holidays and peak seasons in China and Bangladesh; align booking windows for freight and QA slots.
References & On-Site/Virtual Audits
Speak with buyer references. Request factory walkthroughs via video if travel is restricted, focusing on fabric stores, cutting rooms, sewing lines, finishing, and final inspection. Capture date-stamped images and process flow notes to anchor your decision.
Hoodie Costs, MOQs, and Pricing Tiers
Unit cost rides on fabric GSM and fiber blend, embellishment method, trims, labor, compliance/testing, and logistics. MOQs push prices lower through fabric efficiency and line throughput, while raising inventory exposure. Balance style count and colorways against program risk.
| Cost Driver | Typical Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric | Largest share | GSM, cotton/poly blend, finishing; recycled content may add cost (Textile Exchange) |
| Embellishment | Medium–High | Screen vs DTG vs DTF; coverage, colors, placement drive price |
| Trims & Accessories | Low–Medium | Quality zippers, branded tips, eyelets; small parts add up |
| Labor | Medium | Country wage structure, line efficiency, rework rate |
| Compliance & Testing | Low–Medium | Lab tests for REACH/Prop 65, labeling, certifications |
| Freight & Incoterms | Medium | FOB vs CIF; ocean vs air; booking windows and surcharges |
- Global apparel growth outlook steady into 2024–2025 (Source: McKinsey State of Fashion 2024)
- EU textiles strategy advancing circularity targets (2022) (Source: EU Textiles Strategy)
MOQ Strategy
Use tiered MOQs to hit price targets: consolidate fabrics and colors, limit size curves per drop, and align print screens across styles. Maintain buffer stock only when sizing and demand are validated; otherwise expand colorways and trims gradually across replenishments.
Embellishment Costing (Screen, DTG, DTF)
Screen printing suits larger runs and flat colors at scale; DTG favors photoreal designs with lower MOQs but higher unit costs; DTF provides strong color coverage with good edge detail and heat transfer convenience. Map graphics to coverage and sleeve placements to control cost, then confirm wash and rub fastness via lab tests (ISO Colorfastness).
Logistics & Incoterms (FOB vs CIF)
FOB places freight control on the buyer; CIF places insurance and freight with the seller. Model ocean lead times and booking windows against season launches. Track surcharges, port congestion, and customs triggers for US/EU labeling and declarations (US CBP Import Guidance).
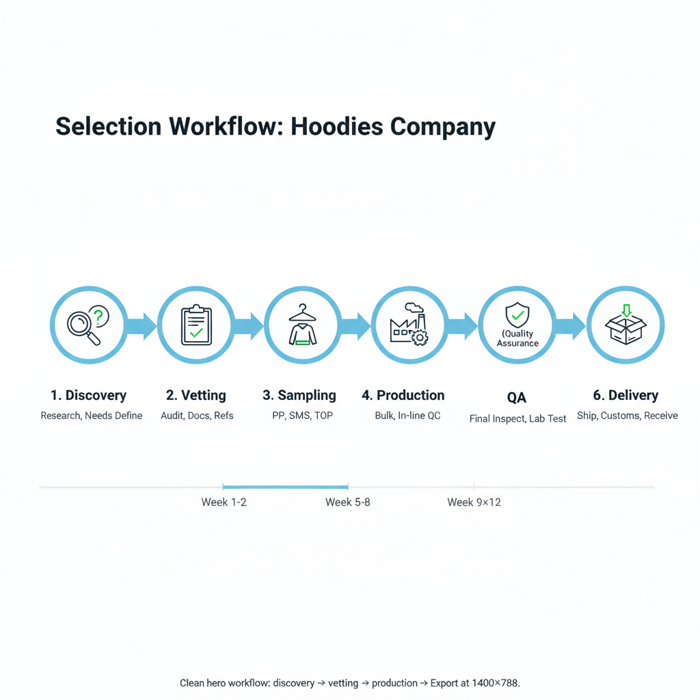
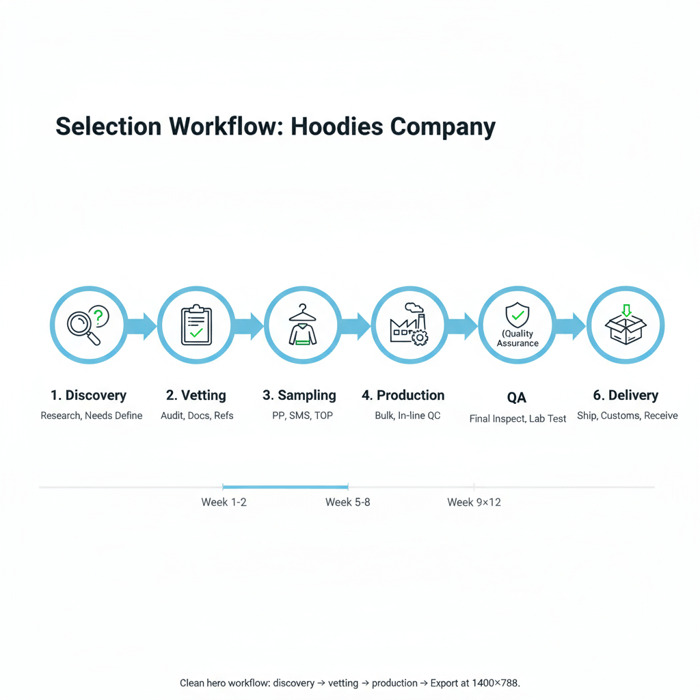
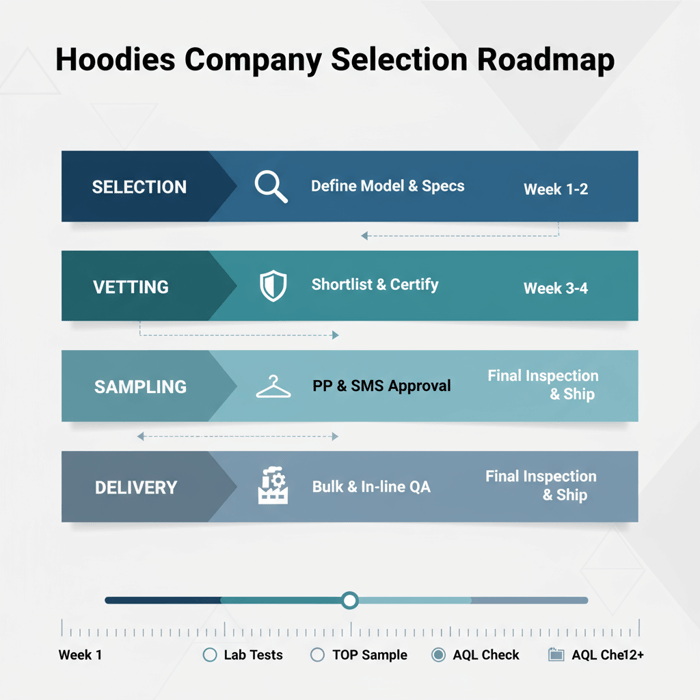
Lead Times & Production Workflow in China and Bangladesh
Typical workflows run from tech pack to SMS, material booking, bulk, QA, and shipment. China offers speed and flexibility; Bangladesh offers scale and value. Split programs to hedge calendar risk and build resilience for peak seasons.
- Tech Pack: measurements, fabric specs, trims, graphics, labels.
- PP Sample: fit and construction; measurement chart validation.
- SMS: colorways, embellishments; retail-ready approvals.
- Material Booking: bulk fabric dyeing/finishing; trims purchase.
- Pre-Production: pilot line setup; operator training; QA plan.
- Bulk Production: cutting, sewing, finishing; in-line audits.
- Final Inspection: AQL sampling; packing and carton checks.
- Shipment: FOB/CIF booking; customs clearance; delivery.
Sampling Calendar (PP, SMS, TOP)
PP locks fit; SMS confirms color and graphics; TOP seals final bulk acceptance. Define pass/fail criteria for each stage with measurement tolerances and lab test results. Keep sealed reference samples to align multi-site output.
Material Booking & Pre-Production
Fabric lead times vary by dyeing and finishing workflow; recycled polyester or specialty cotton may add sourcing windows (Textile Exchange). Pre-production stabilizes QA, trims, and operator steps. Document machine settings and stitch tensions for repeatability.
Bulk Production & In-Line QA
Run in-line audits on measurement and stitching, record defect types, and drive corrective action. Use AQL sampling at multiple checkpoints; measure across sizes and colorways to catch variation early (ISO 2859 AQL).
Final Inspection, Packing & Shipment
Prepare carton specs, label placements, and packing ratios to fit US/EU distribution plans. Final inspection includes measurements, print assessment, and fabric handfeel checks, followed by booking and customs documentation (US CBP).
Sustainability, Compliance & Risk for US/EU Markets
Align materials and testing with US/EU rules, document traceability, and screen for forced labor risks. Certifications and diligent audits support claims and lower import disruptions. Build a document trail that clears retail gatekeeping and border checks.
- Pros: safer materials, improved brand trust, smoother customs.
- Cons: added testing costs, more documentation, longer sourcing windows for recycled content.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fabric variation | Medium | High | Lock GSM, lab dips, preshrink steps; audit suppliers |
| Print defects | Medium | Medium–High | Screen approvals; wash/rub tests; in-line print checks |
| Shrinkage above tolerance | Medium | High | Preshrink and finishing; laundering validation; sealed TOP |
| Shipment delays | Medium | Medium–High | Early bookings; multi-country split; air contingency for key styles |
| Compliance gaps | Low–Medium | High | REACH screening, Prop 65 checks, OEKO-TEX; third-party labs |
| Forced labor exposure | Low–Medium | High | Traceability audits and supplier screening per CBP UFLPA Guidance |
Regulatory Notes for US & EU
For the US, follow Textile Fiber Products Identification rules for labeling and fiber claims, and screen chemicals against Proposition 65 requirements (US FTC Textile Labeling; CA Prop 65). For the EU, comply with fiber labeling, REACH restricted substances, and circularity initiatives in the textiles strategy (EU Textiles Strategy; ECHA REACH). Use OECD due diligence guidance as the process backbone (OECD Due Diligence).
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service connects design support, fabric sourcing, dual-country production, and jacket-grade QA adapted to hoodies. Programs benefit from pattern expertise, embellishment control, and compliance mapping for US/EU retail—built on three decades in outerwear and technical apparel.
| User Need | OEM Service Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Premium fleece with tight shrinkage | Fabric development and lab testing | Stable handfeel and fit across replenishments |
| Custom fit block for US/EU | Pattern creation and grading | Consistent measurements and fast repeats |
| Complex multi-placement graphics | Screen/DTF process control and approvals | Clean prints with verified wash/rub fastness |
| Resilient lead times | Split production across China/Bangladesh | Calendar protection and scalable capacity |
| US/EU lab and labeling compliance | Program-level compliance map | Smoother audits and customs clearance |
Explore Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service to align your hoodies company goals with proven specification discipline, sampling gates, and dual-country delivery.

Use Case 1: Fast-Track Seasonal Drop
A brand needs a 10-style capsule with heavy fleece and three graphics techniques. Eton calibrates blocks for US/EU sizing, validates GSM and shrinkage, runs PP and SMS with sealed measurements, approves print screens, and splits production across China and Bangladesh to hit a tight calendar. Final inspection follows AQL, with FOB bookings arranged on confirmed windows.
Use Case 2: Evergreen Core Program
A retailer builds year-round hoodies in three fabrics and five colorways. Eton locks a master measurement chart and TOP sample, sets a replenishment rhythm with material pre-bookings, and runs measurement audits on each batch. Dual bases smooth out demand spikes, while compliance documents flow with every shipment for consistent store-level quality and fit.
Hoodie Market Trends & What’s Next
Comfort demand persists, with buyers favoring premium fleece, recycled fibers, and performance finishes. Customization and inclusive sizing widen reach. Teams use data to right-size inventory, mixing seasonal capsules with evergreen core programs to keep sell-through reliable.
- Macro apparel outlook suggests steady growth focus on resilience and speed (Source: McKinsey 2024)
- EU circular textiles plan pushes durability and recyclability signals into development (Source: EU Textiles Strategy 2022)
Material & Finish Trends
Recycled polyester blends supported by GRS gain traction, while organic cotton interest tracks retailer sustainability roadmaps (GRS). Moisture-wicking and anti-pilling finishes help cross-season wear; French terry remains favored for transitional collections.
Customization & Inclusive Sizing
Graphics personalization and wider size ranges expand audience and improve loyalty. Brands anchor fit with consistent grading and measurement tolerances across regions. Strong print standards with wash/rub testing maintain quality for repeat purchases.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Define the model for your hoodies company, lock fabric and construction specs, vet factories with audits and sampling gates, and plan calendars across China and Bangladesh. Align compliance for US/EU markets, document traceability, and build replenishment discipline for core programs. With the right partner, speed and quality can move together.
- Week 1–2: Finalize model (OEM/ODM), tech packs, and spec targets.
- Week 2–3: Shortlist suppliers; request certifications and lab reports.
- Week 3–4: PP sampling; measurement audits; lab tests.
- Week 4–6: SMS approvals; material booking and trims purchase.
- Week 6–8: Bulk production; in-line QA; defect corrections.
- Week 8–12: Final inspection; packing; shipment and customs.
References & Sources
- Wikipedia — Hoodie (2024). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hoodie
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024 (2024). https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights/the-state-of-fashion
- European Commission — EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles (2022). https://environment.ec.europa.eu/strategy/textiles-strategy_en
- OECD — Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains in the Garment and Footwear Sector (2018). https://mneguidelines.oecd.org/oecd-due-diligence-guidance-garment-footwear.htm
- US Customs and Border Protection — UFLPA Operational Guidance (2022–2024). https://www.cbp.gov/trade/forced-labor/UFLPA
- OEKO-TEX — Standard 100 (2024). https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/our-standards/oeko-tex-standard-100
- US FTC — Textile Fiber Products Identification Act & Labeling Guidance (2024). https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/threading-your-way-through-labeling-requirements-under-textile-fiber-products-identification
- ECHA — REACH Regulation (Accessed 2025). https://echa.europa.eu/regulations/reach
- OEHHA — California Proposition 65 (Accessed 2025). https://oehha.ca.gov/proposition-65
- ISO — AQL Sampling (ISO 2859) (Accessed 2025). https://www.iso.org/standard/66262.html
- Textile Exchange — Global Recycled Standard (GRS) (Accessed 2025). https://textileexchange.org/standards/grs/
- US CBP — Basic Import/Export Guidance (Accessed 2025). https://www.cbp.gov/trade/basic-import-export
- WRAP — Certification Program (Accessed 2025). https://wrapcompliance.org
- amfori — BSCI Program (Accessed 2025). https://www.amfori.org/content/amfori-bsci
FAQs
What is the difference between OEM vs ODM for hoodies, and which should a brand choose?
When are private label hoodies a smart choice for retailers?
What hoodies GSM range works for premium fleece?
What cotton polyester blend hoodie ratio is best for durability and handfeel?
What hoodie shrinkage tolerance should I set for bulk production?
How do I specify pilling resistance Martindale for hoodies?
What is colorfastness testing for hoodies, and what should I require?
When should I use a flatlock seam hoodie construction?
What rib cuff recovery should I require for hoodies?
How do I assess drawcord and zipper quality for a hoodie program?
What is size grading for hoodies and how do I manage consistency?
What does REACH compliance mean for hoodies entering the EU?
Do California Prop 65 hoodies need special testing?
Why choose OEKO-TEX Standard 100 hoodies materials?
How does AQL sampling for hoodies work at final inspection?
What is a practical MOQ for hoodies and how do I plan it?
Which is better for graphics—screen printing vs DTG vs DTF hoodies?
What do Incoterms FOB vs CIF mean for hoodies shipments?
How should I split China vs Bangladesh hoodies production?
What are PP SMS TOP samples in hoodies development?
Why use recycled polyester GRS hoodies materials?
Do WRAP or BSCI certifications matter when choosing a hoodies factory?
How does UFLPA affect forced labor risk in hoodies sourcing?
French terry vs fleece hoodie—when should I pick each?
What label requirements for hoodies US EU should I follow?
What is the typical lead time for hoodies production from tech pack to shipment?
Why run a pilot production hoodies order before scaling?
What is dual-country production hoodies planning and why use it?
What is a realistic cost breakdown hoodie at FOB?
What measurement tolerances hoodie programs should enforce at PP, SMS, and TOP?
How does a hoodies company manage QA and compliance for US/EU retail?
What are the key PP sample checks for a premium hoodies company order?
Related Articles
Types of Tank Tops: The Complete Style, Fabric, and Manufacturing Guide from a China Clothing Manufacturer
12 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Types of Tank Tops: The Complete Style, Fabric, and Manufacturing Guide from a China Clothing... more »

Custom Merch for Businesses: OEM Manufacturing Guide for US & EU Brands
6 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Custom Merch for Businesses: OEM Manufacturing Guide for US & EU Brands Custom merch for businesses... more »

United States Apparel Sourcing Guide: Top Manufacturers and Strategies for Fashion Brands in 2024
18 minute read
October 13th, 2025
United States Apparel Sourcing Guide: Top Manufacturers and Strategies for Fashion Brands in 2024 In the... more »

Top American Made Companies in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Fashion Brands Seeking Domestic Excellence
14 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Top American Made Companies in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Fashion Brands Seeking Domestic... more »

