Cut and Sew Manufacturers: How to Choose the Right China Clothing Manufacturer for Your Brand
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Garment Industry
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Garment Industry
October 13th, 2025
12 minute read
Table of Contents
- What “Cut and Sew” Really Means in Apparel (and How It Differs from CMT, FOB, FPP)
- How to Choose a Cut and Sew Manufacturer (Criteria, Vetting, and Factory Audits)
- Cost, MOQs, and Lead Times: What US/EU Brands Should Expect
- Region Comparison for Outerwear Procurement
- Tech Packs & QA
- Trends & Sustainability (2024–2025)
- Implementation Steps
- Product Integration
- Risks & Compliance
- Conclusion & Next Steps
- References & Sources
- FAQs
Cut and Sew Manufacturers: How to Choose the Right China Clothing Manufacturer for Your Brand
Cut and sew manufacturers turn patterns, fabrics, and trims into finished garments. For brands planning outerwear, partnering with a seasoned China Clothing Manufacturer gives access to technical capabilities (taping, down handling, thermal testing), stable capacity, and predictable calendars across sampling to bulk. This guide covers selection, costs, region fit, QA, compliance, and a practical rollout plan grounded in supply-side experience.
Cut and sew manufacturers convert materials into finished garments through cutting, stitching, and assembly. For outerwear, choose a China Clothing Manufacturer with OEM/ODM strength, proven QC (AQL), and certifications. Align on tech packs, sampling gates, MOQs, and US/EU compliance to secure cost control, reliable timelines, and product performance at scale.
What “Cut and Sew” Really Means in Apparel (and How It Differs from CMT, FOB, FPP)
Cut and sew is the heart of garment production: fabric is spread, cut to pattern, and stitched into finished pieces. Service scope varies. CMT means you supply all materials; FOB/FPP adds factory-led sourcing and logistics; OEM uses your design; ODM provides factory-developed styles. For outerwear, model choice affects sourcing control, lead time, and technical results.
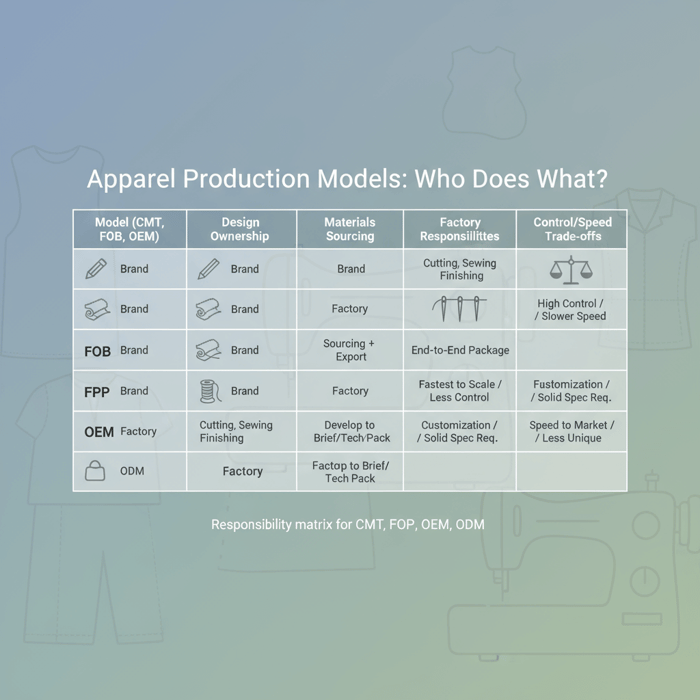
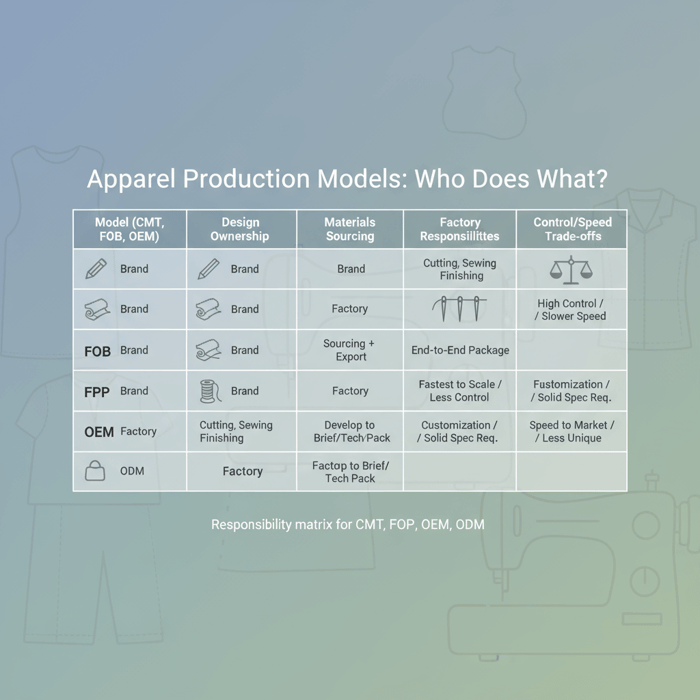
| Model | Design Ownership | Materials Sourcing | Factory Responsibilities | Pros | Trade-offs | Outerwear Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMT | Brand (your tech pack) | Brand | Cutting, sewing, finishing | High material control; price transparency | More vendor management; longer onboarding | Useful if you specify exact insulation, DWR, tape |
| FOB | Brand | Factory | Sourcing + production + export | Turnkey; simpler operations | Supplier RSL diligence needed | Leverage verified mills for PFC-free DWR and seam tape |
| FPP | Brand | Factory | End-to-end package incl. trims, labels | Fastest to scale | Less granular control | Align on lab tests for clo, hydrostatic head |
| OEM | Brand | Factory or brand | Develop to your brief and tech pack | Customization with structure | Requires solid spec discipline | Ideal for brand-specific performance targets |
| ODM | Factory | Factory | Factory proposes styles, you adapt | Speed to market | Less unique design | Great for price points and broad retail calendars |
Core Services in Cut and Sew
- Pattern making and grading from CAD
- Fabric spreading, cutting (manual, die, or auto-cut)
- Stitching and assembly with operation breakdowns (SMV)
- Seam sealing and bonding for technical shells
- Padding/down filling, baffling, quilting
- Finishing: buttonholes, zippers, snaps, bartacks
- Pressing/steaming, trimming threads, packing
- In-line and final quality checks (AQL) and lab testing
OEM vs. ODM: What Changes for Brands
With OEM, you bring the vision and performance spec. The factory supports materials development and production engineering to meet targets (e.g., 10k/10k shell, 700 fill power down, clo ≥ 1.0 at 20 °C). With ODM, you select from a style library; the supplier tweaks materials, fits, and trims to hit a price and calendar, ideal for replenishment and entry programs.
Contract Types (CMT/FOB/FPP): Choosing the Fit
- CMT: best for brands with mill programs, strict RSLs, or proprietary components. Requires stronger procurement and inbound QC.
- FOB: balanced control and speed. Align on nominated mills, test methods, and incoming inspection plans.
- FPP: fast launch and scale. Lock specs via golden samples and PP tests to control variance.
How to Choose a Cut and Sew Manufacturer (Criteria, Vetting, and Factory Audits)
Shortlist factories by category fit (outerwear), capacity, QA maturity, certifications, and compliance record. Validate with samples and audits before scaling. Combine document checks, live floor observation, and pilot production to gauge repeatability, communication, and issue response speed.
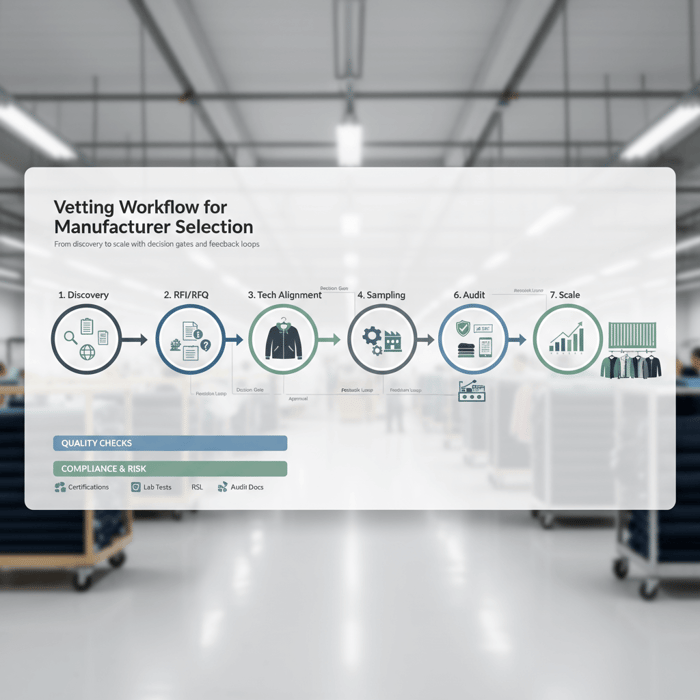
- Discovery: collect case studies, line lists, and client references.
- RFI/RFQ: share a structured brief with target FOB, volumes, and calendar.
- Technical alignment: review seam construction, insulation, tape, DWR, and tolerances.
- Sampling: request proto → fit → SMS with clear change logs.
- Audit: assess social, quality, safety, and environment; review AQL records.
- Pilot: run a 300–1000-piece pilot to test bulk repeatability and line balancing.
- Scale: lock golden sample, PP approvals, and capacity reservations.
Credentials & Certifications to Require
- WRAP or amfori BSCI for social compliance (WRAP; amfori BSCI).
- ISO 9001 for quality management (ISO 9001).
- OEKO-TEX STANDARD 100 for harmful substances in textiles (OEKO-TEX).
- GRS/RCS for recycled materials when applicable (Textile Exchange).
- RDS for down traceability where down is used (Responsible Down Standard).
Product Fit: Outerwear-Specific Capabilities
- Seam sealing: tape brands, bonding parameters, and hydrostatic testing capability.
- Down handling: dedicated rooms, weighing, migration controls, and fill audits.
- Thermal testing: access to clo/thermal resistance testing and fill power validation.
- DWR performance: PFC-free options and spray rating tests under AATCC standards.
- Hardware: expertise with waterproof zippers, injected molds, and bartack patterns.
Require lab reports aligned with your Restricted Substances List (RSL) and EU REACH obligations (ECHA REACH). For children’s wear, align with US CPSIA requirements including lead and phthalate limits (CPSC).
Factory Audit Essentials
- Quality system: documented SOPs, incoming inspections, in-line checks, AQL plans (ANSI/ASQ Z1.4; see ASQ).
- Equipment: auto-cutter/spreader, seam sealing machines, needle detectors, calibrated scales for down.
- Safety: fire exits, EHS training, chemical storage; cross-check with OECD due diligence guidance (OECD).
- Compliance: payroll/time records, age verification, overtime policies; social audits on file.
- Data: defect Pareto charts, CAPAs, on-time delivery history.
Cost, MOQs, and Lead Times: What US/EU Brands Should Expect
Outerwear cost comes from fabric, insulation, trims, labor minutes, and testing. Typical MOQs range 300–1000 pieces per color for jackets, with 75–120 days bulk after materials are ready. Calendars shift with seasonality, port conditions, and duty regimes. Build buffers and confirm at pack with your supplier.
| Item | China (Outerwear) | Bangladesh (Outerwear) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical MOQ per color | 300–800 | 600–1500 | Varies by fabric/dye lot and insulation minimums |
| Lead time: proto → SMS | 3–6 weeks | 4–8 weeks | Faster with stocked greige or library materials |
| Lead time: bulk (ex-mill) | 75–110 days | 90–130 days | Complex shells/down extend by 10–20 days |
| Main cost drivers | Fabric, tape, labor SMV | Fabric, insulation, trims | Testing, compliance, and freight add to landed cost |
| Compliance overhead | Higher for US 301 duties, RSL lab testing | Potential GSP/zero duty to EU on some HS codes | Always verify HS code and duty status with brokers |
- Global freight rates swung sharply in 2024 (Drewry World Container Index). Source: Drewry.
- State of Fashion 2024 cites cost inflation and nearshoring interest for speed. Source: McKinsey.
- EU’s General Product Safety Regulation (2023/988) tightens accountability. Source: EUR-Lex.
Duty and tariff exposure matters. US Section 301 tariffs affect many China-origin apparel lines; confirm latest schedules with official notices (USTR). In the EU, consult TARIC for exact rates and any preference schemes (TARIC).
Region Comparison for Outerwear Procurement
China offers the deepest technical ecosystem and faster development; Bangladesh excels in value and high-volume basics; Vietnam and Turkey balance lead times, duty access, and compliance frameworks. For cold-weather lines, weigh performance complexity against price, duty, and speed-to-shelf.
| Region | Strengths | Considerations | Best-Fit Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Technical capability, trims/mills cluster, rapid sampling | US 301 tariffs; higher labor cost | Performance shells, taped seams, complex down |
| Bangladesh | Competitive pricing, scale, growing technical skill | Longer dev lead time; MOQ constraints | Padded coats, value outerwear programs |
| Vietnam | Trade pacts, solid QA, mid-to-high tech skills | Capacity tight in peak seasons | Mid/high outerwear and athleisure shells |
| Turkey | Nearshoring to EU, fast transit, small MOQs | Higher cost; material sourcing mix | EU drops with short calendars |
China
- Deep supply chains for seam tape, waterproof zippers, and PFC-free DWR chemistries (industry guidance).
- Strong lab networks for hydrostatic head, spray rating, and down fill testing (SGS, Intertek, BV).
Bangladesh
- Cost advantage on padded outerwear and quilting throughput.
- Growing investment in bonding and seam sealing; validate capacity on-site.
Vietnam and Turkey
- Consider trade benefits and transit times to US/EU markets.
- Turkey suits capsule runs with short lead times into the EU.
Tech Packs & QA
A precise tech pack and staged sampling prevent rework and cost surprises. Combine clear tolerances, material specs, construction details, and testing requirements with AQL-driven inspections and third-party lab checks to keep quality on track.
Tech Pack Checklist
- Bill of Materials: fabric composition, weight, finishes, insulation specs (e.g., 120 gsm padding, 700 FP down).
- Construction: seam types, stitch SPI, seam tape brand/width, bonding parameters.
- Pattern & grading: size range, ease, tolerance table, critical POMs.
- Trims: zippers, snaps, toggles, heat transfers with placement diagrams.
- Testing: hydrostatic head, spray rating (AATCC), colorfastness, RSL panel.
- Labeling: fiber, care, country of origin, safety labels per US/EU rules (FTC).
Sampling Workflow
- Proto: confirm silhouette and construction feasibility.
- Fit: lock measurements and mobility; record change logs.
- SMS: sales-ready with colorways; confirm materials and trims.
- Pre-production (PP): golden sample with all approvals, test reports.
Keep change logs versioned and agreed by both sides. Require PP testing for critical performance claims and material compliance before bulk cut.
AQL & Inspections
- Define AQL levels and sampling plans using ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 (ASQ).
- Use in-line checks on first output of each operation; final AQL pre-shipment.
- Commission lab tests for RSL, hydrostatic head, down fill power (accredited labs).
- Document CAPAs with root cause, correction, and prevention steps.
Trends & Sustainability (2024–2025)
Outerwear is shifting toward recycled inputs, PFC-free water repellency, and traceable down. Digital patterning, auto-cutting, and PLM reduce waste and shorten cycles. Expect regulatory pressure on chemicals, durability, and due diligence across the US and EU.
Materials
- Recycled polyester and nylon with GRS/RCS claims (Textile Exchange).
- PFC-free DWR variants with improving spray ratings; monitor PFAS policy in the EU (ECHA PFAS).
- Certified down (RDS) with transparent chain of custody.
- MRSL alignment via ZDHC for upstream chemical inputs (ZDHC).
Automation
- CAD-to-cutter workflows reduce scrap and speed PP approvals.
- Line balancing with digital work aids improves throughput and consistency.
- RFID-enabled packing reduces picking errors and aids traceability.
McKinsey highlights cost pressure and the shift toward shorter lead times; integrating recycling, chemical compliance, and digital tools helps brands keep value and speed aligned (McKinsey).
Implementation Steps
Translate strategy into a clear operating plan: lock specifications, run pilots, and scale with guardrails. Treat each gate as a quality checkpoint that protects margin and calendar.
Preparation
- Define assortment scope, performance targets, and pricing bands.
- Build tech packs with test methods and tolerances.
- Confirm duty pathways and labeling needs for US/EU.
- Shortlist factories with outerwear case proofs and certifications.
Execution
- Sample through PP with version control and test reports.
- Reserve capacity and book mills for critical path items.
- Run pilot production with in-line QA and learning loops.
- Scale to bulk once PP sample and audits are passed.
QA Gates
- Design freeze at PP approval with golden sample photo record.
- Material inbound QC against RSL and performance specs.
- In-line checks on seam construction and down fill weights.
- Final AQL with carton audits and packing verification.
Product Integration
Eton’s Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service supports brands that need technical outerwear with predictable calendars. The team develops to brief, sources performance materials, and runs QA at each gate—from proto through lab testing and AQL—to deliver repeatable results at volume.
| Brand Need | OEM Service Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| PFC-free shell with taped seams | Verified tape and DWR libraries; PP test plan | Target spray rating with reliable sealing |
| Down jackets with tight fill control | Controlled filling rooms and calibrated scales | Consistent warmth and silhouette |
| Value padded coats at scale | Bangladesh line planning and quilting throughput | Stable costs and on-time deliveries |
| Short calendar capsule for EU | China rapid sampling, Turkey/Vietnam options | Faster SMS to store dates |
See how the workflow maps to your line: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service.
Risks & Compliance
Map risks by phase and assign mitigations up front. For US/EU markets, chemical, labeling, and product safety rules shape materials and testing choices. Maintain a living RSL and keep documentation ready for audits and customs queries.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Trigger | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material non-compliance | Supplier switches sub-component | Goods on hold, relabel/rework | Nominated mills; batch-level RSL tests; CoA files |
| Seam leakage | Incorrect tape temp/pressure | Returns, warranty claims | PP sealing SOP; in-line hydrostatic spot tests |
| Down migration | Insufficient down-proof fabric | Visual defects, consumer complaints | Lab tests for down-proof; baffle design checks |
| Schedule slip | Late fabric lab dips | Missed seasonal windows | Color approval SLA; overlap calendars; safety stock |
| Duty/tariff shock | Policy changes mid-season | Margin erosion | Scenario planning; alternate origin options |
US/EU Notes
- CPSIA for children’s products: third-party testing, tracking labels, and CPC required in the US (CPSC).
- EU REACH and SVHC communication duties for articles; maintain supplier declarations and test evidence (ECHA).
- FTC textile/care labeling in the US; fiber content, RN, and country of origin (FTC).
- EU General Product Safety Regulation elevates risk assessment and traceability for consumer products (EUR-Lex).
- Follow OECD due diligence for risk assessment and remediation across the supply chain (OECD).
Conclusion & Next Steps
With an outerwear brief in hand, align on the right model (CMT/FOB/FPP), pick a factory with proven technical depth, and run a disciplined PP-to-bulk plan backed by AQL and lab testing. For brands seeking a steady partner in Asia, Eton combines China and Bangladesh capacity with OEM/ODM development and compliance-first workflows. Textile From Day One.

References & Sources
- WRAP — Certification Programs. https://wrapcompliance.org/
- amfori BSCI — Social Compliance. https://www.amfori.org/
- ISO — ISO 9001 Quality Management (2015). https://www.iso.org/standard/62085.html
- OEKO-TEX — STANDARD 100. https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/our-standards/oeko-tex-standard-100
- Textile Exchange — Standards (RDS, GRS, RCS). https://textileexchange.org/standards/
- ASQ — Sampling and AQL Guidance. https://asq.org/quality-resources/sample-size
- USTR — Section 301 Tariff Actions. https://ustr.gov/issue-areas/enforcement/section-301-investigations/tariff-actions
- EU TARIC — Integrated Tariff of the European Union. https://ec.europa.eu/taxation_customs/dds2/taric/taric_consultation.jsp
- CPSC — Business & Manufacturing, CPSIA. https://www.cpsc.gov/
- ECHA — REACH Regulation. https://echa.europa.eu/regulations/reach
- FTC — Textile and Wool Acts Labeling. https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/threading-your-way-through-labeling-requirements-under-textile-fiber-products
- European Union — General Product Safety Regulation (EU) 2023/988. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/988/oj
- Drewry — World Container Index. https://www.drewry.co.uk/supply-chain-advisors/supply-chain-expertise/world-container-index-assessed-by-drewry
- McKinsey — State of Fashion 2024. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights/state-of-fashion
- ZDHC — Roadmap to Zero MRSL. https://www.roadmaptozero.com/
- ECHA — PFAS (Hot Topic). https://echa.europa.eu/hot-topics/per-and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas
FAQs
What do cut and sew manufacturers do in apparel production?
How do I select a China clothing manufacturer for outerwear?
What is the difference between OEM vs ODM for apparel brands?
How do CMT vs FOB vs FPP models differ in garment sourcing?
What belongs in a tech pack checklist for outerwear?
What is AQL quality control and how is it applied in apparel?
What matters in outerwear seam sealing for performance shells?
How should brands manage down handling and fill power in production?
What is PFC-free DWR and how does it affect outerwear performance?
What is hydrostatic head testing for waterproof fabrics?
What MOQs for outerwear should US/EU brands expect?
What are realistic lead times for outerwear production?
Why does WRAP certification matter when choosing a factory?
What does OEKO-TEX Standard 100 certification guarantee?
What is the RDS Responsible Down Standard and why use it?
How do EU REACH compliance rules affect apparel materials?
What does US CPSIA compliance mean for children’s outerwear?
How do Section 301 tariffs for apparel impact sourcing from China?
Why run pilot production in apparel before scaling?
What is a golden sample and PP approval in garment manufacturing?
What is a Restricted Substances List (RSL) and how is it used?
How do ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 sampling plans work for AQL inspections?
What is the difference between GRS vs RCS recycled materials in apparel?
What is ZDHC MRSL and why does it matter for outerwear sourcing?
Related Articles
Types of Tank Tops: The Complete Style, Fabric, and Manufacturing Guide from a China Clothing Manufacturer
12 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Types of Tank Tops: The Complete Style, Fabric, and Manufacturing Guide from a China Clothing... more »

Custom Merch for Businesses: OEM Manufacturing Guide for US & EU Brands
6 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Custom Merch for Businesses: OEM Manufacturing Guide for US & EU Brands Custom merch for businesses... more »

United States Apparel Sourcing Guide: Top Manufacturers and Strategies for Fashion Brands in 2024
18 minute read
October 13th, 2025
United States Apparel Sourcing Guide: Top Manufacturers and Strategies for Fashion Brands in 2024 In the... more »

Top American Made Companies in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Fashion Brands Seeking Domestic Excellence
14 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Top American Made Companies in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Fashion Brands Seeking Domestic... more »

