Company Clothing: How to Source and Scale with a China Clothing Manufacturer
 Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Garment Industry
Mr. Eton Yip | 32+ Year Garment Manufacturing Expert & Founder of Eton Garment
Garment Industry
October 13th, 2025
15 minute read
Table of Contents
- What "Company Clothing" Means for Fashion Brands (OEM/ODM vs POD)
- Where to Source: China Clothing Manufacturer vs Alternatives
- Cost, MOQ, and Lead Time: How to Model Your Program
- From Concept to PO: Your Step-by-Step Blueprint
- Quality Assurance That Scales
- Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
- Risks, Compliance & Localization for US/EU
- Data-Backed Trends Shaping Company Clothing (2024–2025)
- Conclusion & Next Steps
- References & Sources
- FAQs
Company Clothing: How to Source and Scale with a China Clothing Manufacturer
Company clothing covers branded apparel, uniforms, and outerwear produced at scale. When a US or EU brand chooses a China Clothing Manufacturer, success hinges on clear sourcing models (OEM/ODM vs POD), tight calendars, and compliance-ready processes. This guide gives you a practical blueprint built on 30+ years of jacket and technical outerwear manufacturing.
Company clothing refers to professionally produced branded apparel and uniforms made via OEM/ODM at scale. To source effectively, define your model, compare regions, set MOQs and lead times, build a complete tech pack, and partner with a China Clothing Manufacturer skilled in outerwear, compliance, and QA for reliable delivery.
What "Company Clothing" Means for Fashion Brands (OEM/ODM vs POD)
Company clothing spans corporate apparel, branded uniforms, and outerwear lines built for scale and durability. OEM and ODM unlock tailored design, materials, and workmanship control; POD suits micro runs and fast branding. Technical jackets and padded coats benefit most from experienced OEM/ODM partners with proven seam sealing, insulation handling, and lab testing.
- Corporate apparel: polos, shirts, fleeces, jackets with brand marks for staff and events.
- Workwear and uniforms: durability-first garments with functional features and safety standards.
- Branded merchandise: fanwear, sponsor apparel, and capsule collections for retail.
- Outerwear lines: down jackets, parkas, rainwear, and performance styles needing specialized construction.
Definitions and Use Cases
Corporate apparel typically focuses on consistent branding, repeatable fits, and fabric stability across seasons. Uniform programs prioritize abrasion resistance, care labeling accuracy, and stock service to maintain workforce continuity. Branded lines target retail margins with seasonal design refreshes. Outerwear programs demand material engineering (membranes, coatings), controlled insulation loft, and reliable performance ratings for wet and cold conditions.
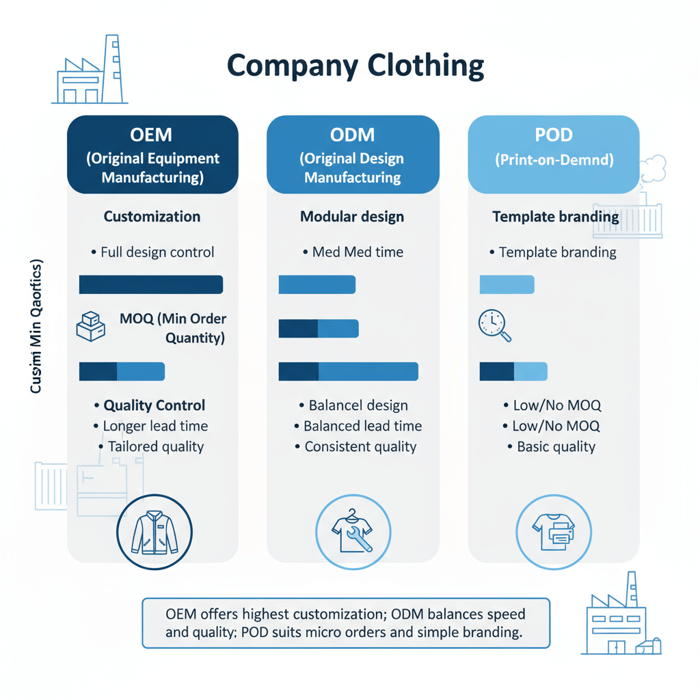
OEM vs ODM vs POD: Which Model Fits?
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing): You supply full design, tech packs, BOM; factory produces to spec. Pros: total control; fit for technical outerwear. Cons: heavier development load; higher MOQs.
- ODM (Original Design Manufacturing): Factory offers ready design blocks and fabric libraries you customize. Pros: speed; proven construction lines; lower development risk. Cons: less unique differentiation than pure OEM.
- POD (Print-on-Demand): Micro quantities with fast branding on existing blanks. Pros: low upfront; rapid launch. Cons: limited fabric/trim choice; not fit for performance outerwear or large-scale programs.
Rule-of-thumb: Choose OEM for unique construction and specialty materials; ODM for "ready-to-customize" outerwear; POD for branded tees or hoodies in low volumes.
Why Outerwear Needs Specialized Manufacturing
Jackets and technical apparel rely on precise craft and testing. Seam sealing parameters must match fabric membranes; down-proof fabrics and baffle design prevent leakage and cold spots; waterproofness and breathability targets dictate fabric selection and construction. Factories with calibrated equipment, skilled needle selection, and experience in bar-tacking, taped seams, and heat-transfer trims deliver consistent performance across large orders.
Documentation You'll Need from Day One
- Tech pack: detailed sketches, construction notes, stitch types, seam allowances, finishing, and care labels.
- BOM (Bill of Materials): fabrics, insulation, trims, thread, zippers, snaps, tapes; supplier references and grades.
- Measurement chart and grading: base size and grading rules across sizes for US/EU ranges.
- Color standards: lab-dip targets, Pantone references, and tolerance specs for approvals.
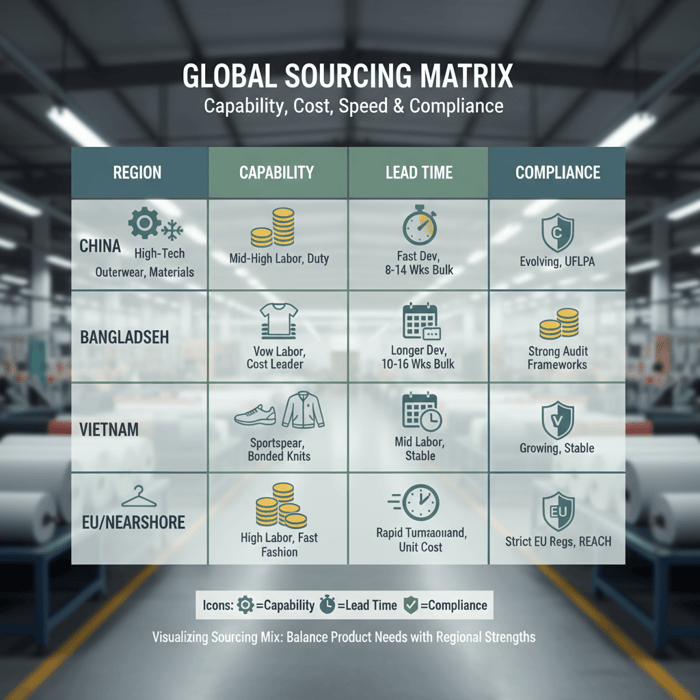
Where to Source: China Clothing Manufacturer vs Alternatives
China excels in technical outerwear, materials access, and speed; Bangladesh wins on cost for volume basics; Vietnam has strong sportswear and footwear-adjacent ecosystems; EU/nearshore brings faster turns at higher cost. Many brands adopt a hybrid path: develop complex jackets in China and scale volume in Bangladesh.
Criteria Overview
Assess capability fit, risk, compliance maturity, cost profile, and ecosystem access. Outerwear complexity favors regions with bonded fabric availability, seam sealing expertise, and experienced QC teams. Volume knits and basics can shift toward cost-efficient regions with strong compliance frameworks and audit readiness.
Decision Framework
- Map product complexity: membranes, insulation, taped seams, or simple knits.
- Set timeline targets: development weeks, sample gates, bulk calendar.
- Model unit economics: fabric/trim MOQs, workmanship minutes, freight, duty.
- Evaluate compliance: audit status, chemical programs, traceability levels.
- Pick single region or hybrid: prototype in higher-capability base; scale in cost base.
- Run a pilot SKU: validate fit, PP results, and inline QA before full range.
China + Bangladesh Hybrid Strategy
Use China for design development, proto/fit refinement, and technical validations (seam sealing, lab tests). Shift stable styles to Bangladesh for bulk once methods are locked. This approach keeps complexity under control and leverages cost advantages for large orders. Maintain shared trims and color continuity to ease transfer.
Incoterms & Logistics Considerations
Choose Incoterms with care. EXW shifts logistics to the buyer; FOB balances cost and control at port of loading; CIF includes freight and insurance to destination port; DDP covers duty and delivery to your door. Your landed cost will hinge on freight class, duty rates by HS code, and last-mile choices in the US/EU.
| Region | Strengths | Challenges | Typical MOQ | Lead Time | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Technical outerwear capability; fast development; deep material/trims | Higher labor cost than Bangladesh; duty exposure | 500–1,000 per color for jackets | 8–14 weeks bulk after PP | Performance jackets, parkas, taped seams |
| Bangladesh | Cost advantages; large-scale capacity; strong compliance programs | Longer development cycles for complex outerwear | 1,000–3,000 per color for volume styles | 10–16 weeks bulk after PP | Volume basics, padded jackets once methods set |
| Vietnam | Sportswear ecosystems; stable workmanship; footwear-adjacent supply | Capacity tight in peak seasons; material lead times | 600–1,200 per color | 9–15 weeks bulk after PP | Activewear jackets, bonded knits |
| EU/Nearshore | Speed; smaller MOQs; simplified logistics | Higher unit cost; limited options for specialized trims | 200–400 per color | 6–10 weeks bulk after PP | Capsules, fast repeats, light technical |
- China+1 strategies rising among US/EU brands — 2024 (Source: McKinsey State of Fashion, 2024)
- Compliance maturity critical for import risk control — 2023–2025 (Source: OECD Guidance, 2023)
- Freight rate volatility requires calendar buffers — 2024–2025 (Source: Industry trackers, 2024)
Cost, MOQ, and Lead Time: How to Model Your Program
Unit cost for jackets and outerwear is shaped by fabric systems, trim complexity, workmanship minutes, and order size. MOQs climb when custom materials are involved. Lead times reflect development rounds, lab testing, and PP approval cycles. A transparent landed cost framework drives better MOQ and timing decisions.
| Cost Driver | Impact on Unit Cost | Mitigation Tactics |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane/coated fabric | Higher material price; specialized seam sealing | Use proven mills; standardize tape widths; consolidate colors |
| Insulation (down/synthetic) | Material variance; fill power impacts | RDS traceable sources; engineer fill weights by size |
| Quilting/taped seams | Added workmanship minutes; equipment time | Simplify quilt patterns; early method validation |
| Custom trims/zippers | MOQ premiums; lead-time risk | Shared trims across styles; pre-book critical zippers |
| Color count | Dye lot and trim minimums raise cost | Limit colors; align palette across styles |
Landed Cost 101
Landed Cost = FOB Unit Cost + Freight + Duty + Brokerage + Last-Mile. Model per HS code to estimate duty and preference programs. Freight varies by mode (sea/air), carton density, and season. Add buffer for port congestion and customs clearance to protect delivery to US/EU DCs.
MOQ Levers
Fabric minimums link to mill capacity and dye lot sizes. Taped seam programs often require higher material minimums. Trim vendors set MOQ for cords, toggles, snaps, and zippers; combine trims across styles to reach economic thresholds. Reduce color count to ease MOQ and improve unit cost.
Lead-Time Playbook
- Development: 3–5 weeks for proto and method trials.
- SMS (Salesman Samples): 2–3 weeks once design is locked.
- PP (Pre-Production): 1–2 weeks for final confirmations.
- Bulk: 8–16 weeks depending on region and complexity.
- FRI (Final Random Inspection) + Ship: 1–2 weeks including paperwork.
Cost Optimization Tactics
- Material engineering: pick proven membranes with available tapes.
- Shared colors: align palette across jackets to consolidate dye lots.
- Simplified construction: reduce unique stitch types and complex panels.
- Phased assortments: pilot a core style, scale once method is stable.
- Duty variance by HS code influences landed cost — 2025 (Source: US/EU customs notices, 2025)
- Air freight spikes during Q4; plan sea freight for bulk — 2024–2025 (Source: Logistics trackers, 2024)
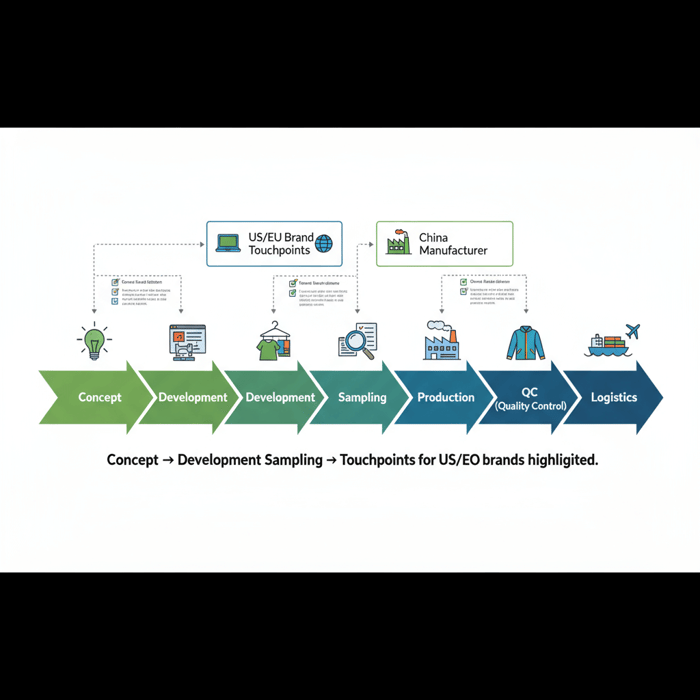
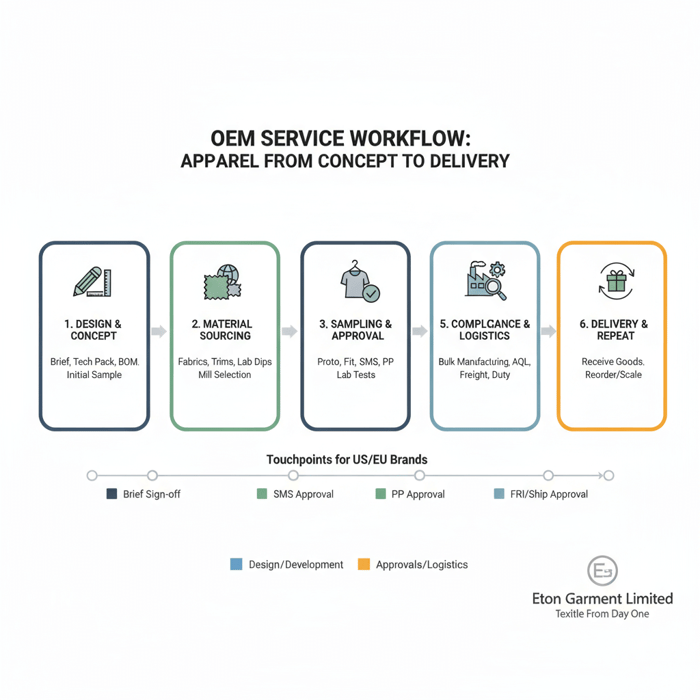
From Concept to PO: Your Step-by-Step Blueprint
Start with a tight brief and complete tech pack. Align on BOM and materials, set the calendar, and run proto, fit, SMS, and PP samples. Lock standards early, then greenlight bulk with QC checkpoints at each stage. For outerwear, validate seam sealing and lab tests before volume commitments.
Preparation: Brief, Tech Pack, BOM
- Brief: target consumer, climate, performance (e.g., waterproof rating), price band, and delivery window.
- Tech Pack: sketches, stitch maps, seam allowances, heat-transfer placements, care label text.
- BOM: fabric families, membrane/coating details, insulation specs, trims, tapes, thread types, zipper gauges.
- Measurement/Grading: base size chart, tolerance table, grading rules for US/EU sizes.
- Color Standards: Pantone targets, lab-dip process, approval gates.
Execution Steps: Samples and Approvals
- Proto: fit and construction feasibility; validate seam sealing on sample panels.
- Fit Sample: confirm measurements, articulation, and comfort in motion.
- SMS: align sales tools with final trims and branding details.
- PP Sample: production-intent sample with full BOM; freeze methods and workmanship.
- TOP Sample: final sample off bulk line; confirm against PP approvals.
Quality Assurance at Every Gate
- Development QA: test tape adhesion, stitch density, and needle selection on target fabrics.
- Inline QC: audits during bulk; focus on seam sealing parameters and down-proof checks.
- FRI: AQL inspection; carton checks; care label verification; packaging compliance.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Late PP changes: lock BOM before PP; avoid trim substitutions after method approval.
- Fabric lead times: pre-book membranes and insulated linings; approve lab dips early.
- Unvalidated seam sealing: run peel and hydrostatic tests on final fabrics before bulk.
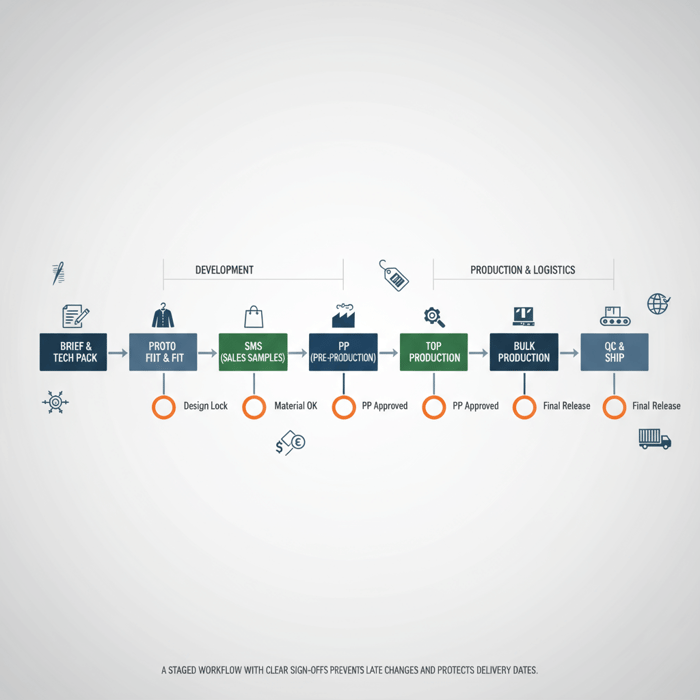
Quality Assurance That Scales
QA begins in development with clear specifications and continues through inline checks and final inspection. For outerwear, add performance testing—hydrostatic head, seam tape adhesion, and down-proof testing—to workmanship controls. The goal: measurable consistency across thousands of units.
- AQL 1.0: Tight tolerance; lower risk of defects in critical programs. Trade-off: higher inspection cost/time.
- AQL 1.5–2.5: Balanced tolerance; suitable for general apparel. Trade-off: defect risk increases slightly with broader acceptance.
| QA Artifact | Purpose | Owner | Timing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fit Report | Record measurement results and changes | Brand Technical | Proto/Fit stages |
| PP Comment Sheet | Freeze construction and BOM decisions | Brand + Factory | PP approvals |
| Inline QC Report | Track production line defect trends | Factory QA | During bulk |
| FRI Checklist | Final AQL inspection and packaging checks | Third-party/Brand | End of bulk |
AQL and Inline/FRI Controls
Define AQL by category severity (critical/major/minor). Inline audits catch early drift—needle, stitch balance, tape adhesion—before defects compound. FRI checks finished goods against PP approvals, care labels, and packaging requirements aligned to US/EU retail standards.
Performance & Lab Testing
- Hydrostatic head (waterproofness) and spray tests for rainwear performance.
- Tape adhesion and seam sealing peel tests to verify durability.
- Down-proof and thermal performance checks for insulated jackets.
- Chemical testing aligned to ZDHC MRSL and OEKO-TEX Standard 100.
Documentation Trail and Change Control
Maintain a single source of truth: approved tech pack, BOM, lab reports, PP comments, and TOP sign-offs. Use PLM handoffs and version control. Any change post-PP should trigger a documented risk assessment and brand approval.
Product/Service Integration: Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service
A full-service OEM partner consolidates design-to-bulk for company clothing programs. Access to technical fabrics, tuned QA systems, and compliance-ready operations across China and Bangladesh simplifies calendars and reduces risk—especially for outerwear with seam sealing, insulation, and performance targets.
| User Need | OEM Feature | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Technical fabric sourcing | Membrane/coated fabric libraries and vetted tape programs | Faster approvals; predictable performance |
| PP management | Structured sample gates with comment tracking | Locked methods; fewer late changes |
| Compliance support | Audit frameworks; chemical programs aligned to ZDHC/OEKO-TEX | Reduced import risk for US/EU |
| Dual-base scaling | China development + Bangladesh bulk | Balanced cost and capability |
Eton Garment Limited has produced jackets, parkas, and technical apparel for global retailers since 1993. For brands ready to move from concept to PO, the Clothing Manufacturing OEM Service brings a calibrated workflow from brief to delivery, with clear assumptions on time and cost ranges for US/EU programs.
Use Case 1: Technical Outerwear (Problem → Solution)
Problem: A retailer needs a waterproof parka with taped seams, RDS down alternatives, and EU chemical compliance in 24 weeks. Solution: Develop in China using proven membranes and tape systems, lock PP with lab approvals, then run bulk with inline tape checks and final AQL 1.5. Delivery hits calendar with validated performance.
Use Case 2: Multi-Region Scaling (Problem → Solution)
Problem: A brand wants 120,000 padded jackets across three colors at a value price, with repeatability. Solution: Prototype and method-set in China; transfer stable styles to Bangladesh for bulk while sharing trims and color standards, keeping QA artifacts aligned. Unit economics improve without sacrificing workmanship.
Risks, Compliance & Localization for US/EU
Build compliance from the start: product safety, chemical restrictions, labor standards, and traceability. US-bound goods must align with UFLPA expectations; EU programs factor REACH, CSDDD, and ESPR. Keep audit trails, supplier documentation, and lab reports aligned to regulations and retailer policies.
- Pros: Reduced import risk; smoother customs; retailer confidence.
- Cons: More documentation; potential material shifts to meet MRSL limits; added testing time.
Risk Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fabric delays | Medium | Calendar slip | Pre-book fabrics; approve lab dips early |
| Lab test failure | Low–Medium | Rework; retest cost | Pilot tests on proto; lock BOM before PP |
| Audit CAP (Corrective Action Plan) | Medium | Shipment hold risk | Pre-audits; monitor CAP closure progress |
| Chemical non-compliance | Low–Medium | Import risk; brand reputation | ZDHC MRSL alignment; OEKO-TEX-certified inputs |
| Traceability gaps (UFLPA) | Medium | Detention; delays | Maintain supplier chain-of-custody documents; materials origin proofs |
Regulatory Notes for US/EU
- UFLPA (US): Strengthen material origin records and chain-of-custody documentation; verify upstream suppliers.
- REACH (EU): Manage restricted substances and lab testing; document control plans per style.
- CSDDD (EU): Formalize due diligence steps, risk mapping, and action reporting; align across supplier tiers.
- ESPR (EU): Prepare for ecodesign expectations; engage on Digital Product Passport for traceability.
Regulations evolve; confirm requirements with your legal/compliance teams and update testing plans accordingly.
Data-Backed Trends Shaping Company Clothing (2024–2025)
Brands balance capability and risk with China+1 strategies, invest in traceability, and tighten calendars. Outerwear demand stays resilient but value-focused; sustainability programs and digital product passports rise for EU-bound goods. These shifts shape sourcing choices and documentation expectations for US/EU importers.
Key Trend 1: China+1 and Dual-Base Strategies
Many brands prototype and validate complex outerwear in China, then scale repeat styles in Bangladesh. This approach protects technical quality and improves unit economics. Stable trims and shared color palettes enable smoother transfers and predictable replenishment calendars (Source: McKinsey, 2024).
Key Trend 2: Compliance and DPP/Traceability
Documentation depth increases with UFLPA and EU initiatives. Digital Product Passports will push structured data on materials and processes. Factories prepared with ZDHC and OEKO-TEX programs, plus audit-ready records, reduce import risk and speed customs clearance (Source: European Commission, 2024–2025).
- Traceability investment growing across apparel — 2024–2025 (Source: Industry insights, 2024)
- Outerwear remains resilient with value-tier focus — 2024 (Source: McKinsey State of Fashion, 2024)
Conclusion & Next Steps
Define your model, pick the right region, align cost/MOQ/lead time, and run a staged program with QA and compliance built in. Start with a pilot style to validate fit, PP, and performance tests. Once stable, scale across colors and sizes with a reliable OEM partner and clear documentation trails.
- Weeks 1–2: Brief, tech pack, BOM, and calendar set.
- Weeks 3–5: Proto and fit approvals; early seam sealing validation.
- Weeks 6–7: SMS for commercial needs; align trims/colors.
- Weeks 8–9: PP sample; lock methods; confirm lab tests.
- Weeks 10–18: Bulk production with inline QC; FRI and ship.
- Repeat: Transfer stable styles to scale region; standardize trims and packaging.
Eton — Textile From Day One — supports brand teams from concept to delivery across China and Bangladesh with calibrated outerwear programs and compliance-ready operations for US/EU markets.
References & Sources
- OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains in the Garment and Footwear Sector
- McKinsey & Company — The State of Fashion 2024/2025
- US CBP — Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) guidance
- European Commission — Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD)
- European Commission — Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR)
- ZDHC Roadmap to Zero — MRSL
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100
- WRAP (Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production)
FAQs
What is company clothing in the context of sourcing from a China clothing manufacturer?
How does OEM manufacturing work with a China clothing manufacturer for outerwear?
What are the differences between ODM and OEM when choosing a China clothing manufacturer?
Is print-on-demand (POD) suitable for company clothing programs with a China clothing manufacturer?
What is a tech pack and why is it essential for working with a China clothing manufacturer?
How do you create a bill of materials (BOM) for company clothing sourced from China?
What minimum order quantity (MOQ) should I expect from a China clothing manufacturer for jackets?
What lead times are typical for outerwear production with a China clothing manufacturer?
Why is seam sealing important in outerwear manufactured in China?
How does quality assurance (QA) work in apparel manufacturing with a China clothing manufacturer?
Related Articles
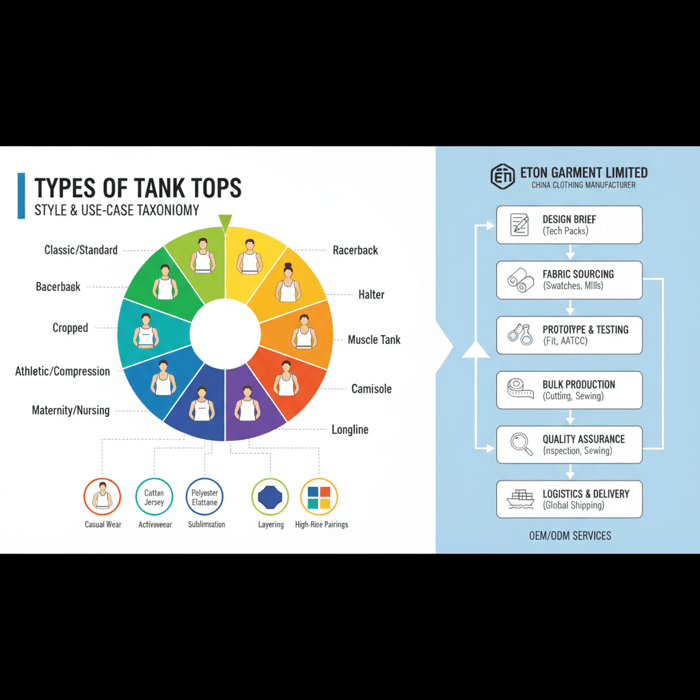
Types of Tank Tops: The Complete Style, Fabric, and Manufacturing Guide from a China Clothing Manufacturer
12 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Types of Tank Tops: The Complete Style, Fabric, and Manufacturing Guide from a China Clothing... more »

Custom Merch for Businesses: OEM Manufacturing Guide for US & EU Brands
6 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Custom Merch for Businesses: OEM Manufacturing Guide for US & EU Brands Custom merch for businesses... more »

Top American Made Companies in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Fashion Brands Seeking Domestic Excellence
14 minute read
October 13th, 2025
Top American Made Companies in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Fashion Brands Seeking Domestic... more »

United States Apparel Sourcing Guide: Top Manufacturers and Strategies for Fashion Brands in 2024
18 minute read
October 13th, 2025
United States Apparel Sourcing Guide: Top Manufacturers and Strategies for Fashion Brands in 2024 In the... more »

